Page 1 :
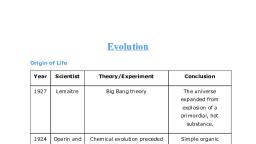
Evolution, The process of gradual development over millions of years in organisms through generations by inheriting the traits of their previous generations is termed as evolution., The evolution eventually leads to the evolvement of new species. According to J B S Haldane, life on earth may have started as a simple organic molecule and has developed into a complex organism with the changing conditions on earth during various periods., Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist who proposed the idea of “evolution of species by natural selection’ although he was not aware of the mechanisms responsible for the variations., Natural selection refers to the selection of some traits of a population that favour their survival making them adapt to the environment., It was Mendel who proposed the mechanism behind the inheritance of traits. Both these scientists worked on their theories independently., These traits that are inherited may be acquired also., Speciation:, A group of organisms that are similar in their traits and are capable of breeding within themselves are termed species., The mechanism or process by means of which a new or distant species is formed from the pre-existing species due to various factors is termed as speciation., This process leads to the formation of different species within a population that is not capable of reproducing among themselves., The occurrence of speciation is due to the following reasons:, Genetic drift – A random change in the frequency of alleles over successive generations in a population., Gene flow – This speciation occurs between populations which are partly separated but not completely separated., Natural selection – Nature selects and consolidates those organisms which are more suitable and adaptable. They also possess favourable variations., Geographical isolation – This is caused by mountains, rivers, and other geographic features. This form of isolation leads to reproductive isolation. As a result, there is no flow of genes in the separated groups of the population., Origin of species, After a successful expedition on HMS Beagle, Charles Darwin wrote a book on what he observed at the Galapagos Islands., In the booked named ‘The Origin of Species’, he wrote a detailed theory of evolution which was mostly based on Natural Selection., Origin of life – Haldane’s theory, JBS Haldane was a British Scientist who theorized that life originated from organic and lifeless matter., His theory was proved to be correct by Urey and Miller’s experiment., It was called the theory of abiogenesis., Evolution and Classification:, Every species goes through a phase of evolution. The similarities among organisms that allow them to be grouped are based on the characteristics or the details of the appearance or behaviour that is seen for a particular form or a function., There are some basic characteristics that are shared by most of the organisms like, the cell being the fundamental unit of life. But the next level of grouping or classification may not be common for all the organisms, like the cell may have a nucleus or not. This classification goes further as whether the nucleated cells are single celled or multicellular. This allows a hierarchy to be created in the evolution process that helps us in the classification of groups., Thus the more common characteristics are shared by two species, the more closely related they are. The more closely they are related, indicates that they have had common ancestors recently. Example - In a family, a brother and a sister are closely related with common ancestors as parents. Now the girl and her cousin too are related as they common ancestors, grandparents. But they are distant than her brother as they common ancestors in second generation., Thus small group of species with recent common ancestors are built, followed by distant common ancestors and this goes on backwards in the evolutionary process., Molecular phylogeny, The evolutionary relationship among different biological species is called phylogeny., It gives rise to an evolutionary tree., In molecular phylogeny these relationships are studied at the hereditary molecular level, mainly using DNA sequences., It involves the analysis of DNA composition and gene comparison between different species., Tracing Evolutionary Relationships:, In the evolutionary relationships, the occurrence of common characteristics are the basis of classifying them into groups. These common characteristics can be identified as being of 2 types, namely:, Homologous characteristics: These are those characteristics that are present in different organism but look similar and they have a have a common ancestor. They may have the similar basic organ structures but with a different function in various organisms. Example - Mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians have four limbs, but each serves a different purpose and are modified to perform that function., Analogous characteristics: These are those characteristics that have the similar function in different organisms and they have evolved independently for different ancestors. Example - the wings of bats and of birds look similar as they serve to perform the same function of flying, but the wings of a bat are actually a fold of skin between the fingers., Hence these different types of characteristics help in tracing the evolutionary relationships between species to a great extent., Fossils:, To study the evolutionary relationships, the current species as well as the species that are no longer in existence also needs to be considered., The body of an organism usually decomposes when it dies, but due to some environmental conditions like hot mud or lava, their bodies may be buried in them, harden and eventually leave an impression of the body parts. This preserved traces of the living organisms that existed in a past geological period are termed as fossils., The fossils help in determining the various evolutionary stages of the species. The process of conversion of an organism into a fossil is termed as fossilisation and its study is referred to as palaeontology., Evolution by Stages:, It is well established that evolution is a gradual process that takes place over thousands of years. The complex organs that have evolved in organisms is not due to a single DNA change but due to thousands of such changes over a large period of time., If the eyes of an octopus and the vertebrates are considered then it is different in both of them suggesting that they have evolved independently., It is also to be noted that a change brought on for a particular feature may have later evolved into a different function altogether., For example, the purpose of feathers initially was considered to provide insulation in cold weather and this is seen in some of the reptiles like the dinosaur, who could not fly. In the evolutionary process birds adapted these feathers for flight. This leads to the belief that birds were closely related to reptiles., Similarly some structures that are dissimilar have evolved from common ancestors. The best example of it would be wild cabbage that humans have used as food for over two thousand years., They generated different types of vegetables out of the would cabbage by artificial selection and developed the cabbage with short leaves, broccoli which is arrested flowers, cauliflower, the swollen parts as kohlrabi, or leafy kale. If not for artificial selection in this, it would not be known that they originated from a common ancestor., The change in the DNA is yet another way to understand evolutionary relationships. The comparison of the DNAs of different species would give an insight into the changes that have happened in their evolutionary process., Evolution Should Not be Equated With Progress:, The evolution of a new species does not indicate that the old species has been eliminated or they are inefficient than the new one. It indicates that the new species have evolved as a result of changing environmental conditions., It can be said that evolution is a process of creating a diversity of species due to natural selection and genetic drift. This creates a population that is not capable of reproducing with the original species. For example, humans and chimpanzees may have had common ancestors and with time they have evolved in separate directions leading to the present species., Hence there is no progress that can be mapped during evolution. Each and every species diversifies in order to reproduce and survive and adapts itself accordingly., The only factor is that more and more complex organs have developed in the evolutionary process. That does not indicate the simplest older species like the bacteria are extinct. They can survive in diverse conditions of hot springs, Antarctica etc. Humans are the most evolved, but they are just another species in the evolutionary process., Human Evolution:, The evolutionary relationship in humans has also been traced by the various methods of excavation, time-dating, studying the fossils, and DNA sequences. Great diversity exists among the people of the world in their features, colours, etc. Many times, groups of humans were grouped based on their skin colour. But there is no biological reason for that as all humans are part of a single same species. Everyone belongs to the species - Homo sapiens., A large number of genes are present in this gene pool which is the source of the vast variations found in humans. This is the reason that no two individuals are alike in looks, abilities, etc, which leads to the diversity in skin colour, height, hair colour, etc., Though the humans inhabit different parts of the modern world, all of them originated from Africa. The original inhabitants of Africa migrated to across to West Asia, central Asia, Eurasia etc and all this while they were travelling back to Africa too. This lead to a diverse gene pool in a staggered manner as the population across the world increased., Sex Determination:, There is a various mechanism that determines the sex of a new born organism. It may be based on the temperature where the fertilised eggs is kept as in few reptiles, or they may changes ex as in snails. Humans on the other hand the sex of a newborn child is determined predominantly by the genes inherited from the parents., All the chromosomes in humans are not paired. There are generally a pair of 22 chromosomes, with one of the pair being from each of the parents. These generally determine all the traits., There is a pair of chromosomes known as the sex chromosomes that differ in males and females. The females have a correct pair and they are termed as X chromosomes, but men have an X chromosome and its pair as Y. So the genotype of women is XX and men is XY., If we look at the inheritance pattern of a male and female, we can see that X is inherited by the child from their mother by default and the sex of the child depends on which pair of the sex chromosome is being inherited from the father., If it X, then the pair becomes XX and the child is a girl and if Y is inherited, then it becomes XY and thus the chid is a boy.