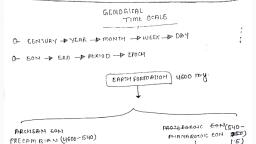
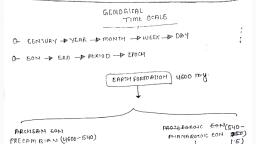
Page 2 :
INTRODUCTION, Any change in the DNA sequence of a cell. Mutations may be caused by, mistakes during cell division, or they may be caused by exposure to, DNA-damaging agents in the environment. Mutations can be harmful,, beneficial, or have no effect. If they occur in cells that make eggs or sperm, they, can be inherited; if mutations occur in other types of cells, they are not, inherited. Certain mutations may lead to cancer or other diseases. A mutation is, sometimes called a variant., , DEFINITION, mutation is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to mistakes, when the DNA is copied or as the result of environmental factors such as UV, light and cigarette smoke., HISTORY, , CAUSES OF MUTATION, , ● Over a lifetime our DNA? can undergo changes or ‘mutations?’ in the, sequence of bases?, A, C, G and T., ● This results in changes in the proteins? that are made. This can be a bad, or a good thing., ● Mutations can occur during DNA replication? if errors are made and not, corrected in time., ● Mutations can also occur as the result of exposure to environmental, factors such as smoking, sunlight and radiation., ● Often cells can recognise any potentially mutation-causing damage and, repair it before it becomes a fixed mutation., ● Mutations contribute to genetic variation? within species?., ● Mutations can also be inherited, particularly if they have a positive effect.
Page 3 :
EXAMPLE OF MUTATION, ● For example, the disorder sickle cell anaemia? is caused by a mutation in, the gene? that instructs the building of a protein called haemoglobin?., This causes the red blood cells? to become an abnormal, rigid, sickle, shape. However, in African populations, having this mutation also, protects against malaria?., ● However, mutation can also disrupt normal gene activity and cause, diseases, like cancer?, ● Cancer is the most common human genetic disease; it is caused by, mutations occurring in a number of growth-controlling genes. Sometimes, faulty, cancer-causing genes can exist from birth, increasing a person’s, chance of getting cancer., , TYPES OF MUTATION, 1. Cell Mutation, ● Somatic cell mutation
Page 4 :
●, , Germ cell Mutation
Page 5 :
MAJOR TYPE OF MUTATION, 1. Chromosomal Numer Mutation
Page 6 :
2. Chromosomal structure Mutation
Page 7 :
Gene Mutation