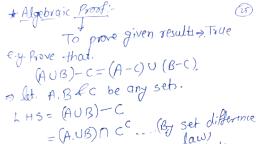Page 2 :
Set Theory, , 2-9, , Discrete Mathematics (B.Sc.-IT-MU), , Proof, (AnB, , A°UB°, , Let x e (AnB, xE, , AnB, , A, , or x£ B, , x E A or xe B, , E (AUB), , (AUB= A°nB, , (b), , 2.4.4, , Cartesian Product, The Cartesian product AXB, , ofthe sets A and B, is the set of all possible, , ordered pairs, , (a, b) where a e A and beB, AXB {(a, b) l ae A, be B}, , Example, B {4,6}then, {(1,4), (1, 6), (2,4), (2,6), (3,4), (3,6)}, ((4, 1), (4,2), (4,3), 6, 1), (6, 2), (6,3), , A {1,2,3), , AxB, , BxA, , AxB # BxA, , Note:, 2.4.5, , n{A) = m and n(B), , =, , m then, , Identity Law, For any set A, AUO, , 2.4.6, , =, , A, , Complement Law, , AUA=U, , AnA =, 2.4.7, , Double Complement Law, , A= A, , but AXBBxA4, n(AxB) n(Bx A) m.n w.w.w.
Page 3 :
Discrete, , 2.4.8, , Mathematics (B.Sc.-IT-MU), , SetTheory, , 2-10, , Idempotent Law, For any set A, AUA A, , AnA, , A, , Universal Bound Law, , 2.:4.9, , AUU, , =U, , AnU, , = A, , 2.4.10 Absorption Law, For any sets A and B, AU(AnB), , An(AU B), , =, , A, , =, , A, , 2.4.11 Set Difference Law, , A-B AOB°, B-A BnAC, , Intersection and union where are set is a subset of other., Theorem 1:, , For any sets A and B., A, , If ACB then, , n, , AUB=B, , B=A and, , Proof, IfAC B, , and, , XEA, , Then XE B, X, , EA, , and, , x E B, , X E AnB, , . x ¬ A implies, , A, , X, , EAnB, , ..(2.4.1), , C AnB, , Since A n BCA, , .(2.4.2) (By definition of intersection), , ByEquations (2.4.1) and (2.4.2) ,we get AnB, Bydefinition of union BCAUB., , A, , .2.4.3)
Page 4 :
2-11, , Discrete Mathematics (B.Sc.-IT-MU), Let x e, x, , SelThe, , AUB, A, , E, , or, , xEB, , xE B, AUB, , xE, , AUB, , By, , implies x EB, (, , B, , get, Equations (2.4.3) and (2.4.4), we, , AUB=B, , Syllabus Topic: Disproofs, , 2.5, , Disproof, Proving any, Prove, , that propertu, that is called disproving, erty., and, false, property or results.is, , (A - B) U B-C), , or disprove:, , Where, , A, B and C, , Let, , are, , any sets, , A, , = {1, 2, 3, 5}, , B, , = {2.4, 5, 6}, , C, , {3, 5, 6, 7}, , A-B, , =, , {1,3}, , B-C =, , {2,4), , (A-B) UB-C), , =, , A-C, , {1,2,3, 4}, {1,2}, , Here {1, 2, 3, 4} # {1, 2}, , (A - B) U(B -C)#, , A-C, , =, , A-C, , by example