Page 4 :
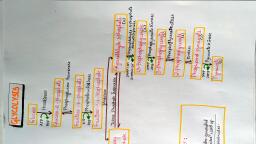
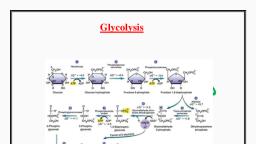
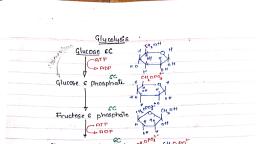
526, Chapter 14 Glycolysls, Gluconeogenesis, and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway, Nattne reaction but are encoded in different genes are, called isozymes., the boiled sermu revealed that inonganie phosplate was, responsible for the stinmlation Ilarlen and Young soon, discovered thuat ghicose added to their yeast extract was, converted to a hexose bisplosplate (the "I larden-, Young ester," eventually identified as fructose 1,6-, bisphosphate) This was the beginning of a long series, of investigations on the role of organic esters of phos-, phate in biochemistry, which has led to our current un-, derstanding of the central role of phosphoryl group, transfer in biology, (2 Converslon of Glucose 6-Phosphate to Fructose 6-Phasphate Isomeri, The enzyme phosphohexose isomerase (phospho-, glucone isomerase) catalyzes the reversible isomer-, ization of glucose 6-phosphate, an aldose, to fructose, 6-phosphate, a ketose:, 6 meml, CH,OH PYAane, qlucwse, fananos, fru, CH,OPO;-, CH,OPO;-, 1 Phosphorylatlon of Glucose In the first step of glycol-, ysis, glucose is activated for subsequent reactions by its, phosphorylation at C-6 to yield glucose 6-phosphate,, with ATP as the phosphoryl donor:, Mg, H HO, O11 11, Но, phepluhet, emerae, н но, Fructose 6-phosphate, CH-OPO-, Glucose 6-phosphate, CH2-OH, АТР, II, ADP, AG" = 1.7 kJ/mol, II, II, H., II, The mechanism for this reaction is showrm in Figure, 14-4. The reaction proceeds readily in either direction,, as might be expected from the relatively small change, in standard free energy. This isomerization has a criti-, cal role in the overall chemistry of the glycolytic path-, way, as the rearrangement of the carbonyl and hydroxyl, groups at C-l and C-2 is a necessary prelude to the next, Lwo steps. Thıe phosphorylation that occurs in the nexL, reaction (step ) requires that the group al C-1 first, be convertedl from a carbonyl to an alcohol, and in the, subsequent reaction (step) cleavage of the bond be-, tween C-3 and C-4 requires a carbonyl group al C-2, (p. 485)., OH H, OH H, hesokine, ÓH, Glucnse, Glucose 6-phosphate, AG" = -16.7 kJ/mol, This reaction, which is irreversible under intracel-, lular conditions, is catalyzed by hexokinase. Recall that, kinases are enzymes Uat catalyze the transfer of the, teuinal phosphoryl group from ATP to an acceptor nu-, cleophile (see Fig. 13-10). Kinases are a subclass of, transferases (see Table 6-3). The acceptor in the case, of hexokinase is a hexuse, normally n-glucose, although, hexokinase also catalyzes the phosphorylation of other, common hexoses, such as D-fnictose and D-mannosc., Ilexokinasc, likc many other kinascs, requircs Mg*, for its activity, because the true substrate of the cnzyme, is not ATP-buut the MgATT complex (sce Fig. 13-2)., Mg* shields the negative charges of the phosphoryl, groups in ATP, making the terminal phosphorus atotn an, easier target for mucleophilic attack by an-OH of ghi-, cose. Hexokiase undergoes a profound change in, shape, an induced fit, when it. binds glucose; two do-, mains of the protein move about 8 A closer to each other, when ATP binds (see Fig. 6-22). This movement brings, bound ATP closer to a molecule of glucose also bound, to the enzyme and blocks the access of water (from the, solvent), which might otherwise enter the active site, and attack (hydrolyze) the phosphoanhydride bonds of, ATP. Like the other nine enzymes of glycolysis, hexo-, kinase is a soluble, cytosolic protein., Hexokinase is present in all cells of all organisms., Hepatocytes also contain a form of hexokinase called, hexokinase IV or glucokinase, which differs from other, forms of hexokinase in kinetic and regulatory proper-, ties (see Box 15-2). Two enzymes that catalyze the, 3 Phosphorylation of Fructose 6-Phosphate to Fructose 1,6-, Bisphosphate In the second of the two priming reactions, of glycolysis, phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) cat-, alyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to, fructose G-phosphate to yield fructose 1,6-bisphos-, phate:, CH,OPO-, CH,-OH, ATP, ADP, н но, phusphuiuctukne-1, (T'FR-1), ÓH H, Fructose 6-phusphate, CH,OPO, CH2-OPO;-, н но, OH H, Fruclose 1,6-bisphosphale, AG" = -14.2 kJ/mol, Scanned with CamScanner