Page 1 :
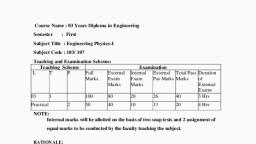
Course Name : 03 Years Diploma Engineering, Semester, , : Second, , Subject Title : Engineering Physics-II, Subject Code : 203/ 206, Teaching and Examination Scheme:, , L, , Teaching Scheme, T, P, , 03, Practical, , 2, , Full Marks. External, Exam, Marks, , Examination Scheme, Internal, External, Total Pass Duration of, Pas Marks Marks, Exam, External, Marks, Exams, , 100, , 80, , 20, , 26, , 40, , 3 Hrs, , 50, , 40, , 10, , 13, , 20, , 4 Hrs, , NOTE:, Internal marks will be allotted on the basis of two snap tests and 2 assignment of equal, marks to be conducted by the faculty teaching the subject., , RATIONALE:, Basic science forms the foundation of Engineering. In particular Physics provides, fundamental facts, principles, l aws, and proper sequence of events to streamline Engineering, knowledge., , Objectives : The Student will be able to :, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Analyze the basic properties of light., Differentiate between field intensity and potential., List the advantages of optical fibre., Describe principal of working of optical fibre., Differentiate between conductor, Insulator and semi conductor on the basis of band, theory., 6. Know simple idea of Nano Technology., 7. Know simple idea of non conventional sources of energy.
Page 2 :
Contents : Theory, Chapter, , 1., , Name of the Topic, LIGHT, Properties of light, Reflection, refraction, Snell’s law, physical significance of, refractive index, definition of dispersion of light along with, ray diagram., (Numericals on refractive index), , Hours, , Marks, , 03, , 06, , 05, , 08, , 05, , 08, , 03, , 06, , 03, , 08, , 05, , 08, , 05, , 08, , Electric Field and Potential, 2.1 Electric field, Electric charge, Coulomb’s inverse square law, Definition of, unit charge, Electric field, Electric lines of force and their, properties, Elect field intensity, Electric flux, Electric flux, density., (Numericals on Coulombs law, Electrical Intensity), 2.2 Electric Potential, 2., , Concept of potential, Definition and unit, Potential due to, point charge using integration method, Potential difference, between two points, Definition of dielectric strength and, breakdown potential., (Numericals on electric potential), 2.3 Capacity & Condensers, Electrostatics capacity & its S.I unit, Capacity of parallel, plate condenser, Condensers in series & parallel (Formula, only,no derivation), Uses of condensers., , (Simple problems), , 3, , CURRENT ELECTRICITY, Ohm’s law, Resistance and its unit, Specific resistance, Factors, affecting resistance, Kirchhoff’s law and its application to Wheat, stone bridge circuit., , Fiber Optics, , 4, , Introduction, Total internal reflection, critical angle,, acceptance angle. Structure of optical fiber, Numerical, Aperture, Fiber optic materials, Types of optical fibers,, Applications in communication systems., (Numerical on critical angle, numerical aperture), , 5, , Band Theory of Solids, Energy levels in solids, Valence & conduction bands,, forbidden gap, Conductors, Semiconductors and Insulators,
Page 3 :
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductors, p-type and n-type, semiconductors, P-N junction diode-forward and reversed, biased characteristics., , MODERN PHYSICS., 7.1 Photo electricity, Concept of photon, Plank’s hypothesis, properties of photon,, photo electric effect, Laws of photoelectric effect, work, function, Einstein’s photoelectric equation( no derivation),, Basic Concept of Solar Energy., (Numericals on Energy of photon, work function,, photoelectric equation), 7.2 LASER, Properties of laser, Characteristics and applications of Laser, 7.3 X-rays, Introduction to X-rays, production of X-rays using Coolidge, tube, minimum wavelength of X-rays, properties and, applications. of X-rays, , 6, , 03, , 06, , 01, , 04, , 02, , 06, , 03, , 06, , 04, , 06, , (Numericals on minimum wavelength of x-rays), , Introduction to nanotechnology, Definition of nanoscale, nanometer & nanoparticle,, applications of nanotechnology- electronics, automobiles,, medical, textile, cosmetics, environmental, space and, defence., , 7, , Non- Conventional Sources of energy, Introduction- Non Renewable and renewable (Alternate), energy sources, Examples- Solar Energy, Wind Energy,, Tidal Energy, Geo-Thermal Energy and Bio-Mass., Advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy., , 8, , Total, , 42, , 80, , Practical :, Skills to be, Developed :, Intellectual, Skills :, , , , , Proper selection of measuring instruments on the basis of range, least count, precision, and accuracy required for measurement., To verify the principles, laws, using given instruments under different conditions., To read and interpret the graph.
Page 4 :
, , , To interpret the results from observations and calculations., To use these results for parallel problems., , Motor, Skill :, , , , , , Proper handling of instruments., Measuring physical quantities accurately., To observe the phenomenon and to list the observations in proper tabular form., To adopt proper procedure while performing the experiment., , List of Experiment :, 1. To represent simple harmonic motion with the help of vertical oscillation of spring to, determine spring constant (K) (Stiffness Constant)., 2. To determine time period of oscillation of compound bar pendulum and calculate, acceleration due to gravity (g)., 3. To calculate refractive index of material of prism using spectrometer device., 4. To determine effective capacitance of series and parallel combination of capacitors by, calculating its reactance., 5. Verification of Ohm’s Law., 6. To convert galvanometer into ammeter of required range using appropriate value of, shunt., 7. To verify Total Internal Reflection (TIR) phenomenon for given glass slab and to, calculate critical angle of incidence., 8. Determination of Energy Gap (Forbidden Gap) of a semi-conductor., 9. To determine I-V characteristics of P-N junction Diode., 10. To verify inverse square law by using photoelectric cell.