Page 1 :
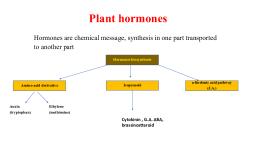
Fruit Cracking, , This disorder defines the phenomenon of surface or tissue cracking, in a wide range of levels that depend on varietal susceptibilities,, nutritional deficiencies, and environmental conditions. Among, quality disorders, fruit cracking is a prime concern where nutrient, calcium status has provided insights of its involvement in the, physiological process of the cellular adhesion lost. Calcium, represents the most studied internal factor involved in tissue, cracking, although other external factors considered as, environmental conditions (e.g., drought, high temperature,, excessive water, and high solar radiation) have been determined as, elements for cracking resistance. The concern for its management, is to have the minerals in balanced availability at the early stages of, fruit formation. Boron and silicon as part of the structure of cell walls, might have also been involved in cracking, although the thresholds, and distribution ranges inducing the disorder have not been defined, for each commodity. Control of this mineral deficiency also requires, the combination of weather conditions as well, as germplasm tolerant to cracking. The single incorporation of, mineral amendments has been ineffective in increasing structural, minerals and cracking prevention., Calcium (Ca) is an essential nutrient required for growth of plants. It, also works as secondary messenger. Fruit plants absorb Ca in the, form of divalent cation (Ca2+) that is needed for numerous key, physiological processes related with ripening, cell wall structure,, integrity of membranes, activity of certain enzymes, and signal, transduction. The deficiency of Ca in fruits may result in various, physiological disorders of significant economic value like fruit, cracking,, Fruit cracking is a common phenomenon in the production of fruits and vegetables, and it is, generally easy to appear in the middle and late stages of fruit growth., After the fruit is cracked, the quality of the fruit will decline, and the pathogens will easily, invade, cause rot, and cause serious losses., But now when it comes to fruit cracking, most people will first consider calcium deficiency,, and even think that as long as calcium is supplemented, the fruit will not crack. This idea is, actually wrong. There are many reasons for the formation of cracked fruit, involving, moisture, fertilization, and management. In the actual operation, it is necessary to, comprehensively analyze the causes of the cracking and comprehensively prevent cracking.
Page 2 :
Comprehensive analysis, there are following 5 reasons for fruit cracking, , 1. Variety, Fruit cracking has a lot to do with the physiological and genetic characteristics of the variety., The fruit type size, peel thickness, fruit water content, cell compactness, sugar content and, acid content, and peel development quality will all affect fruit cracking., E.g:, Among grape varieties, varieties with thin skins and brittle flesh are prone to cracking, and, varieties with fast root water absorption and large water absorption during the coloring period, are prone to cracking., Among nectarine varieties, those with higher sugar content and lower acid content have, heavier cracking., For melons, watermelons and other melons and fruit varieties, the ones with thin and crisp, skin have heavier cracking., , 2. Improper management measures, (1) Temperature changes., The temperature in the early stage of fruit development is low, and then the temperature rises, suddenly. The fruit expands rapidly, causing fruit cracking., (2) The rapid change of soil moisture causes fruit cracking., In the early stage of crop growth, if frequent rainfall occurs during the rapid fruit, expansion period, the water transported by the root system to the fruit will increase rapidly,, and the pulp cells will rapidly expand. At this time, the peel is mostly aging, and the peel, cells are slow to expand due to the restriction of the cuticle. There will be cases where the, pulp bursts into the peel., This kind of fruit cracking is more common on grapes, jujubes, and pomegranates. If there is, a lack of water in the early stage, it will affect the expansion of the young fruit. During the, coloring period, continuous rainfall or flooding will cause a large number of fruit cracks., , Reason: High temperature, strong light, drought and other factors will, produce cork layer near the fruit pedicle, and the fruit sugar concentration, will increase. After long time drought, rainfall and sudden large amounts, of water will cause the pulp in the fruit to expand rapidly, and the osmotic, pressure increase, it will cause the peel to swell and crack, and the cracks, are mostly in the fruit shoulders.
Page 3 :
3) The supply of water and fertilizer is uneven, and the radish is prone to crack roots., During fruit growth, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium have the greatest impact on fruit, cracking, followed by elements such as magnesium, boron, zinc, iron, copper, and, manganese., When one or several elements are excessive and the content of other elements is low, fruit, cracking will increase., In actual production, in the later stage of crop growth, the phenomenon of fruit cracking due, to lack of calcium and excess potassium is very common., For example: One of the main reasons for the fruit cracking in the navel of tomatoes is the, lack of mineral calcium., Therefore, in order to prevent the imbalance in the supply of mineral elements during the fruit, growth period, the application amount of nitrogen fertilizer should be appropriately, controlled, the application amount of trace element fertilizers should be appropriately, increased to meet the fertilizer nutrients required for fruit growth and development, and, calcium and boron fertilizers and appropriate amounts of trace element fertilizers should be, supplemented in time , Adjust the ratio of various nutrient elements in the soil, nitrogen, fertilizer and potassium fertilizer should not be too much, otherwise it will affect the plant's, absorption of calcium., (4) Fruit cracking caused by improper operation., In the daily vegetable production and cultivation management process, in order to increase, the ventilation and light transmission in the shed, and to improve the coloring degree of the, fruit, the leaves are excessively thinned., Vegetable farmers only leave a few upper leaves, and the lower leaves are all removed., The functional leaves are insufficient, the photosynthetic products produced are insufficient,, and the fruits cannot get sufficient nutrition and show the phenomenon of fruit cracking., , 3. Improper use of plant growth regulators or imbalance of plant, endogenous hormones, Improper hormone treatment when eggplant is dipped into flowers can easily cause calyx, cracks., In the low temperature environment in winter, it is difficult to set fruit without hormone, treatment. However, if the concentration of 2,4-D growth regulator is too large, or it is used, repeatedly, or used in advance to the young bud stage, or used when the high temperature, evaporation is large at noon, it is easy to induce the formation of calyx cracked fruit and, deformed fruit., , Diseases and pests
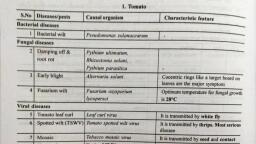
Page 4 :
The damage of anthracnose, rust tick, and red spider is related to fruit cracking, so attention, should be paid to the prevention and control of pests., Anthracnose causes cotton boll cracking, 5. Soil problems, At present, the problem of soil acidification is becoming more and more prominent. The, lack of middle and trace elements or the imbalance caused by this are very common, which, has aggravated the occurrence of fruit cracking., Usually use more organic fertilizers and use them in conjunction with bacterial fertilizers, to reduce the amount of chemical fertilizers. Adjust the degree of soil acidification and, reduce the degree of fruit cracking.