Page 1 :
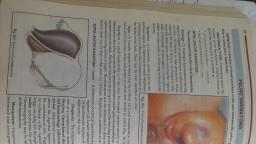
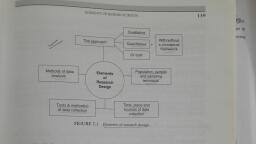
sie, FORMULATION OF RESEARCH PROBLEM , EXAMPLE, , , , , , , , , , , , , Initially a researcher selects a broad area for, , Selection of a research, study, such as Hospital-Acquired Infections, , ‘Opic, , , , , , , , , To know what already has been done in this, area, and to develop an original and unique, research problem, an extensive review of, , literature and theories is done at this stage, , , , , , , , , , , Reviewing the literature, , , , , , , , , , , , , HAI is very broad area, so at this stage,, researcher delimits the topic from HospitalAcquired Infections to the incidence of VAP, , Delimiting-the-research, topic _, , , , , , , , At this stage, researcher evaluates the research, problem for feasibility, substantive,, methodological, and ethical dimensions., , , , , , , , , Evaluating the research, problem, , , , , , , , , Finally, a statement of problem is formulated, keeping in mind basic components of research, problem. Example, ‘A descriptive study on, incidence of VAP among patients on MV, admitted in ICU of AIIMS, Rishikesh’., , , , , , , , , , , Formulating the final statement, of the research problem ~~, ——, , , , , , VAP: Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia; MV: Mechanical Ventilator, , FIGURE 3.2 Steps for formulation of research problem, , example, initially a researcher decides to conduct a study on female feticide; later, in, this stage, the researcher limits it to a specific research topic: A study on perception, of women about causes and prevention of female feticide in selected rural communities, of district Shimoga, Karnataka. In this stage, the researcher clearly identifies, variables, population, and setting of research study. Furthermore, at this stage,, ‘the researcher is quite clear about the phenomenon to be studied where, and on whom.