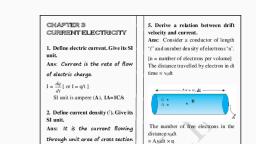
Page 1 :
B.Sc. |-E lectronics (CBCS Pattern) Semester - | Paper -|, Basic Circuit Theory and N etwork Analysis, Unit 1, , Circuit Elements, , , , , , Active and passive elements, Resistors, Capacitors, | nductors, Transformers, Relays, and F uses (Classification, Specifications and Applications only), , , , Electronicsisa branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the, emission, behavior, and effects of electrons and with electronic devices., , Electronic circuit or network: An electronic circuit is an electrical connection of, various sources (power supply) and electronic components., , Source: A source is a device which provides power to the circuit., , Component/element: components are those which consume the power from source, for operation to produce desired output., , Voltage: V oltage also known as potential difference per unit charge between two, pointsin an electric field. W ecan also define as amount of potential energy, between two pointsin the circuit., , It is measured in Volts (V), Current: The rate of flow of charge is called as current. Its SI unit is Ampere., There are two types of components:, , 1) Active components 2) Passive components, , Active components: The electronic component which needs an external power, supply for its operation is called as active components. Active components deliver, the energy to the circuit. It is also called as energy donors., , Example: Diode, transistor, LED, SCR etc., , Passive components: The electronic component which does not need any external, power supply for its operation. They only pass the electric current. I t is also called, as energy acceptors., , , , Phule S.P.|Dept.of Electronics|SM College Page 1
Page 2 :
Active components Passive components, , transistor ienistor) <i ~<A, Diode ez SF LDR ee ~eLep a bs Thermistor e a, Photodiode @ Capacitor = lI, , psec" : Inductor (mM) rw, sesrisises? BE swtecn ge Se, aoa A suizzs 6 OOo, , Resistor: A passive electrical component with two terminals that are used for, either limiting or regulating the flow of electric current in electrical circuits. The, main purpose of resistor is to reduce the current flow and to lower the voltage in, any particular portion of the circuit. | t is made of copper wires which are coiled, around a ceramicrod and the outer part of the resistor is coated with an insulating, paint., , The SI unit of resistor is Ohm., , D efinition of resistance: Resistanceis a property of resistor which opposes the, flow of current or electrons., , Symbol of resistance is as —WA—, , Classification of resistors:, , There are two basic types of resistors as follows:1) Linear resistor 2) N on-linear, resistor, , 1) Linear resistors: The resistors whose values change with change in applied, temperature and voltage are known as linear resistors. |n this type current is, directly proportional to the voltage. There are two types of linear resistors:, , a) Fixed resistors: These resistors have a specific value and these values cannot, be changed. These resistors have two terminals. F ollowing are the different, types of fixed resistors:, , e Carbon composition resistors, , « Wirewound resistors, , , , Phule S.P.|Dept.of Electronics|SM College Page 2
Page 3 :
¢ Thin film resistors, , ¢ Thick film resistors, , b) Variable resistors: These resistors do not havea specific value and the values, can be changed with the help of knob and screw. These resistors find, applications in radio receivers for controlling volume and tone. These, resistors have three terminals. Symbol of variable resistor is as follows, , F ollowing are the different types of variable resistors: Potentiometers, Rheostats,, Trimmers, 2) Non-linear resistors, , The resistor values change according to the temperature and voltage applied and is, not dependent on Ohm's law. F ollowing are the different types of non-linear, resistors:, , 1) Thermisters 2) Varistors 3) Photo resistors, , Resistor, v, , Linear resistor Non -Linear resistor, ‘Thermisters, Fixed resistor variable resistor Varistors, carbon composition potentiometer Photo resistors, wire wound, preset, film type Rheostats, , cracked carbon, , Specifications of resistors:, , F or selection of the resistor for circuit design, the designer must know the, specifications of resistor. These are as follows:, , 1) Tolerance: Tolerance means that possible variation from the nominal or, marked resistance value. |t means that actual resistance of the resistor, may be greater or lesser than its indicated value., , F or example 1000 ohm resistor with a tolerance of 10% will have actual, , resistance in between 900 ohm and 1100 ohm. I t is expressed in terms of, %., , 2) Power handling capacity: | t is defined as maximum power that can be, handled by resistor without damage. | t is expressed in W att., , , , Phule S.P.|Dept.of Electronics|SM College Page 3
Page 4 :
3) Maximum operating voltage It is defined as maximum voltage that can, be handled by resistor without damage., , 4) Maximum operating temperature: | t is defined as maximum value of, temperature that which resistor is operated without damage., , 5) Temperature Coefficient of Resistance: The temperature coefficient of, resistance is generally defined as the change in electrical resistance of a, substance with respect to per degree change in temperature. It is, expressed in part per million per degree Celsius., , Specifications of carbon composition resistors:, , The tolerance will be+5%, +10%, +20%, , The resistance value ranges from 1 M ega to 22 Mega Ohms, M aximum temperature of resistance 120°C, , Higher reliability, low cost, and small size, , M aximum V oltage ratings 800V, , Power handling capacity 1/8w ,1/4w to 2w, , Specifications of wire wound resistors, , The tolerance will be+1%, +10%,%, , The resistance value ranges from 1ohm to 150K Ohms, Higher reliability, low cost, and small size, , M aximum V oltage ratings 500V, , Power handling capacity 1w to 50w, , Applications of carbon composition resistors:, , 1) It is used in electronic equipments., 2) |t is used in high frequency applications., 3) It is used in low power controlling circuits., , Applications of wire wound resistors:, , 1) The wire wound resistors used in power supply circuit., 2) 1t is used power controlling circuit., 3) It isused in inverters, U PS(U ninterrupted Power Supply), , Colour coding of fixed resistors:, , There are many methods are used to indicate the value of resistance, these methods, are colour coding, straight numerical value printing method etc. F or fixed resistors, like carbon composition, film resistors a colour coding method is used for indicate, their value. |n colour coding method the three, four, five colour bands printed on, , , , Phule S.P.|Dept.of Electronics|SM College Page 4
Page 5 :
the body for resistor for indicating their values., , “B.B. ROY of Great Britain has a V ery Good Wife”, , You can remember the order of color codes by remembering the order of capital, letters in the above sentence., , following chart shows the color coding scheme., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Colour Significant digit | Multiplier Tolerance in, +/-%, Black 0 10°=1 Brown 1 10'=10 1, Red 2 107= 100 2, Orange [3 10°= 1000 Yellow 4 107=10000 Green 5 10°= 100000 0.5, Blue 6 10°= 1000000 0.25, Violet 7 10’=10000000 [0.1, Gray 8 10°=100000000 [0.01, White 9 10°= 1000000000 | 0, Gold - 10 '=0.1 5, Silver - 107= 0.01 10, Nocolor |- : 20, , , , , , 4-Band Code =, , , , 1 digit, t digit, , Multiplier, Tolerance, , , , 4 x10 =47000=47kQ, , If the value of resistanceis less than 10 ohm then multiplier is used is either Gold, , and silver., , For exampleY V_ Gold, , 4 7 0.1 =4.7 0hmwith 20%, , tolerance, , , , Phule S.P.|Dept.of Electronics|SM College, , Page 5