Page 1 :
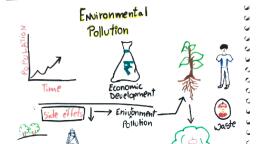
UNIT-II, ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, , 1. Define pollution., “The unfavorable alteration of our surroundings” is called pollution., 2. Name any four air pollutants, and their sources and effects., Name of pollutant, , Sources, , Effects, , Carbon-monoxide, , Cigarette smoking, incomplete, Coma, brain cell damage., burning of fossil fuels., , Nitrogen dioxide, , Burning of fossil fuels., , Acid rain, lung damage., , Sulphur dioxide, , Coal burning, , Breathing problem, acid, rain., , Lead, , Paint, smelters, leaded petrol., , Mental retardation, harm to, wild life., , 3. Define noise pollution., Noise pollution is defined as the unwanted, unpleasant or disagreeable sound that causes, discomfort for the all living beings., 4. Define thermal pollution., Thermal pollution is defined as the addition of excess of undesirable heat to water that, makes it causes harmful to man, animal or aquatic life., 5. What are the types of solid wastes?, ➢ Municipal wastes., ➢ Industrial wastes., ➢ Hazardous wastes., 6. When a sound causes noise pollution?, Noise beyond 120 dB causes noise pollution., 7. Write any four major water pollutions., ➢ Pesticides and biocides,, ➢ Heavy metals, mercury, crude oil, plastics., ➢ Industrial and agricultural wastes., ➢ Thermal pollution., 8. Define photochemical smog., The brownish smoke like appearance that frequently form on clean, sunny days over, large cities with significance amount of automobile traffic. It is mainly due to chemical reactions, among nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbon by sunlight.
Page 2 :
9. Define hazardous wastes., Wastes like toxic chemicals, radioactive or biological substance which contribute to an, increase in mortality or in serious irreversible illness to human health and environment are called, hazardous wastes., 10. How does earthquake occurs?, The earth crust has several tectonic plates of solid rock. These plates move slowly along their, boundaries. When friction prevents these plates from slipping, stress develops and results in, sudden fractures along the fault lines within the plants. This causes earthquakes and the violent, vibrations in the earth., 11. Define the term Tsunami., A Tsunami is large wave that are generated in a water body when the sea floor is, deformed by seismic activity. This activity displaces the overlying water in the ocean., 12. Write any two causes of soil pollution., ➢ Industrial wastes, ➢ Urban wastes, ➢ Agricultural practices, ➢ Radioactive pollutants, ➢ Biological agents, 13. When a sound does cause noise pollution?, The sound intensity is measured in decibel, which is tenth part of the longest unit bel. One, dB is equal to the faintest sound a human ear can hear. If the intensity of the sound exceeds 1 dB,, noise pollution occurs., 14. How nuclear hazards can be disposed safety., Nuclear hazards are disposed safety by dumping then in a big concrete tank and throwing it, in a deep sea., 15. Define soil pollution., Soil pollution is defined as the contamination of soil by human and natural activities, which causes harmful living thing is called soil pollution., 16. Difference between recycling and reuse., (i) Reuse of waste materials, ➢ The refillable containers, which are discarded after use, can be reused, ➢ Rubber rings can be made from the discarded cycle tubes also reduce the wastes., (ii) Recycling of materials, ➢ Recycling is the reprocessing of the discarded materials into new useful products
Page 3 :
Examples, ➢ Old aluminium cans and glass bottles are melted and recast into new cans and bottles., ➢ Preparation of fuel pellets from kitchen wastes, 17. What are the roles of women in environmental protection?, ➢ Buy non phosphate detergents to reduce the incidence of water pollution, ➢ In urban areas, they go shopping using cloth bags to reduce white pollution., ➢ Women choose green products instead of poor quality that harm the environment., 18. State the role and responsibility of an individual in the prevention of pollution., ➢ Plant more trees and Reduce deforestation, ➢ Help more in pollution prevention than pollution control, ➢ Use CFC free refrigerators and natural gas than coal, ➢ Use less polluting substitutes for harmful cleaning agents, paints and other products, 19. What is meant by BOD and COD?, BOD is the amount of oxygen required for biological decomposition of organic matter, present in water is called biochemical oxygen demand, COD is the amount of oxygen required for chemical oxidation of organic matter using, some oxidizing agent like K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4., 20. Mention the sources of soil wastes., ➢ Domestic wastes – food wastes, waste paper, etc, ➢ Commercial wastes–cans, bottle, etc., ➢ Construction wastes – wood, concrete etc, ➢ Bio medical wastes–food, tea leaves, egg shells, polythene bags glass etc.
Page 4 :
UNIT-II, Environmental Pollution, Environmental pollution may be defined as, the unfavorable alteration of our, surrounding. It changes the quality of air, water and land which interferes with the health, of humans and other life on earth., 1. Explain the sources, effects and methods of control of Air pollution., , The presence of one or more contaminants like dust, smoke, mist and odour in atmosphere, which are injurious to human beings, plants and animals., , Composition of Atmospheric Air:, Constituents, , %, , Nitrogen, , 78, , Oxygen, , 21, , Argon, , <1, , Carbon dioxide, , 0.037, , Water vapour, , Remaining, , Ozone, Helium etc, , Trace amount, , Sources of air Pollution:, Natural Sources, , :, , These are caused by natural sources. Example: Forest fires, Volcanoes etc., Man made sources:, These are caused by human activities. Example: Power plants, Factories, Vehicle etc., Classification of Air Pollutants:, Primary air pollutants:, Those are emitted directly in the atmosphere in harmful form., Example: CO, NO, SO2, Secondary air pollutants:, Some primary air pollutants may react with other one another to form new pollutants., Example: NO/NO2 moist, , (HNO3/NO3)
Page 5 :
Major Air Pollutants and Their Effects:, , Pollutant, CO, , Description, Colorless , odorless gas,, , Sources, , Effects, , Automobile industry,, , Poisonous to air-breathing Oil refineries, Cigarette, animals, and bidi smokes, , It causes, poisoning, , hemoglobin, , and, , blood, , It causes headache, paralysis, It effects on heart and lungs, It increases the global temperature, , NO2, , Reddish brown irritating Fossil fuel burning in It causes respiratory diseases like lungs, gas, vehicles., congestion, Reacts with water to form Power industrial plants, nitric acid, , SO2, , Colorless, Irritating gas., , Coal burning, plants, , Its formed from burning of, coal & oil, Industrial process, , It causes eye irritation and Acid Rain, Corrode the metal, soil & trees, , power It causes, asthma, , respiratory, , diseases, , like, , It causes eye irritation and throat pain., Damage the trees and soils, , Ozone, , Heavily irritating gas with Chemical reaction with Moderate the climate, unpleasant odor,, volatile solvent &NO, Formed in troposphere, , Photo, chemical, smog, , Lead, , Its brownish smoke, , Chemical reaction with Breathing problem & nose, throat, NO & HC, irritation and heart disease., Damage the plants & trees, , Solid toxic metal ,Emitted Lead manufacture, into form of SPM, Storage batteries,, Leaded petrol, , Hydro, Carbons, , Formed due to decay of Agri, decay of plants, vegetable matter, , Damage the brain & nervous system, Mental retardation, Digestive & health problems, Produce oil film & they react to form, secondary pollutants
Page 6 :
Control measures of air pollution, a) Source control, 1. Use only unleaded petrol, 2. Use petroleum products and fuels that have low sulphur & ash content., 3. Reduce the no of individual vehicle & use public transport., 4. Growth the plants & trees in busy streets it absorbs the CO & noise., 5. Industrial and waste treatment sites are kept outside the city., 6. Use catalytic converter to help control the emission of CO., b) Control measure in industrial caners., 1. The emission rate should be restricted to permissible level in all industries., 2. Incorporation of air pollution control equipments must be made mandatory., 3. Continuous monitoring for the atmosphere for the pollutants emission level., , Equipments used to control air pollution:
Page 7 :
2. Explain the sources, effects, and control measures of Water pollution., The alteration of physics, chemical & biological changes in water and causing damaging, to the entire living organism is called water pollution., , Types, effects and sources of water pollution:, Pollutant, 1., , Example, , Infectious Bacteria, Viruses, , agents, , Sources, , Effects, , Human & Animal, , Variety of diseases, , Wastage, , 2.Oxygen, , Organic Wastages Like Sewage, Paper Mills Fish and other aquatic organism, , demanding, , Animal Manure & Plant And, , wastages, , Debris, , 3.Inorganic, , Water Soluble Chemicals Surface, , chemicals, , Acids, Compounds Of Industrial Effluents unsuitable water, , Food will be die., , Processing Facilities, , Toxic Metals Etc, , And, , Run, , Off, It can make clean fresh water into, , Household, , Cleaners., , Causes, , skin, , cancers, , &, , neck, , damage, Harm fish and other aquatic life,, lower crop yields, , 4.Organic, , Oil, Plastics, Pesticides Industrial Effluents, Nervous system damage and cancer, , chemicals, , And Detergents, , Household Cleaners, & Surface Run Off., , 5.Plant, , Water, , nutrients, , Compounds, , Soluble Sewage,, , Growth of algae and plants leads to, , Containing Agricultural Runoff reduce the dissolved oxygen and, , Nitrate And Phosphate And, , 6. Sediment, , Harmful to fish and wildlife, , Ions, , Fertilizers, , Soil, Slit, , Land Erosion, , Urban kill the fish., , Reduce the photosynthesis and, cloud water
Page 8 :
Control measures of water pollution, •, , The administration of water pollution control should be in the hands of government., , •, , Scientific techniques are necessary to be adopted for pollution control, , •, , Plants, trees and forest control pollution and they act as natural air conditioners, , •, , The global destruction of forest should be discouraged or at least minimized, , •, , The industries should be develop close – loop water supply system for irrigation, , •, , Highly qualifies person should be consulted to time to time for effective control, , •, , Public awareness regarding adverse effects of water pollution is a must, , •, , Basic and applied research in public health engineering should be encouraged, , •, , The possible reuse or recycle of treated sewage effluents and industrial wastes should be, encouraged, , •, , Suitable laws and standards should be formed and regulated, , 3. Waste water (or) Sewage treatment., 1. Preliminary treatment, Corse solids and suspended impurities are removed by passing waste water through, bar and mesh screens, 2. Primary treatment or settling process, Suspended inorganic and organic solids are removed from the liquid sewage by, settling., In order to felicitate quick settling added alum, ferrous sulphate. Finely divided, organic matter settled rapidly., 3. Secondary (or) biological treatment, a) Trickling filter process, It’s a circular tank and is filled with either coarse or crushed rock. Sewage is spared, over this bed by means of slowly rotating arms., When sewage starts percolating downward, microorganism present in the sewage, grow on the surface of filtering media using organic material of the sewage as food. Then its, taken into sewage tank and sludge is removed., b) Activated sludge process, It has large no of aerobic bacteria’s, which can easily oxidize the organic, impurities. The sewage effluent from primary treatment is mixed with the required, amount of activated sludge.
Page 9 :
Then the mixture is aerated in the aeration tank. Organic impurities of the sewage, get oxidized rapidly by micro organisms, After aeration the sewage is taken in the sedimentation tank sledges are settle, down its called activated sludge. This process removes 90 – 95 % of BOD, 4. Tertiary treatment, After secondary treatment sewage effluent has lower BOD 25ppm which can be, removed by this method, The effluent is introduced in to the flocculation tank, where lime is removed from, phosphates here the PH is maintained to 11. The effluent is allowed to pass through, activated charcoal; where minute organic wastes are absorbed by charcoal. Finally it’s, treated with disinfectant., 5. Disposal of sludge, •, , Dumping into low lying areas, , •, , Burning of sludge, , •, , Dumping into the sea, , •, , Using it as allow grade fertilizers.
Page 10 :
4. Explain the sources, effects and control measures of Soil pollution., The contamination of soil by human and natural activities which causes harmful living, thing is called soil pollution, Composition of soil:, Components, , %, , Mineral matter, , 45, , Organic matter, , 5, , Soil water, , 25, , Soil air, , 25, , Types effects and sources of soil pollution, 1. Industrial wastes, 2. Urban wastes, 3. Agricultural practices, 4. Radioactive pollutants, 5. Biological agents, 1. Industrial wastes, Sources:, Plastics factories, chemical plants, oil refineries, nuclear waste disposal activity,, Coal-fired power plants, metals production factories and other heavy industry all, contribute to land pollution, Effects:, i) These pollutants alter the chemical and biological activities of the soil., j) As a result hazardous chemical enter in to the human body by food chain and causing, damages to, , the living organisms, , 2. Urban wastes, It comprises both commercial and domestic wastages .Its commonly referred as, Refuse Constituents., It contains garbage and rubbish materials like plastics, glasses, paper, rubber,, fiber etc, Urban domestic wastages disposed off separately from the industry cab still be, dangerous. This is so because they cannot be easily degraded.
Page 11 :
3. Agricultural practices, •, , The large amounts of herbicides, pesticides, artificial fertilizers, are added to, increase the crop yield., , •, , Apart from this manure, slurry, soil erosion containing inorganic chemicals and, causes soil pollution, , 4. Radioactive pollutants, •, , Radioactive substances resulting from the nuclear explosion dust and radioactive, wastes penetrate the soil and pollute., , •, , Ex – radio nuclides of Ra, Th, U & Isotopes off K–40 and C–14 are mostly in, racks., , •, , Radioactive wastes containing Sr-90, I-129,CS-137 are more dangerous, , •, , Nuclear reactor produce wastes Ru-106,I-131,Bs – 140&Cs-137 its half life is 30, yrs, , 5. Biological agents:, ➢ Soil get large amount of human And animals excreta leads to pollution. In addition, to this municipal garbage, waste water and wrong methods of agri includes large, soil pollution., Control measures of soil Pollution, 1. Control of soil erosion, It can be controlled by variety of forestry and form practices, •, , Trees may be planted on barren slopes, , •, , Contour cultivation can be practiced instead of shifting cultivation, , •, , Reducing substitution of chemical manures & animal wastes, , 2. Proper dumping of unwanted materials, Excess of waste product by man and animals cause chronic problem, so organic, waste can be dumped in places far from residential areas., 3. Production of natural fertilizers, Excessive use of chemical fertilizers should be avoided. Bio pesticides should be, used instead for chemical fertilizers., Organic waste contain in animal dung can be used for prepare bio gas instead of, waste., 4. Public awareness, Informal and formal public awareness programs should be imparted to educate the, people.
Page 12 :
5. Recycling and reuse of wastes, Inorganic materials such as metals, glass and plastic, but also paper, can be, reclaimed and recycled., 6. Ban on toxic chemicals, Ban should be imposed on chemicals and fertilizers like, DDT,BHC et, , 5. Explain the sources, effects and control measures of Marine pollution., Discharge of waste substances in tot the sea with resulting harmful to marine, organisms, their environment and human food and health., Coral reefs, Coral reefs are under water structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals., Coral are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine water containing few nutrients., Important of coral reefs, •, , Reefs support more than one million species, , •, , They provide feeding, breeding and nursery areas to fish and shell fish, , •, , They offer buffer to ocean waves and protects coastal lines., , Factors affecting the coral reefs, •, , The sediment from deforestation carried by run off, , •, , The agriculture and industrial chemicals to reaching the sea through rivers, , •, , Rising ocean temperature & ocean acidifications, , Sources of marine pollution, 1. Dumping the wastes, •, , The dumping of unwanted untreated wastes and sewage onto the ocean by the, coastal towns and cities., , •, , The river contains large amount of feticides, sewage, garbage, agricultural, discharge they are all added to sea., , Effect : Many marine birds ingest plastic that causes gastro intestinal disorder, 2. Oil pollution of marine water, •, , The great damage of water is imposed by petroleum and its products., , •, , Oil enters from the water from cracks of tanker, accidental spillage and also from, street cleaning., , Effect, •, , The continuous oil film inhibit photosynthesis and the formation of oxygen, , •, , This inhibits growth of plankton
Page 13 :
Effects of marine Pollution, The presence of heavy metals and organic pollutants cause more damage in birds, as thinning of eggshell., Oil pollution cause damage to marine fauna and flora includes algae, fish etc, Oil films are able to retard significantly the rate of oxygen uptake the water., The continuous oil films inhibit photosynthesis and formation of oxygen., Control measures of marine pollution, Plan for conserving marine biodiversity must be taken into the account, People should be educated about marine ecosystem and its benefit, Local communities must be involved to protect and manage coastal recourses, Social and economic incentives must be offered for conserving marine recourses, The fact that all the oceans in the world are connected must be reflected in the, polices, Other control measures, •, , The industrial units on the coastal lines should be equipped with pollution control, instruments., , Methods of removal of oil, 1. Physical method, •, , The floating oil can be absorbed using suitable absorbing material like polyurethane, foam., , •, , Chemical can be used to coagulate the oil, , 2. Chemical methods, i., , Dispersion, , ii., , Emulsification, , iii., , Using chemical activities., , 6. Explain sources, effects and control measures of Noise pollution., The unwanted and unpleasant sound that causes discomfort for the entire living organism, is called noise pollution., Unit of noise is decibel – DB (35-60 DB – normal) (above 140 its painful), Types and sources of noise pollution, 1. Industrial Noise, 2. Transport Noise, 3. Neighborhood Noise
Page 14 :
Industrial Noise, Highly in tensed sound is caused by machines. There exists a long list of sources of noise, pollution including different machines and industries and mills., Ex – in steel industry the workers near the heavy industrial blowers are exposed to 112 db, for 8 hrs suffer from occupational pollution., Transport noise, The main noise comes from transport including (Road, Rail and Aircraft traffic noise), The no of road vehicles like motors, scooters, cars, buses, trucks & particularly diesel engines, increased largely in recent years., Neighborhood Noise, These types of noise includes disturbance from household gadgets and community., Common noise makers are musical instruments, TV, VCR, Radios, Telephones and, loudspeakers., Effect of noise pollution, It affects the human health, comport and efficiency. It causes the concentration of blood, vessels and leads to high blood pressure., It causes muscles to contract leading to nervous breakdown, tension etc.,, It increases the heart beat, contraction of blood vessels, a d dilation of pupil of eye., It affects healthy efficiency and behavior. Cause damage into brain, kidneys, liver etc, In addition to serious loss of hearing due to excess noise causes psychological and, pathological disorder, The buildings and materials may get damaged by exposure to infrasonic / ultrasonic, waves and even get collapsed., Recently it has been proved blood is also thickened by excessive noise., Control measures of Noise Pollution, Source control, This is including source modification like acoustic treatment, design changes and limiting, operation timings., Transmission path intervention, This include containing a sore insulting material inside the machine and noise barrier etc, Oiling, Proper oiling will reduce the noise from the machines, Planting more trees around houses can also act as a noise barriers, Different types of absorbing materials can be used as a control interior of noise.
Page 15 :
By banning to the usage of loudspeakers in the habitant zones except for important, meetings, Ambient noise level dB, Zone, , Day time, , Night time, , Silent zone, , 50, , 40, , Residential zone, , 55, , 45, , Commercial zone, , 65, , 55, , Industrial zone, , 70, , 70, , 7. Explain sources, effects and control measures of Thermal pollution., Increase in the normal temperatures of natural waters caused by intervention of, human activities and causing damage to the entire living organism is called thermal, pollution., Sources of thermal pollution, 1. Nuclear power plants, •, , Nuclear power plants including drainage from hospitals, research institutes and, explosions discharge the lot of unutilized heat into the water streams., , •, , Nuclear reactors, power reactors and nuclear fuel processing units are also, responsible. It affects the aquatic flora and fauna, , 2. Coal fired power plants, Coal fired power plants condenser coils are cooled with the water from nearby, lake or river and discharge of hot water in to the stream it increasing the 15o C of, temperature, It decreases the dissolved oxygen and leads to killing fish and other aquatic, organisms., 3. Industrial effluents, Industries like pulp, textile and paper also releases the heat in water. The, discharged water from stream-electric power industry using turbo generators at, temperature range., In modern stations producing 100 MW, nearly one million gallons are discharged, in one hour with increase in temperature of the cooling water passing by 8 to 100 C .
Page 16 :
4. Domestic sewage, Domestic sewages enter in to the river by without waste treatment. The municipal, sewage normally contain high temperature so dissolved oxygen decreases and demanding, oxygen increases hence anaerobic condition will be formed., Introduction of thermal pollution into streams by human activities, •, , Industries and power plants use water to cool machinery and discharge into stream, , •, , Stream temperature increases when the trees and vegetation matters are cut down, , •, , Soil erosion caused by construction, , •, , Deforestation and poor farming practices, , Effects of Thermal Pollution, Reduction in dissolved oxygen, Concentration of dissolved oxygen decreases with increase in temperature of, water, Increase in toxicity, A 100 C rise in temperature doubles the toxic effect of KCN, while a 800 C rise in, the temperature triples the toxic of O – xylene causing massive morality of fish., Interference with biological activities, The temperature changes totally disrupt the entire ecosystem including biological, activities Interference with reproduction, Several activities like nest building, spauning hatching and reproduction etc, depend on the optimum temperature., Food storage for fish:, Change in the temperature alters the seasonal variation in the type and abundance, of lower organism, Control measures of thermal pollution, 1. Cooling towers:, Cooling towers are designed to control the temperature of water. Cooling towers, transfer some of heat from hot water to the surrounding atmosphere by the process of, evaporation. Its generally used to dissipate the recovered waste heat to eliminate problem, of thermal pollution., Types of cooling towers, A. Wet cooling tower., B. Dry cooling tower:
Page 17 :
A. Wet cooling tower., Hot water coming out from the condenser is allowed to spray over baffles. Cool, air, with high velocity, is passed from sides, which takes away the heat and cools the, water., B. Dry cooling tower:, Hot water is allowed to flow in a long spiral pipes. Cool air, which the help of fan,, is passed over the hot pipes, which cools down the hot water. This can be recycled., 2. Cooling ponds:, Heated effluents on the surface of water in cooling ponds maximize dissipation of, heat to the atmosphere and water area and volume. This warm water wedges like acts a, cooling pond., 3. Spray ponds, The water coming out from condenser is allowed to pass in to the ponds through, sprayers. Here the water sprays trough nozzles of fine droplets. Heat from the fine droplets, gets dissipated to the atmosphere., 4. Artificial lakes, Artificial lakes are manmade bodies of water. The heated effluents can be discharged, into the lake at one end and the water for cooling purposes may be withdrawn from other, end. The heat eventually dissipated through evaporation.
Page 18 :
8. What are the sources of nuclear hazards (pollution) or radioactive pollution?, The radiation n hazard in the environment comes from UV, visible, cosmic rays and, microwave radiation which produce genetic mutation for man, 1. Natural sources, Space, which emits the cosmic rays, soil, rocks; air, water, food etc also contain, radioactive substances., 2. Manmade sources, Nuclear power plants, X rays , nuclear accidents, nuclear bombs etc., Effects of nuclear hazards, • Exposure of the brain and central nervous system to high doses of radiation causes, delirium., • The use of eye is vulnerable to radiation, • Acute radiation sickness is marked by vomiting; bleeding of the gums causes mouth ulcers, • Internal bleeding & blood vessel damage may show up as red spots on the skin, • Unborn children are vulnerable to brain damage & mental retardation, Control measures from nuclear hazards, •, , Nuclear activities should never be exploded in air. Suppose it’s extremely necessary, mean should be exploded in underground., , •, , In nuclear reactors, closed – cycle coolant system with gaseous coolant may be used., , •, , Decrease the radioactive emission by using tightly sealed boxes and closed cycle system., , •, , Production of radioisotopes should be minimized, as once produced they cannot be, rendered., , •, , Minimum no of nuclear installations should be commissioned., , •, , Fission reaction should be minimized as the rate of decay of radionuclides., , •, , In nuclear and chemical industries the use of radioisotopes may be carried under a jet of, soil., , •, , In nuclear mines, wet drilling may be employed along with underground drainage., , •, , Extreme care should be exercised in the disposal of industrial wastes containing radio, nuclides., , •, , Use of high chimneys and ventilations at the working place where nucleus wastes is high., , Disposal of radioactive wastes, 1. High level wastes – spent nuclear fuel, 2. Medium level wastes – Filters, Reactor components etc, 3. Low level wastes–solid or liquid contain the traces of radioactivity
Page 19 :
Nuclear hazards are disposed safety by dumping then in a big concrete tank and, throwing it in a deep sea., , 9. Write a brief notes on Solid waste management., Types and sources of solid wastes, 1. Urban or municipal wastes, 2. Industrial wastes, 3. Hazardous wastes, 1. Sources of urban (Municipal) wastes, a) Domestic wastes Ex – food wastes, waste paper, etc, b) Commercial wastes: Shops, markets, hotels, offices etc., c) Construction wastes : Ex – wood, concrete etc, d) Bio medical wastes: Mostly organic wastes – Ex –food, tea leaves, egg shells., 2. Sources of Industrial wastes, ➢ Nuclear power plants, , ➢ Chemical industries, , ➢ Thermal power plants, ➢ Other industries – packing material, rubbish, organic wastes, acids, alkalis, glass., 3. Hazardous wastes, ➢ Toxic wastes: These are poisonous even in very small amounts., ➢ Reactive wastes: these waste react vigorously with air, water & heat generate the, toxic gases., ➢ Corrosive wastes: it destroys the materials & living tissues by chemical, reactions., ➢ Radioactive wastes: it’s from nuclear power plants & persists in the, environment., ➢ Infectious wastes: used bandages, human tissue from surgery etc., Effect of solid wastes (or) effect of improper solid waste management, •, , Due to improper disposal of municipal solid wastes on the road side, biodegradable, materials undergo decomposition. This produces foul smell and breeds various types, of insects., , •, , Industrial solid wastes are the sources of toxic metals and hazardous wastes which, affect the soil characters and productivity of the soil., , •, , Toxic substances may percolate in the ground and contaminate the ground water, , •, , Burning of industrial wastes or domestic wastes produce furans and dioxins.
Page 20 :
Process of solid wastes management or waste shed management, Steps involved in solid waste management, 1. Reduce, Reuse and Recycle (3R), 2. Discarding wastes, 1. Reduce, Reuse and Recycle, •, , If the usage of raw materials are reduce, the generation of the waste are reduced, , •, , The refillable containers, which are discarded after use, can be reused, , •, , Rubber rings can be made from the discarded cycle tubes also reduce the wastes, , •, , Recycling is the reprocessing of the discarded materials into new useful products, , •, , Old oil cans and glass bottles are melted and recast into new cans and bottles, , •, , Preparation of fuel pellets from kitchen wastes, , 2. Discarding wastes, (A) Landfill, Solid wastes are placed in sanitary landfill system in alternate layers of 80 cm, thick refuse, covered with selected earth fill of 20 cm thickness. After two to three years, solid waste volume shrinks about 25 % and the land is used to parks, roads and small, buildings., The most common and cheapest method of waste disposal is dumping in sanitary, landfills which is invariably employed in Indian cites suitable intervals, Advantages, •, , It’s simple and economical and Segregation not required, , •, , Land filled areas can be reclaimed and used for other purposes., , •, , Natural resources are returned to soil and recycled, , Disadvantages, •, , A large area is required, , •, , Since land is available in away from town transportation is high, , •, , Bad odors, if landfills are not properly managed its sources of mosquitoes and flies., , •, , Causes fire hazard due to the formation of methane in wet weather., , (B) Incineration (or) thermal process, In this method the municipal solid wastes are burnt in a furnace called, incinerator. The compostable substances such as glass metals are separated before, feeding to incinerators. The noncombustible materials can be left out for recycling and, reuse. The left out ashes and clinkers from the incinerators may be accounted for only about, 10 to 20 % which need further disposal either by sanitary landfill or some other methods
Page 21 :
The heat produced in the incinerator from turbines. The municipal solid wastes, generally wet but it has very high calorific value so it has dried before burning. The, temperature normally maintained in the combustion chamber is about 7000 to 10000 C., Advantages, •, , The residue is only 20 – 25 % of original weight; the clinker can be used after, treatment, , •, , It requires very little space and Safest from hygienic point of view., , Disadvantages, •, , Its capital and operating coat is high and Need skilled personnel, , •, , Formation of smoke, dust, and ashes needs further disposal due to air pollution., , (C) Composting, In this method bulk organic waste is converted into fertilizing manure by biological, wastes. The separated compostable waste is dumped in underground earthen trenches in, layers of 1.5 m and is finally covered with earth about 20 cm and left over for, decomposition. Sometimes certain microorganisms such as actinomycetes are introduced for, active decomposition. Within two to three days biological action starts, organic matter are, destroyed and lot of heat liberated of the compost by about 750C and finally the refuse is, converted to powdery brown colored, odorless mass known as humus and has a fertilizing, value which can be used for agricultural field. The compost contains lot of nitrogen essential, for plant growth apart from phosphates and other minerals., Advantages, •, , When the manure is added to the soil, it increases the water retention and ion, exchange capacity of soil, , •, , No of industrial solid wastes can also be treated by this method and recycling –, occurs, , Disadvantages, •, , The non – consumables have to be disposed separately, , •, , Use of compost has not yet caught up with farmers and hence no assured market.
Page 22 :
10 .Role and Responsibility of Individual Participation in Environmental Protection, •, , Plant more trees and Reduce deforestation, , •, , Use water, energy, and other resources efficiently and Increase the use of renewable, resources, , •, , Use CFC free refrigerators and natural gas than coal, , •, , Use less polluting substitutes for harmful cleaning agents, paints and other products, , •, , Use organic manures instead of commercial fertilizers and reduce the garbage by, recycling., , •, , Use of eco friendly products., , •, , Slow population growth., , •, , Reduce garbage by recycle and reuse., , Role of Women in Environmental Protection, •, , In rural areas, women plant trees and grass, grow vegetable with the drip-irrigation, method in order to save water., , •, , In urban areas, they go shopping using cloth bags to reduce white pollution., , •, , They value paper and thus protect trees., , •, , They refuse to eat meat, so variety of animals is preserved., , •, , Buy non phosphate detergents to reduce the incidence of water pollution, , •, , Reduce the amount of trash they dispose off so as to recycle natural resources., , •, , Choose green products instead of poor quality materials and use cloth bags for shopping.
Page 23 :
11. Write short notes on Disaster Management. (or) state the calamities with their, effects and preventive measures., 1. Floods, Whenever the magnitude of water flow is increases its capacity; the excess of water, flow on the surroundings causes floods., Causes of floods, • Heavy rain, rainfall due to cyclones, • Sudden snow melt raises the quantity of water, • Sudden and excess release of water from the dams, • Clearing the forest for agriculture and reduce area of river, Effects of floods, • It cause suffering to people living in lower areas and their properties are washed, away, • Damage the standing crops and livestock and cause great economic loss, Flood management, • Encroachment of flood ways should be banned, • Diverting excess water through canals to areas like river lake etc, • River networking in the country also reduce the flood, • Optical and microwave data from IRS is also used for flood management, • Instead of raising building in flood plain, it can be used for habitat of wildlife,, parks etc, • Floods warning also given by the central water commission, 2. Cyclone, Cyclone is metrological phenomena, intense depression formed over the open seas, and moves towards the land, Occurrence, Tropical cyclones in the warm ocean are formed because of heat and moisture and, its speed 10-30 km /hour
Page 24 :
Different names of cyclones, Name, , Place, , Hurricanes, , Atlantic, Caribbean and USA, , Typhoons, , Southern coast of china and Japan, , Cyclones, , Bangladesh and India, , Willy willies, , Australia, , Effect of cyclones, • The damage depends on the intensity of the cyclones. They damage human life,, crops, roads, transport, communications, canals etc, • Cyclone occurrence slow down the developmental activities of the area, Cyclone management, • Satellite images are used by metrological departments for forecasting weather, conditions., • Radar system should be used to detect the cyclone used for cyclone warning, • For observing the exact location of cyclone, every half hour satellite pictures are, analyzed, 3. Landslides, The movement of earthy materials like rock, mud etc are debris from higher region, to lower region is called landslides, Causes of landslides, • Downhill movement of earth is mainly caused by rain forces increasing the materials, weight, • Movement of heavy vehicles on the unstable sloppy region and Erosion, • Earthquake, shocks, vibrations are also create the landslides, • Underground caves and underground mining also leads to subsidence, Effects of landslides, • Landslides blocks the roads and diverts the passage, • Sudden landslide damage the houses, crop yield, livestock etc
Page 25 :
Landslides management, •, •, •, •, , It’s very difficult to control but it can be minimized by the following ways, Unloading the upper parts of the slope, Steepness of the slope can be reduced by developing benches, Improving the cultivation in the sloppy region, roofs retards the flow of water and, erosion, • Concrete support can be made at the base of the slope, 4. Earth – quacks, A sudden release of vibration caused on the earth surface by tremendous energy, release from the rocks is called earth-quack., Causes of earth quack, • Earthquakes are caused due to disequilibrium in any part of the earth crust. (Its, caused by volcanic eruptions, hydrostatic pressure man made water bodies etc), • Underground nuclear testing and reduce the ground water level., Richter scale, , Severity, , of, , earth, , quake, Less than 4, , Insignificant, , 4 – 4.9, , Minor, , 5 – 5.9, , Damaging, , 6 – 6.9, , Destructive, , 7 – 7.9, , Major, , Effects of Earthquake, • It leads to land slide which damage the settlements and transport system, • It also collapse the houses and other structures due to poor construction leads to dies, • Severe earth quake results in deformation of ground surface, •, , Tsunami, the seismic waves caused and leads to great economic loss., , Earthquake Management, • It reduced by constructing earth quake resistant building in the it prone area, • Seismic hazard map should given the information about the magnitude of intensity, of anticipated earthquakes, • Wooden houses are preferred in earthquake prone area like Japan.
Page 26 :
5. Tsunami, A large high speed wave coming from the sea to land by seismic activities is called, Tsunami, • Tsunami travel across the deep sea at very high velocity at around 800 – 900, km/hr., • The rate of loss of its energy in inversely proportional to wavelength., • it height near the sea shore ranges from 15 – 60 m, Causes of Tsunami, • Seismic activities like earthquake, landslides, volcanic eruptions, explosion etc, • Deformation of the sea floor due to the movement of plates, Effects of Tsunami, • Tsunami attacks mostly coastlines, causing damage and loss of life, • It also kills lot of human beings, livestock’s etc, • It also spreads lot of water born diseases, Tsunami Management, Step I: Earthquakes under water are monitored by sensors on the floor of the sea, Step II: The sensors send the information of floating buoys on the surface, Step III: The information is then relayed to satellites, which passes in to the earth, stations, Step IV: The stations giving the warning system are the of the danger approaching, Step V: Finally the country make the alert through the media
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic






































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









