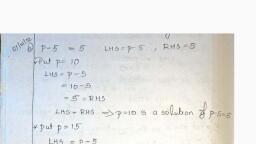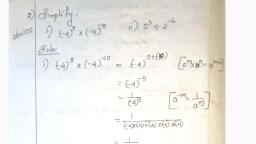Page 1 :
Chapter, , Relations and Functions, , . Let R bea relation on the set N of natural numbers, defined by nRim if 1 divides m. Then R is:, (a) Reflexive and symmetric, (b) Transitive and symmetric, (c) Equivalence, (d) Reflexive, transitive but not symmetric., , . If the set A contains 7 elements and set B contains, 10 elements, then the number of one-one functions, from A to B is:, , (a) %c, (b) "C,«7!, (c) 7° (d) 107, , . Let N be the set of natural numbers and the function., f:N—N be defined by f(n) = 2n +3 V € N. Then fis, (a) surjective (b), (c) bijective (d) none of these, , . Set A has 3 elements and the set B has 4 elements., Then the number of injective mappings that can be, defined from A to B is:, , (a) 144 (b) 12, (c) 24 (d) 64, , . If A = {a, b, c} and B = (4, 5, 6}, then number of, functions from A to B is:, , (a) 9 (b) 27, (c) 18 (d) 81, , . Let f: R > R be defined by f(x) = x2 + 1. Then, pre, images of 17 and - 3, respectively, are:, (@) 6, (4-4) b) B-3L6, (©) (4-446 (a) {4,-4} (2,-2}, , . For real numbers x and y, define xRy if and only ifx, -y+ J2 is an irrational number. Then the relation, Ris:, , (a) reflexive (b) symmetric, (c) transitive (d) none of these, , . Let A={2, 3, 6}. Which of the following relations on, , A are reflexive?, , (a) R={@, 2), G, 3), ©, 6)}, , (6) R={(@ 2), G,3) (3, 6), 6 3)}, (c) R={2, 2), G, 6), (2, 6)}, , (d) None of these, , . Let R be the relation on N defined by R = {(x, y):x+, 2y = 8}. Then, the domain of R is:, , (a) (2, 4,6, 8} (b) {2,4 8}, (c) {2,4, 6} (d) {1, 2,3, 4}, , injective, , 10., , ., , 12., , 13., , 14., , 15., , 16., , 17., , 18., , 2x, ifx>3, x ,ifl<x<3_, 3x, ifx <1, , Let f: R > R be defined as flx) =, , Then fl- 1) + f(2) + f(4) =, (a) 9 (b) 14, (c) 5 (d) None of these, The relation R in the set of natural numbers N, defined as R= {(x, y) :y=x+5andx<4}is:, (a) reflexive (b) symmetric, (c) transitive (d) None of these, For the set A = (1, 2, 3}, define a relation R in the set, Aas follows, , R=({(1, 0, @, 2), 3, 3), 2, 3}, Then, the ordered pair to be added to R to make it, the smallest equivalence relation is :, , INCERT Exemplar], , (a) (13) &) G1) (©) (1) () (1,2), If A= {x ¢ Z:0 <x < 12} and R is the relation in, A given by R = {(a, b) : a = b). Then, the set of all, elements related to 1 is :, , {a) {1,2| (b) {2,3}, , () {1} (d) {2}, , f':X > Yis onto, if and only if:, , (a) range of f= Y (b) range of f# Y, (©) range of f<¥ (d)_ range of f2Y, , The number of all one-one functions from set A =, {1, 2, 3} to itself is :, , (a) 2 (b) 6 (.) 3 (@) 1, , Let A ={1, 2,3, ..., and B={u, b}. Then the number, of surjections from A into B is:, , (a) "P, (b) 27-2, , ( 2-1 (d) None of these, , If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B, contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one, and onto mappings from A to B is :, , (a) 720 (b) 120, , (0 (d) None of these, , The greatest integer function f: R > R, given by, fix) = [x] is:, , (a) one-one, , (b) onto, , (©) both one-one and onto, , (d) neither one-one
Page 2 :
19., , 20., , 21., , 22., , 23., , 24., , 25., , 26., , 27., , 29., , Set A has 3 elements and the set B has 4 element, then the total number of injective mapping :, , (a) 144 b) 12, , (c) 24 (d) 64, , The relation of the relation R = {(x, x2) :x is a prime, number less than 13}:, (a) (2,3,5,7}, , (©) {2,3,5, 7,11}, , (b) (4,9, 25, 49, 121), (d) {1,4, 9, 25, 49, 121}, , x2-8, Let f: R + R be defined by fix)= “575 - then fis:, , (a) One-one but not onto, , (b) One-one and onto, , (c) Onto but not one-one, , (d) Neither one-one nor onto, , Let R be the relation on the set A = {1, 2, 3, 4} given, by R = {(1, 2), (2, 2), (1, 0), (4, 4), (3, 3), (2, 3), (1, 3)}., then:, , (a) Ris’ reflexive, transitive, , and symmetric but not, , (b) Ris reflexive and transitive but not symmetric, (c) R is symmetric, reflexive, , and transitive but not, (a) Ris an equivalance relation, , Risa relation from {11, 12, 13} to {8, 10, 12} defined, by y=x-3 then Rlis:, , (a) {(8, 11), 10, 13)}, , (b) {(11, 8), (13, 10)}, , (©) {(0, 13), , 11), 8, 10}, , (d) None of these, , Which one of the following is an identity relation?, (a) (1,2), (2,3), (13) (b)_ 6,5), 4 4), @ 2), , (c) (1,3), G3, 1), (2,3) (d)_ None of these, , Let T be the set of all triangles in the Euclidean, plane and let a relation R on T be defined as, aRb if a is congruent to b for all a, b € T, then R is:, (a) Reflexive but not symmetric, , (b) Transitive but not symmetric, , (c). Equivalence, , (d) Neither symmetric nor transitive, , One-one, onto function is also called :, , (a) Injective function (b) Surjective function, , (c) Bijective function (d) All of these, , The relation R on R defined by R = (a, 6): 4 s, Bis:, , (a) Reflexive, , (c) Transitive, , (b) Symmetric, (d) None of these, , . The maxium number of equivalence relations on, , the set A = (1, 2, 3} are: [NCERT Exemplar], (a) 1 b) 2 ©) 3 (@) 5, , If a relation R on the set {1, 2, 3} be defined by R=, {(, 2)} then R is : [NCERT Exemplar], , 31., , 32., , (a) reflexive transitive, , (ce) symmetric, , (), , (d)_ none of these, , . Let us define a relation R in Ras aaRbifa>b. Then, , Ris:, (a) an equivalence relation, (b) reflexive, transitive but not symmetric, , INCERT Exemplar], , (c) symmetric, transitive but not reflexive, , (d) neither transitive nor reflexive but symmetric, Let A = {1, 2, 3} and consider the relation R = {(1, 1),, (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), 2, 3)}, , Then R is:, , (a) reflexive but not symmetric, (b) reflexive but not transitive, (c) symmetric and transitive, , INCERT Exemplar], , (d)_niether symmetric nor transitive, , Let R be the relation in the set {1, 2, 3, 4} given by, R={G, 2), 2, 2), 0, 0, 4, 4), 1, 3), 3, 3), B, 2)., Choose the correct answer. [NCERT], , (a) Ris reflexive and symmetric but not transitive, (b) Ris reflexive and transitive but not symmetric, (c) Ris symmetric and transitive but not reflexive, (d) Ris an equivalence relation, , . Let f: R > R be defined as fix) = x4. Choose the, , correct answer : [NCERT], (a) fis one-one onto, , (b) fis many-one onto, , (c) fis one-one but not onto, , (d) fis neither one-one nor onto, , , , , , Choose the correct option :, , (a) Both (A) and (B) are true and R is the correct, explanation A., , Both (A) and (R) are true but R is not correct, explanation of A., , (b), , Ais true but R is false., , ©, (d) A is false but R is true., , , , , , 36., , 37., , Assertion (R) : The function f(x) = | x | is not one-one., Reason (R) : The negative real number are not the, images of any real numbers., , . Assertion (A) : A function y = f(x) is defined by, , x2—cos !y =n, then domain of f(, , , , Reason (R): cos! y € [0, 7]., , Assertion (A) : If f(x) is odd function and g(x) is even, function, then f(x) + g(x) is neither even nor odd., Reason (R) : Odd function is symmetrical in opposite, quadrants and even function is symmetrical about, the y-axis., , Assertion (A) : Every even function y = /(x) is not, one-one, ¥ x € Dy., , Reason (R) : Even function is symmetrical about the, yeaxis.
Page 3 :
38., , 39., , 40., , 41., , 42., , 43., , 45., , 46., , 47., , 48., , Assertion (A) : The function f(x) = x2 -x +1, x2, , nie, , 3), | then the number of solutions, , , , 1, and g(x)= 5+ G, , 4, , of the equation f(x) = 9(x) is two., Reason (R) : f(x) and g(x) are mutually inversion., , Assertion (A) : f(x) = sin x + cos ax is a periodic, function., , Reason (R) : @ is rational number., , Assertion (A) : The least period of the function,, F(X) = cos (cos x) + cos (sin x) + sin 4y is 7., , Reason (R) :*." f(x + 1) =f (x)., , Assertion (A) : If f (x + y) + f(x - 1) = 2A) - FY), Vx,y € Rand f (0) #0, then f(x) is an even function., , Reason (R) : If f(- x) = f (x), then f(x) is an even, function., , Assertion (A) : The equation x4 = (Ax - 1)? has atmost, two real solutions (is 4 > 0)., , Reason (R) : Curves f(x) = x4 and g(x) = (Ax = 1? has, atmost two points., , Assertion (A) : The domains of f(x) = cos (sin), , and g(x) = sin (C053) are same., , Reason (R) : -1 < cos (sin x) ¢ 1 and - 15, sin (cos x) <1, , . Assertion (A) : If f(x) = x5 — 16x + 2, then f(x) = 0 has, , only one root in the interval [-1, 1]., Reason (R) : f (- 1) and f(1) are of opposite sign., Assertion (A) : The domain of the function, , f(x) =sin-! x + cost x+ tare! xis [-1, 1]., , Reason (R) : sin! x and cos! x is defined in, |x| <1 and tance! x defined for all x., , Assertion (A) : The period of f(x) = sin 3x cos [3x] —, , cos 3x sin [3x] is ; where [ | denotes the greatest, , integer function S x., , Reason (R) : The period of {x} is 1, where {x} denotes, the fractional part function of x., , Assertion (A) : The relation R given by, , R= ((1, 3), (4 2), (2, 4), (2, 3), @ D} onaset A = {1, 2,, 3} is not symmetric., , Reason : For symmetric relation R= Ro}., , The price of the oranges in the market is dependent, on the amount of oranges (in kgs) which can be, represented as y = 3x + 5. Reema went to buy the, oranges for a family function in her house. The, total number of oranges she wants lo buys is 5 <x, £10 according to her assumption of people coming, to the party. Answer the following questions on, the basis of the given information., , , , () How many ordered pairs can be represented for, the equation y = 3x +5 for 5<x<10?, , (a) 4 (b) 5, () 6 (d) 7, (ii) What is the domain of the given relation R =, {, 20), (6, 23), (7, 26), (8, 29), (9, 32), (10, 35)} ?, (a) 5,-4,0,1,2} (6) {0,1,2,3,4, 5}, (c) 14,5, 6, 7, 8} (a) {5,6,7,8,9, 10}, (iii) How can range of the relation be represented, for the relation R = {(5, 20), (6, 23), (7, 26), (8, 29),, (9, 32), (10, 35)} ?, (a) {(@y) | y=x+3;3:175x< 32}, (b) {yl yax+3: 205x535), (c) {@,y) ly=x43:17 <x <32}, (d) {@, y) | y=x43:20<x<35}, (iv) What is co-domain for the given relation ?, (a) {@, y) ly=x4+3:17<x< 32}, (b) {(%, y) | y=x+3:20<x< 35}, (©) (@ y) ly=x43:17 <x <32}, (d) (@,y) ly=x+3:20<x<35}, (v) How many subsets are there for the given, , relation R = {(5, 20), (6, 23), (7, 26), (9, 29), (9, 32),, (10, 35)}?, , (a) 16 (b) 32, (c) 64 (d) 128
Page 4 :
49. There is a circular track in a playground where, little kids come to play. Mohan whose son is in the, 11'* standard had taken him to the park. His son, is having the difficulty in grasping the concept of, the relations. Mohan saw the track and realised, that he can teach his son the concept using the real, world example. He asked his son to imagine the, playground as the mathematical figure of circle and, imagine the equation of the circle to be x2 + y? = 8., , , , , , (i) What is the relation called ?, , (a) Set of ordered pair, (b) Function, (c) x-value, (a) y-value, , (ii) Which of the following sets will certainly, represent the given relation accurately ?, (a) {(0, 8), (1, 7), 2, 20}, (b) ((0,2V2),1,07),(2,2), (2) (0,0), V7), 2,-2)}, (A) (0, 2V3), 4,7), (2, 2)], , (ii) From the given graph, what values of the x can, be in the given relation ?, (a) Inside the circle, (b) Outside the circle, (c)_ above half of the circle only, (d) Lower half of the circle only, , (iv) What is the maximum value of the range of the, given relation ?, (a) 0 (b) -2, (©) -2N2 (d) 22, , (v) Waht is the co-domain of the given circle ?, , 50., , (-2V2, 2v2), [- 2V2, 2v2], , (a) 2,2) (b), , (e) [-2,2] (d), , Sherlin and Danju are playing Ludo at home during, Covid-19. While rolling the dice, Sherlin’s sister, Raji observed and noted the possible outcomes of, the throw every time belongs to set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}., Let A be the set of players while B be the set of all, possible outcomes., , , , 51., , (i) Let R : B > B be defined by R = {(x, y): y is, disivible by x} is:, (a) Reflexive and transitive but not symmetric, (b) Reflexive and symmetric and not transitive, (©) Not reflexive but symmetric and transitive, (d) Equivalence, (ii) Raji wants to know the number of functions, from A to B. How many number of functions, are possible ?, (a) @ — (b) 26 (©) 6! (da) 22, (ii) Let R be a relation on B defined by R = {(1, 2),, (2,2), (13), (3, 4), 3, 1, 4, 3), 5, 5)}. Then R is :, (a) Symmetric (b), (c) Transitive (d), (iv) Raji wants to know the number of relations, possible from A to B. How many numbers of, relations are possible ?, @ @ (b) 2°, (©) 6 (a) 2, (v) LetR: B > be defined by R= {(1, 1), (, 2), 2, 2),, (3, 3), (4, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}, then R is:, (a) Symmetric, (b) Reflexive and Transitive, (©) Transitive and symmetric, (d) Equivalence, Students of Grade 9, planned to plant saplings, along straight lines, parallel to each other to one, side of the playground ensuring that they had, enough play areasevtanay rete Aas ah, , Reflexive, None of these three
Page 5 :
one of the rows of the saplings along the line y =, x-4. Let L be the set of all lines which are parallel, on the ground and R be a relation on L., , , , (i) Let relation R be defined by R., L, where L,, L, € L} then Ris, (a) Equivalence, (b) Only reflexive, (c) Not reflexive, (d) Symmetric but not transitive, , , , Cy Diet, Ul, , , , (ii) Let R= {(L,, Ly): L, +L, where L,, L, € L} which, of the following is true ?, (a) R is symmetric but neither reflexive nor, transitive, (b) K is reflexive and transitive but not, symmetric, (c) R is reflexive but neither symmetric nor, transitive, (d) Ris an equivalence relation, (iii) The function f: R — R defined by f(x) = x - 4, is:, (a) Bijective, (b) Surjective but not injective, (c)_ Injective but not surjective, (d) Neither surjective nor injective, (iv) Let f: R > R be defined by /(x) = x-4. Then the, range of f(x) is :, (@ R (b) Z, () W (d) Q, (v) Let R= ((Ly, Ly) Ly is parallel to Ly and Ly: y=, x — 4} then which of the following can be taken, as Ly?, (a) 2x-2y+5=0 © (b) 2x+y=5, (c) 2x+2y4+7= (d) xty=, , , , , , , Solutions, , 1. (d) Reflexive, transitive but not symmetric, , Explanation :, Since n divides n, Vn €N, R is reflexive. R is not, symmetric since for 3,6 € N, 3 R646R3., , ‘ ais ae n, R is transitive since for n, m, r whenever — and, m, , m, r, , nn. - wet, => —, ie. n divides m and m divides r, then n, r, , will divide r., , 2. (b) Mc, «7!, , Explanation :, , Number of elements in set A =7, , Number of elements in set B = 10, , Selection of 7 elements from set B is AG,, , and these elements related to one-one to set A, is7 1., , *. Total relations one-one from set A to set B =, , WG, «71., 3. (b) injective, Explanation :, For one one f(x) =f(x2), 2n,+3=2n,+3, 2n, =2n,, , ny =n, , , , => fis one-one., Let, , , , so, f(1) is not onto., , 4.) a, , Explanation :, , ‘The total number of injective mappings from the, set containing 3 elements into the set containing, 4 elements is “P3 = 4! = 24., , - (b) 27, , Explanation :, Here, A ={n,b,c} and B= {4, 5, 6}, n(A) =3 and n(B) =3, So, number of functions from A to B, =33=3x3%x3=27., , 6. © {4,-4.6, , , , , , Explanation :, , Since for f-! (17) =x, , > f(x) =17 orx?+1=17, > x=t4, , or sId7 =(4-4, , and for — f-(-3) =x, , > fix) =-3, , > ve+1=, , => ea-4