Page 1 :
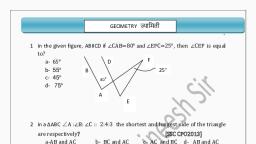
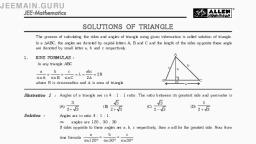
The “angle between internal 4 E, bisector of a base angle and, external bisector of the other, base angle is half of the, remaining vertex angle. i.e, 2ZBEC = ZBAC., , , , , , , , In AABC, AE 1 BD A, , and AD is angle \\, bisector of A, then, , ZEAD = 5|8-<¢, , Sine Rule B D C, , a b C, , ==, , sina sinB_ sinc, , cosA=, , bem + cen =a? +mn], , . CENTERS OF TRIANGLE, , Cosine Rule, b? +¢* a4 ¢ b, 2be, , Stewart's Theorem:, , , , <—— a>, , the, | |, , Circumcenter:, , The length from all 3 vertices, circumcenter is equal and is, called circumradius., , ZQCR = 2.7QPR, Circumradius of a triangle, where PQ,QR and PR are, sides ¢, a, and b, , P, , to L\, , Q ey R, respectively., a abe , A(area ofA}, , , , Location of circumcenter, The circumcenter of an acute triangle is inside the triangle., The circumcenter of an obtuse triangle is outside the, , triangle, , LN (>, B C D, , -AB+BC-AC, , . RELATION BETWEEN R(IN, , , « The circumcenter of a right-angled triangle is on the, , hypotenuse., It is the midpoint of hypotenuse., , hypotenuse length ., 2, , So, R = in right triangle, , . INCENTER, , BIC 90+,, , ZAC =90" +,, , ZBIA = 90° + <, , Al: ID= b+c: a, BI: IE= a+c: b;, , , , Cl: P= a+ b:¢, , Inradius of a right angle AABC, , 2, , , , Area ofsany triangle is product of inradius and semi, , , , perimeter, A=TS, . EX-CIRCLE, A, ZBEC= 90° - 2, Ex-radii :, A A, Ya = i Vb = sD, S-a s~—b, A, i= —, S-C, , RADIUS) ,R(CIRCUMRADIUS) AND ANGLES OF, TRIANGLE, , , , B, , D, The distance (d) between the circumcenter (1) and, , incentre (1, ) of a triangle is d=, (2 ~ Qf