Page 1 :
BEEE, , Information Technology Semester ||, (Unit 2)-Basic Electrical Quantities, by, , MEENAKSHI RASTOGI, , Lecturer- Electrical Engineering, Government Polytechnic Lucknow
Page 4 :
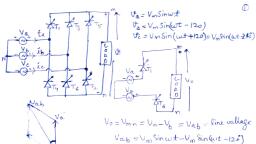
Electric Voltage, , *Voltage (also known as electric potential difference,, electromotive force emf, electric pressure, or electric tension) is, defined as the electric potential difference per unit charge, between two points in an electric field. Voltage is expressed, mathematically (e.g. in formulas) using the symbol “V” or “E”., , * In a static electric field, the work required to move per unit of, charge between two points is known as voltage. Mathematically,, , the voltage can be expressed as,, workdone(W), , charge(Q), Where, work done is in joules and charge is in coulombs., , voltage(V) =
Page 5 :
Unit of voltage, , 1 volts = 1 joule, vos = 1 coulomb, , * We can define the voltage as the amount of potential energy between, two points in a circuit., , * One point has a higher potential and the other polis have lower, otential. The difference in charge between higher potential and, ower potential is called a voltage or potential difference., , * The voltage or potential difference gives the force to the electrons to, flow through the circuit., , * The higher the voltage, the greater the force, and hence the more, electrons flowing rong the circuit. Without voltage or potential, difference, electrons would move randomly in free space.