Page 1 :
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , “6. Animal Classification”, , “How are the animals classified”, , ❖ There are seven major levels of classification: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order,, Family, Genus, and Species., , ❖ The two main kingdoms we think about are plants and animals. Scientists also list four, other kingdoms including bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, and protozoa., , Kingdom, Generally, scientists agree there are six kingdoms. The animal kingdom (called, Kingdom Animalia) is just one of those. In case you’re interested, the others are, Achaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungi and Plants, Phylum, Within the animal kingdom, the animals are divided into more than 30 phyla (which is, the plural of “phylum”). You might be interested in Phylum Chordata — it’s the one, humans and all animals with backbones, Class, The third level of classification is class. For example, Phylum Chordata has classes in it, like birds, mammals (Mammalia) and reptiles., Order, The next level, or rank, is order. Orders are smaller groups within the different, classes. Lepidoptera is the order of moths and butterflies., Family, The fifth rank of classification is family. (When you get to this rank, people sometimes, disagree about which family an animal belongs to, so you may find that different, sources tell you different things., Genus, This rank looks like “genius,” doesn’t it? It’s the second-to-last rank, and a genus may, have only one or two animals in it. If animals are in the same genus, they are really, closely related., Species, If animals can breed together successfully, they are a species. When an animal is, called by its scientific name, then that means it is being identified by its genus
Page 2 :
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , “Traditional method of animal classification”, ❖ the animal kingdom has been divided into two groups, ❖ Non-chordates and Chordates., A. Non-Chordates : Characters of non-chordate animals are as follows, 1. Body is not supported by rod-like notochord., 2. Pharyngeal gill-slits are absent., 3. Nerve cord; if present, it is on ventral side. It is solid & paired., 4. Heart, if present, it is on dorsal side., , Chordates : Characters of chordates are as follows, 1. Body is supported by notochord., 2. Pharyngeal gill-slits or lungs are present for respiration., 3. Nerve cord is present on dorsal side of body. It is hollow., 4. Heart is present on ventral side of body., , “new system of classification”, “The Protist Kingdom”, ❖ When Linnaeus created his taxonomy, microorganisms were almost unknown., ❖ As scientists began studying single-celled organisms under the microscope, they, generally classified them as either plants and or animals., ❖ For example, bacteria are single-celled organisms, some of which make their own, food. They were classified as plants, which also make their own food., , “The Bacteria Kingdom”, ❖ a bacterial cell, a protozoan cell, and an animal cell., ❖ When you compare the three cells, what differences do you see? The major, difference is that, unlike the protozoan and animal cells, the bacterial cell does not, contain a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane., ❖ Instead, its DNA is found in the cytoplasm of the cell. Organelles in the bacterial cell, also lack surrounding membranes.
Page 3 :
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , “The Fungi Kingdom”, ❖ Fungi are eukaryote organisms such as mushrooms and molds., ❖ Up until then, fungi had been classified in the plant kingdom. Whittaker separated, fungi from plants on the basis of differences in metabolism, ❖ . Plants make their own food in the process of photosynthesis, whereas fungi obtain, nutrients by breaking down dead organisms., , “Kingdom Plantae”, ❖, ❖, ❖, ❖, , The kingdom Plantae is filled with all eukaryotes which have chloroplast., Most of them are autotrophic in nature, but some are heterotrophic as well., The Cell wall mainly comprises of cellulose., Plants have two distinct phases in their lifecycle.
Page 4 :
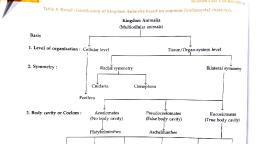
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , “Kingdom Animalia”, ❖ All multicellular eukaryotes which are heterotrophs and lack cell wall are set aside, under this kingdom., ❖ The animals are directly or indirectly dependent on food on plants. Their mode of, nutrition is holozoic. Holozoic nutrition encompasses ingestion of food and then the, use of an internal cavity for digestion of food., ❖ Many of the animals are adept for locomotion., ❖ They reproduce by sexual mode of reproduction., , “ Body Symmetry”, ❖ symmetry refers to a correspondence of body parts, in size, shape, and relative, position, on opposite sides of a dividing line or distributed around a central point or, axis., What are the 3 types of body symmetry?, , ❖ Animals can be classified by three types of body plan symmetry: radial, symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and asymmetry., ❖ Asymmetrical Body : In case of such body, there is no any such imaginary axis of, the body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Amoeba, Paramecium, ❖ Radial symmetry : In this type of body, if imaginary cut passes through central axis, but any plane of body, it gives two equal halves. Ex. Star fish. I, ❖ Bilateral symmetry: In this type of body, there is only one such imaginary axis of, body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Insects, fishes, frog, birds,, human, etc.
Page 5 :
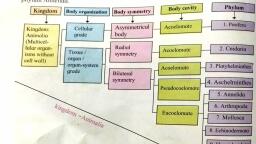
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , “Body cavity (Coelom)”, ❖ Cavity between the body and internal organs is called as body cavity/coelom, , “Body Segmentation”, ❖ If the body of animals is divided into small, similar units, then such body is called as, segmented body and each small unit is called as segment. Ex. Animals like, earthworm, , Phylum- Porifera, 1. These animals are with simplest body plan and are called as ‘Sponges’. They bear, numerous pores on their body. Those pores are called as ‘Ostia’ and ‘Oscula’., 2. These are aquatic animals. Most of them are marine and few are fresh water dwellers., 3. Most of the animals have asymmetrical body., 4. These animals have special types of cells- collar cells. 5. These animals are always, attached to substratum,, , “Phylum - Coelenterata/Cnidaria”, 1. Body of these animals is cylindrical or umbrella-like. If it is cylindrical, it is called as ‘Polyp’, and if it is umbrella like, it called as ‘Medusa’., 2. Most of these animals are marine. Only few are fresh-water dwellers., 3. Body of these animals is radially symmetrical & diploblastic., 4. Cnidoblast bearing tentacles are present around the mouth., , “Phylum – Platyhelminthes”, 1. Body of these animals is slender & flat like a leaf or strip. Hence, they are called as, ‘flatworms’., 2. Most of these animals are endoparasites. Few are free-living & aquatic., 3. Body is acoelomate & bilaterally symmetrical., 4. These are triploblastic i.e. their body is made up of three germ layers- endoderm., , “Phylum – Annelida”, 1. Body of these animals is long, cylindrical & metamerically segmented., 2. Most of the animals are free-living, but few are ectoparasites. Free-living animals may, be marine or fresh water dwellers or terrestrial., 3. These animals are triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical and eucoelomate.
Page 6 :
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , “Phylum- Arthropoda”, 1. These animals have jointed appendages. Hence they are called as arthropods., 2. Planet Earth has highest number of animals from this phylum. Hence, this is largest, phylum with highly successful animals in animal kingdom., 3. These animals are found in all types of habitats ranging from deepest oceans to highest, mountains., 4. Body of these animals is triploblastic, eucoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical and, segmented., , “Phylum- Mollusca”, 1. Body of these animals is soft and slimy. Hence they are referred as mollusc., 2. This is second largest phylum in animal kingdom., 3. These animals are aquatic or terrestrial. Most of the aquatic molluscs are marine, but, few are fresh water dwellers too., 4. Body of these animals is triploblastic, eucoelomate, non-segmented and soft. Except, animals like snail, their body shows bilateral symmetry., , “Phylum- Echinodermata”, 1. Calcareous spines are present on the body of these animals; hence they are called as, echinoderms., 2. These animals are found only in ocean., 3. Their body is triploblastic, eucoelomate. And it is radially symmetrical in adult stage., However, they show bilateral symmetry in larval stage., 4. They perform locomotion with the help of tube-feet. Tube feet are also useful for, capturing the prey. Some animals are sedentary., , “Phylum- Hemichordata”, 1. Body of these animals is divided into three parts as proboscis, collar & trunk., 2. Notochord is present in proboscis region only. Hence, they are called as hemichordates., 3. These animals are also called as ‘acorn worms’., 4. These are marine animals, live in burrows in sand., , “Phylum- Chordata”, 1. Notochord is present in the body during at least any developmental stage., 2. Pharyngeal gill slits are present in the body during at least any developmental stage.
Page 7 :
Search :- New Indian Era on youtube, , 3. Single, tubular spinal cord is present on dorsal side of body., 4. Heart is present on ventral side of body., , “A. Sub phylum – Urochordata”, 1. These are marine animals., 2. Their body is covered by skin-like test or tunic., 3. Larvae of these animals are freely swimming, and notochord is present in only tail region of larvae., Hence, they are called as Urochordata., , “B. Sub phylum -Cephalochordata”, 1. These are small, fish-like, marine animals., 2. Notochord is present throughout the body length., 3. Pharynx is very large and contains gill-slits., , “C. Sub phylum -Vertebrata/Craniata”, 1. In these animals, notochord is replaced by vertebral column., 2. In these animals, head is well developed., 3. Brain is protected by cranium., , “Best of luck”