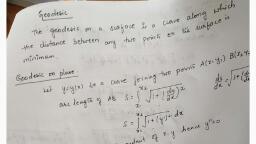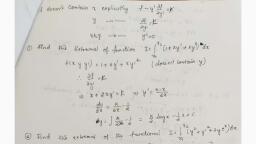Page 1 :
MATHEMATICS, DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS, SESSION 13, ENVELOPES
Page 2 :
Envelopes, Consider the equation y = m𝑥 + c. This equation represents a straight, line. By giving different values to 𝑚 (the value of 𝑐 remaining the, same). We obtain different straight lines. The totality of all these, straight lines obtained by assigning different values to ' 𝑚 ' is said to, be a one parameter family of curves. The variable 𝑚 which is different, for different straight lines is called the parameter for the family. The, equation (𝑥 − 𝛼)2 + 𝑦 2 = 1 where 𝛼 is the parameter represents a, family of circles with centres (𝛼, 0), Note : If there are two parameters in the equation of a curve then it is, called a two parameter family of curves. Generalizing, an equation of, the form f(𝑥, y, 𝛼) = 0 represents a one - parameter family of curves in, the 𝑥𝑦 -plane when 𝛼 takes different values for different members of, the family. 𝛼 of the family. is called the parameter, Consider a family of circles with their centres on 𝑥 -axis and which, pass through the origin whose equation is given by (𝑥 − 𝛼)2 + 𝑦 2 =, 1 (𝛼 is the parameter). Then the line 𝑦 = ±1 circle of the family and at, each of its points the line is touched by some circle of, the family. We call the pair of lines 𝑦 = ±1 as the envelope of the, family considered., , A curve C which touches every member of a family of curves and at, each point of C is a point of contact between C and some member of, the family .Then the curve C is called the Envelope of the family F.
Page 6 :
Squaring and adding ( 1 ) and (2) we get, 𝑥2, 𝑎2, , 𝑦2, , 𝑦2, , = (1 − 𝑏 2 ) + 𝑏2, , x=+-a, The envelope is made up of two straight lines parallel to the y -axis.