Page 1 :
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM, The Body’s Transport System, , COMPILED BY HOWIE BAUM
Page 3 :
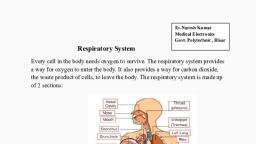
The circulatory system, sometimes called, the cardiovascular system, consists of the, heart, blood vessels, and blood., It transports oxygen, hormones, nutrients to all the cells in the body, , and, , It picks up waste products generated by, metabolic processes and delivers them to, other organs for disposal., The heart provides the "muscle" needed, to pump blood throughout the body., The system circulates blood in two, circuits:, , The Pulmonary circuit and Systemic, circuit.
Page 4 :
PULMONARY CIRCULATION, Heart: your heart pumps blood through two, major pathways., 1) Pulmonary, circulation, Transports, oxygen-poor blood, from the right, ventricle to the, lungs where blood, picks up a new, oxygen supply.
Page 5 :
SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION, 2) Systemic circulation, , It returns oxygen rich, blood and nutrients to the, left atrium and is pumped, out all over the body, , It also picks up carbon, dioxide and other waste, products.
Page 6 :
• Hormones from, glands help, regulate cell, activity., Oxygenpoor blood, enters the, heart from, the body, (blue, top, left) and is, pumped, out to the, lungs (blue,, top right), , Oxygen-rich, blood enters, the heart, from the, lungs (red,, right side), and is, pumped out, to the body, (top), , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMBSU-2GK3E, , • Oxygen from, the lungs, combines with, nutrients to, provide energy., • Nutrients from, the digestive, system provide, food for the, cells.
Page 7 :
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM WORKS IN CONJUNCTION WITH, OTHER BODY SYSTEMS, TO KEEP THE IT WORKING PROPERLY., , ❖ When your blood circulates through your digestive system, it, picks up nutrients your body absorbed from your last meal., ❖ Your blood also carries oxygen inhaled by the lungs. Your, circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients to your heart and, the other cells of your body then picks up any waste products, created by these cells, including carbon dioxide, and delivers, these waste products to the kidneys and lungs for disposal., ❖ The circulatory system carries hormones from the endocrine, system, and the immune system’s white blood cells that fight off, infection., ❖ The circulatory system provides your brain with a constant supply, of oxygen-rich blood while your brain regulates your heart rate and, blood pressure., ❖ Your circulatory system delivers oxygen-rich blood to your bones., Meanwhile, your bones are busy making new blood cells.
Page 8 :
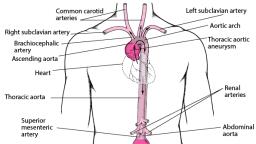
BLOOD VESSELS - Over 60,000 miles of blood vessels transport, your blood throughout your body. There are 3 types of blood vessels., • Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to, other parts of the body. They are much thicker than Veins because, of the high pressure of blood coming from the heart., , • Veins: Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back to the, heart., • Capillaries: Tiny tubes that carry blood from the arteries to the, body’s cells, and then back to the veins.
Page 9 :
CAPILLARIES, • Body tissues contain a, vast network of thin, capillaries., • Capillary walls are only, one cell thick, allowing, exchange of gases,, nutrients, and wastes., • Capillaries are so fine, that red blood cells, must line up single-file, to go through them.
Page 10 :
ARTERIES, VEINS, AND CAPILLARIES
Page 11 :
❖ BLOOD, Blood forms about one-twelfth of the, body weight of an adult, amounting to, about 5 liters (11 pints) in volume., 45% – 50% is red Blood Cells, , Roughly 50–55 % of blood is plasma,, the liquid-only portion in which cellular, components are distributed., Plasma contains 90 per cent water with, dissolved substances such as glucose, (blood sugar), hormones, enzymes, and, also waste products such as urea and, lactic acid., Plasma also contains proteins such as, albumin, fibrinogen (important in, clotting), and globular proteins or, globulins.
Page 12 :
RED BLOOD CELLS (ERYTHROCYTES), They are Transporters of, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Red Blood Cells, Lack a nucleus, Contain hemoglobin, Disk-shaped, , Their shape is described as, Bio-Concave as they have, depressions on both sides,, so they have a maximum, amount of surface to absorb, oxygen from the lungs, , They are produced in red bone, marrow of the:, ribs, Humerus (upper arm bone), Femur (upper leg bone), sternum, and other long bones, They live for 120 days, Old red blood cells are destroyed in, the liver and spleen
Page 14 :
WHITE BLOOD CELLS, • White blood cells, defend against, disease by, recognizing, proteins that do, not belong to, the body., • They are able to, ooze through the, walls of, capillaries to, patrol the, tissues and, reach the lymph, system.
Page 15 :
PLATELETS, • Platelets are cell, fragments used in, blood clotting., • They are derived, from, megakaryocites., • Because they lack, a nucleus,, platelets have a, short lifespan,, usually about 10, days.
Page 17 :
THE 4 BLOOD TYPES, The Rhesus (Rh) factor is an inherited protein found on the surface of red, blood cells., , If your blood has the protein, you're Rh positive. If your blood lacks the, protein, you're Rh negative., Rh positive is the most common blood type., There are four blood types., and O., 1., , A+, A-, , 2., , B+, B-, , 3., , Ab+, Ab-, , 4., , 0+, O-, , A, B , AB,, , ~ All blood has a Rh, ~ The Rh determined the blood type.
Page 18 :
WHY DO MOSQUITOES, LIKE ME ?, Do you find that mosquitoes, and other biting insects, choose you, rather than other, people ?, Did you ever wonder why ?, , If you have Type O blood, they, prefer you twice as much,, than others, who have, Type A !! People with Type B,, fall in the middle of these 2., An estimated 20 percent of, people, it turns out, are, especially delicious for, mosquitoes, and get bit more, often on a consistent basis
Page 19 :
BLOOD PRESSURE, As blood is moved through your body, it exerts pressure, against the walls of blood vessels., • Systolic Pressure: as, your heart contracts to, push blood into your, arteries, your blood, pressure is at its highest, point., • Diastolic Pressure: As, your heart relaxes to, refill, blood pressure is at, its lowest point.
Page 20 :
There is an electrical system inside, your heart that controls the rate, (speed) and rhythm of your heart., A normal heart rhythm is called, normal sinus rhythm (NSR)., When there is a problem with your, heart rhythm or rate, it is called, arrhythmia., The heart’s electrical system, It starts with an electrical signal in, the right atrium, at the SA Node, (sinoatrial node). The electrical, signal then spreads throughout the, heart from top to bottom (from, atria to ventricles). As one part, contracts, the others relax in a, sequence.
Page 21 :
WHAT IS AN ECG OR AN EKG? - An electrocardiogram (ECG, or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by, measuring the electrical activity of the heart., , With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through, your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood, from the heart., An ECG measures and records the electrical activity that passes, through the heart. A doctor can determine if this electrical activity is, normal or irregular.
Page 22 :
ANGIOPLASTY, BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY, AND STENTS, Your heart’s arteries can become blocked or narrowed from a buildup, of cholesterol, cells or other substances (plaque) which can reduce, blood flow to your heart and cause chest discomfort., Angioplasty opens blocked arteries and restores normal blood flow to, your heart muscle. It is not major surgery., It is done by threading a catheter (thin tube) through a small, puncture in a leg or arm artery to the heart. The blocked artery is, opened by inflating a tiny balloon in it., , https://www.youtube.c, om/watch?v=p3z9FLYij, rQ
Page 23 :
A pacemaker is a battery-operated device placed in the, body to produce electrical pulses that cause the heart, to beat at a normal rate.
Page 24 :
Over the last 60 years, the size of Pacemakers have, been reduced a lot, .
Page 25 :
WORLD’S SMALLEST, PACEMAKER, Medtronic’s Micra, Pacemaker was, approved by the FDA, for use in the United, States on April 6,, 2016., This tiny device is, implanted inside the, patient’s heart and, small tines then attach, to the heart wall., , It is 93% smaller than, conventional, pacemakers, and about, the size of a large, vitamin capsule.
Page 26 :
Recent research studies have described the use of energy, harvesting to power a pacemaker to eliminate the battery they use,, so a future operation isn’t needed to replace the unit and battery., The goal for energy harvesting in this case is to eliminate the need, for a battery by generating electricity derived from an external, source and possibly from the movement of the heart and, surrounding organs !!
Page 27 :
This video shows a rabbit heart that has been kept beating outside, of the body in a nutrient and oxygen-rich solution., The new cardiac device -- a thin, stretchable membrane imprinted, with a spider-web-like network of sensors and electrodes -- is, custom-designed to fit over the heart and contract and expand with, it as it beats.
Page 28 :
BIOLIFE4D MINIATURE HEART, Chicago-based biotech outfit Biolife4D, claims to have 3D bio-printed a, miniaturized human heart — chambers,, ventricles, and all., , The company used a proprietary bio-ink, — the company described it as “similar in, properties to gelatin” — that was, designed from the ground up to replicate, actual human biomaterials., To help with structural integrity during the, printing process, Biolife4D printed an, additional support scaffold encasing the, heart., https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DcUtKiAsuUQ (set at .75 speed)
Page 29 :
The problem - More than, 3,200 people are on the, waiting list for a heart, transplant in the United States., The solution - Take a pig, heart, soak it in an ingredient, commonly found in shampoo, and wash away the cells until, you're left with a protein, scaffold that is to a heart what, two-by-four framing is to a, house.
Page 30 :
Then inject that ghost heart, as it's called, with hundreds, of millions of blood or bone-marrow stem cells from a, person who needs a heart transplant, place it in a, bioreactor -- a box with artificial lungs and tubes that, pump oxygen and blood into it -- and wait as the ghost, heart begins to mature into a new, beating human heart.
Page 31 :
It’s interesting that there are other colors of blood, than, our own red. The colors shown below are the real, colors of various other creatures.
Page 33 :
COOL FACTS ABOUT YOUR CIRCULATORY, SYSTEM, ❖ The body of an adult contains over 60,000 miles of blood, vessels!, ❖ An adult's heart pumps nearly 4,000 gallons of blood each, day!, ❖ In one day your heart beats 100,000 times, which, comes out to about 30 million times a year which is at, least 2.8 billion times during the average life span –, and with resting between beats !, , ❖ A "heartbeat" is really the sound of the valves in the heart, closing as they push blood through its chambers., ❖ Women’s hearts beat faster than men’s., ❖ A single drop of Blood contains 250 million red blood cells, and 275,000 white blood cells !
Page 34 :
In ten years, a cell will have travelled over 59,654 miles –, equivalent to 2.4 times the distance around the earth!
Page 35 :
Human lips have a reddish color because of the great, concentration of tiny blood capillaries just below the skin., The blood in these capillaries is normally highly oxygenated, and therefore quite red. This explain why the lips appear pale, when a person is anemic.
Page 36 :
AND NOW SOME HEART HUMOR…
Page 38 :
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused when your, heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen-rich blood.
Page 39 :
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused when your, heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen-rich blood.
Page 40 :
"And now, for the winner of the echocardiogrammy!"