Page 2 :
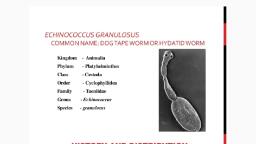
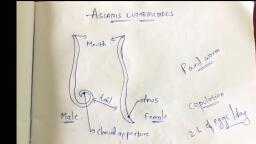
INTRODUCTION, • Ascaris lumbricoides (round worm) is the largest nematode parasitizing the, human intestine, • It is an intestinal worm found in the small intestine of man, • More common in children than adult, • As many as 500 to 5000 adult worms may inhabit a single host, • The human is an intermediate and final host, • The adult worm is present in the small intestine whereas the larva in the lungs, • The infective stage is the ovum
Page 3 :
• The round worm resembles to earthworm. It is elongated tapering to both, end, anterior being thinner than posterior., • Freshly excreted worm is yellowish pink in color, which gradually changes to, white., • The worm is sexually dimorphic., ➢Adult male: 15-30 cm in length, 3-4 mm in diameter,, tail curved, ➢Adult female: 20-40 cm length, 2-6mm diameter,, tail straight
Page 4 :
LIFE CYCLE, • The life cycle of Ascaris completes in single host: Human, • Adult worm lives in small intestine, • Stages in life cycle:, • Stage I: Eggs in faeces, ➢Sexually mature female produces as many as 200,000 eggs per day, which are, shed along with faeces in unembryonated form. They are non infective., • Stage II: Development in soil, ➢Embryonation occurs in soil as optimum temperature of 20-25C with sufficient, moisture and oxygen, ➢Infective larva develops within egg in about 3-6 weeks.
Page 5 :
• Stage III: Human infection and liberation of larvae, ➢Human get infection with ingestion of embryonated egg contaminated food and, water, ➢Within embryonated state inside egg, first stage larvae develops into second, stage larvae. This second stage larvae is known as Rhabditiform larvae, ➢Second stage larva is stimulated to hatch out by the presence of alkaline pH in, small intestine and solubilization of its outer layer by bile., , • Stage IV: Migration of larvae through lungs, ➢Hatched out larvae penetrates the intestinal wall and carried to liver through, portal circulation, ➢It then travels via blood to heart and to lungs by pulmonary circulation within 4-7, days of infection., ➢The larvae in lungs molds twice, enlarge and breaks into alveoli.
Page 6 :
• Stage V: Re-entry to stomach and small intestine, ➢From alveoli, the Larvae then pass up through bronchi and into trachea and, then swallowed., ➢The larvae passes down the oesophagus to the stomach and reached into small, intestine once again., ➢Small intestine is the normal habitat of Ascaris and it colonises here., ➢Within intestine parasite molds twice and mature into adult worm., ➢Sexual maturation occurs with 6-10 weeks and the mature female discharges, its eggs in intestinal lumen and excreted along with faeces, continuing the life, cycle., ➢The life span of parasite is 12-18 months
Page 8 :
PARASITIC ADAPTATIONS, • Parasitic adaptations are a series of changes that occurs over time in a parasitic, organism to bear with the factors present in the host., • Ascaris is an endoparasitic roundworm residing in the internal organs like, intestine, heart, liver, lungs etc. of humans., • To suit its parasitic mode of life it has to overcome to several adverse conditions., And accordingly this roundworm shows several parasitic adaptations., • The following are the important parasitic adaptations of Ascaris., 1.The presence of though, thick and resistant cuticle. This cuticle covers entire, body and gibes protection against the action of the digestive enzymes and, antitoxins of the host. On the other hand Ascaris itself also secreted several antienzymes to protect itself from digestive enzymes of host.
Page 9 :
2. Though these worms do not have adhesive suckers and spines, their ability of, locomotion helps them counteract the peristaltic movement of the host’s, intestine. Its power of locomotion helps it from getting displaced and it remains, in the intestine of the host., 3. The muscular pharynx helps in ingestion of food particles through its sucking, action, 4. They are located in the regions where there is continuous supply of food, material and so their alimentary tract is simple without any special storage, organs., 5. The food they ingest is pre-digested and so there is no need for digestive, glands, 6. The function of absorption, transport and distribution of food, oxygen and, waster products is served by pseudocoleomic fluid. As a result there is no need, of circulatory system.
Page 10 :
7. Anaerobic mode of respiration and extremely low metabolic rate helps the worms live, inside the intestine of the host where there is no availability of free oxygen., 8. As these worms are endoparasites living well protected inside the human intestine,, there is no need of special and complicated sensory organs., 9. The transfer to a new host is an extremely hazardous and passive process depending, entirely on accidental ingestion of embryonated eggs by specific host. For example each, egg laid by pig Ascaris must be consumed by another pig for its growth and, development similarly the eggs laid by human Ascaris must be ingested by humans only., Also the temperature and environment must suit the development of the eggs. Thus to, overcome all these conditions, these worms reproduce enormously to produce, numerous eggs to increase chances of survival. So a single mature female lays as many, as 27 million eggs per day., 10. The resistant shell on the zygotes protects them from unfavorable environmental, factors. This shell also increases the viability of the zygote for years., 11. Also the minute size and resistant nature of eggs helps wide dispersal of the, parasites.
Page 11 :
• Ascariais disease, • Infection: The disease caused by the roundworm, Ascaris is known as ascariasis., ➢Humans catch the infection by consuming food and water contaminated by the, infective stages of this parasite. Ascariasis is more pronounced in children than, in adults and this could be due to the sanitary habits., • Pathogenesis: Larvae cause hemorrhages and are considered more dangerous, than the adult roundworms. The larvae also bore through the intestinal, epithelium and enter general circulation to finally land in the organs like, kidneys, spinal cord, brain or muscles and cause serious destruction. Infection of, larvae of Ascaris is followed by fever, anemia, leukocytosis and eosinophilia., • On the other hand the adult roundworms cause enteritis. They migrate into, vermiform appendix, gall bladder and bile duct to cause serious inflammation., The adults get their nourishment from the contents of the intestine. They also, suck the blood from the intestinal walls. The adult worms produce toxins which, irritate the mucous membrane which manifests in the form of convulsions,, delirium, coma and nervousness.
Page 12 :
• The toxin produced by these worms combines with trypsin and interferes with, the protein digestion finally leading to protein deficiency in the human body., This may also cause stunted growth among children. The presence of a few, parasites may also show up symptoms like colic pains, abdominal discomforts,, diarrhea, vomiting and mild temperature., • Treatment and therapy: Generally stool examination is done to diagnose the, presence of Ascaris eggs. Ascariasis can be treated with a dose of hexylresorcinol, crystals in a gelatinous capsule after about 12 hour fasting. This dose followed, by another 4 hours of fasting kills the worms. The killed worms can be expelled, out by a purgative like sodium sulphate., • Also anti-helminthic drugs like Chenopodium oil (Medicinally important fastgrowing weedy annual plant). This oil is highly toxic to the worms. Some drugs, like tetrachloroethane are used to irritate the worms which thus entangle, themselves blocking the lumen. The mixture of Chenopodium oil and, tetrachloroethane is considered very effective. Other anti-helminthic drugs like, heterazan, piperazine hydrate, tetramisole and dithiazanine are also used in the, treatment of this disease.
Page 13 :
• Prophylaxis, ➢Soil pollution is the chief source of infection and it should be prevented., ➢Children must learn and observe sanitary habits to prevent infection., ➢Vegetables must be thoroughly washed and cooked before consuming., ➢Regular trimming of finger nails is very important to avoid accumulation of, eggs under them. Also hands should be thoroughly soap-washed before using, them to eating.