Page 1 :
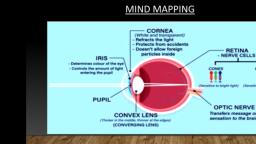
EduLiv, EduLiv, EduLiv, EduLive, EduLiv, EduLi, The Hyman Eye and the Colourful World, CHAPTER – 11, In this chapter we will study Human eye that uses the light and enable us to see the, duLive, will also use the idea of refraction of light in some optical phenomena i, i.e. Rainbow formation, twinkling of star, blue and red colour of sky etc., Human Eye :A Sensitive sense organ, It acts like a camera, enable us to capture the colourful picture of the surroundings., It forms an inverted, real image on light sensitive surface Retina, EduLive, Ciliary muscles, EduLiv, Cornea, Retina, The Various, Edubiye, Cornea : It is a thin membrane through which light enters. It forms the, transparent bulge on the front of eyeball. Most of the refraction occurs at the, outer surface of the cornea., ve, and their functions, ive, EduLiv, 2. Eyeball : it is approximately spherical in shape, with a diameter of about, 2.3cm., Iris : It is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of pupil. It, behind the cornea., Edul, Pupil : It regulates and control the amount of light entering the, black opening between aqueous humour & lens., 5. Crystalline eye lens : Provide the focussed real & inverted image of the, EduLiv, object on the retina. It is composed of a fibrous, jelly like material. This is, convex lens that converges light at retina., Edue EduLiv, EduLiv, is the, EduLNe, 114, EduLe, EduLe, Live, Live, Live, Page 1 of 10, ive, ive, ive, Edu EduLive, ive, EveEd aEduLive, ive, EduiveEdive EduLi, ive, LIKeEduLive, e Live, Live
Page 2 :
EduLiv, EduLi, EduLiv, EduLiv, EduLi, Ciliary muscles : It helps to change the curvature of eyelens and hence, changes its focal length so that we can see the object clearly placed at different, positon., Edulive, 7., Retina : Thin membrane with large no. of sensitive cells., 8., When image formed at retina, light sensitive cells gets activated and generate, electrical signal. These signals are sent, these signals after which, Iow pupil works ?, we perceive c, brain via, Example : You would have observed that when you come out of the cinema hall, after watching movie in the bright sun light, your eyes get closed. And when you, entered the hall from the bright light, you won't be able to see and after some time, you would be able to see., Edulkiv Eive, nerue. Brain analyse, Here the pupil of an eye provide a variable aperture, whose size is controlled by iris, When the light is bright : Iris contracts the pupil,, When the light is din : Iris expand the pupil,, Edub, EduLiv, Pupil open completely, when iris is relaxed., Persistence of Vision : It is the time for which the sensation of an object continue, in the eye. It is about 1/16" of a second., Power of Accommodation:, so that less light enters the, that more light enters, The ability of eye lens to, help of ciliary muscles., it focal length is called accommodation with the, Edul, Ciliary Musl, ive, ive, 1. Eye lens become thin, 2. Increases the focal length, 3. Enable us to see distant object clearly, Relaxed, 1. Eye lens become thick, 2. Decreases the focal length, 3. Enable us to see nearby object, Edul EduLike duv, EduLiv, Near point of the Eye, It is 25cm for normal eye. The, minimum distance at which object can, be seen most distinctly without strain., Edue EduLiv, EduLiv, For point of the, It is infinity for normal eye. It is the, farthest point upto which the eye can, see object clearly., EduLe, 115, EduLie, Live, Live, Live, Page 2 of 10, ive, Live, ive, ive, Elive, EdLive, ive, Live EduLiv, ive, EduLie duL EduLie EduLiv, Live