Page 1 :
MALAPPURAM DISTRICT HIGHER SECONDARY CHEMISTRY TEACHER’S ASSOCIATION, HIGHER SECONDARY MODEL EVALUATION FEBRUARY 2022, OXYCHEMISTRY 2.2, HSE (II), , Time: 2Hr, , Maximum: 60 Scores, , PART I, A. Answer any five questions from 1 to 9. Each carries 1 score., 1. Thionyl chloride is preferred to convert alcohols to chloroalkanes. Why?, Answer: The byproducts formed are gases which escape from reaction, mixture and we get pure haloalkane, 2. Which method is used to separate o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol?, Answer: steam distillation, 3. Which of the following aldehyde doesn’t give Fehling’s test, a) Formaldehyde b) Benzaldehyde c) Acetaldehyde d) none of these, Answer: b, 4. The reaction in which an amide is converted into a primary amine by the, action of bromine and alcoholic NaOH is known as…….., Answer: Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction, 5. Give any two examples for polysaccharides., Answer: starch, cellulose, 6. Name a substance that can act as both antiseptic and disinfectant., Answer: phenol, 7. Which one is more acidic, chloroacetic acid or fluoroacetic acid?, Answer: fluoroacetic acid, Con.H2SO4/443K, , 8. CH3CH2OH →−−−−−−−−−−−→ ………, Answer: CH2 = CH2, 9. Name the compound formed when chloroethane is treated with NaI in dry, acetone., Answer: iodo ethane, B. Answer all questions from 10 to 13. Each carries 1 score., 10. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is used for the preparation of which type, amines., Answer: primary amine, 11. Which is the chemical substance discovered by Paul Ehlrich for the, treatment of syphilis?, Answer: salvarsan, 12. Name a fat soluble vitamin., Answer: vitamin A, 13. What is Glycosidic linkage?, Answer: The C-O-C linkage formed between two sugar units, PART II, A. Answer any two questions from 14 to 17. Each carries 2 scores., 14. What are enantiomers?, Answer: Two sterioisomers related to each other as non-super imposable, mirror images are called enantiomers., 15. Identify the product when acetaldehyde is treated with Grignard reagent., 𝐻20, , Answer: CH3CHO + CH3MgBr →, , CH3CH(OH)CH3+Mg(OH)Br, , Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
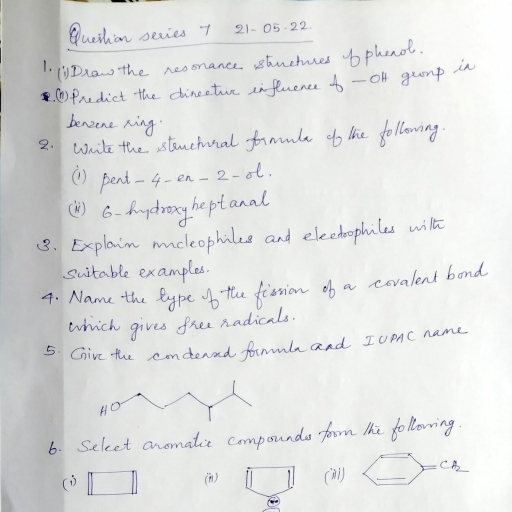
Page 2 :
16. Write any two tests used to distinguish between propanal and propanone., Answer: propanal gives both tollens test and Fehling test but propanone, doesn’t give this test., 17. What is denaturation of protein? Give an example., Answer: When a protein is subjected to physical or chemical changes it, loses the biological activities. It is called denaturation of protein, B. Answer any two questions from 18 to 20. Each carries 2 scores., 18. Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?, Answer: primary amines can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds while, tertiary amines cannot form intermolecular hydrogen bond, 19. How will you distinguish between 2-pentanone and 3-pentanone?, Answer: 2-pentanone gives positive iodoform test. 3-pentanone doesn’t, give this test, 20. Differentiate between globular protein and fibrous protein., Answer: globular proteins are spherically arranged and water soluble., Fibrous proteins are thread like molecule and water insoluble, PART III, A. Answer any three questions from 21 to 24. Each carries 3 scores., 21. Explain Cannizzaro’s reaction with suitable equation., Answer: 2HCHO → HCOONa + CH3OH, 22. How can you distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines using, Hinsberg’s reagent., Answer:, i) Primary amines react with Hinsberg’s reagent to form alkali soluble, N-alkyl benzene sulfonamide., ii) Secondary amines react with Hinsberg’s reagent to form alkali, insoluble N,N-dialkyl benzene sulfonamide, iii) Tertiary amines does not react with Hinsberg’s reagent., 23. Ethanol is an important alcohol., i) How ethanol is prepared industrially?, ii) What is meant by denatured spirit?, Answer:, i) Ethanol is prepared industrially by the fermentation of cane sugar, 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻, , 𝑖𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑎𝑠𝑒, , C12H22O11 + H2O →, C6H12O6 + C6H12O6, 𝑧𝑦𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑒, C6H12O6 →, 2 CH3CH2OH + 2CO2, ii) Ethanol is made unfit for drinking by adding poisonous substance like, CuSO4 , pyridine, methanol etc. This known as denatured spirit., , Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
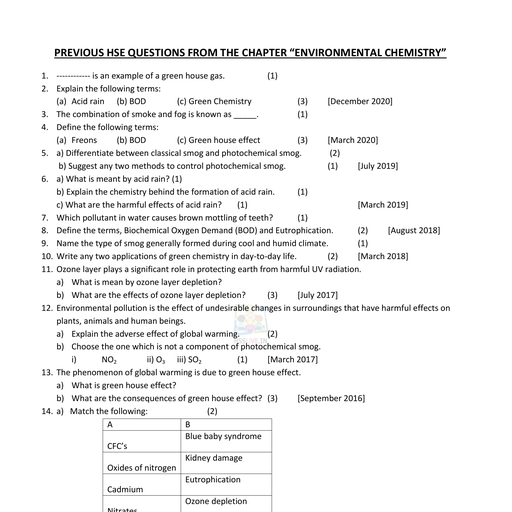
Page 3 :
24. Write the therapeutic actions of the following drugs., i) Analgesics ii)Antibiotics, iii) Tranquilizers, Answer:, i) drugs used to achieve relief from pain ii) drugs produced by, microorganisms and can destroy other microorganisms iii) Drugs used for, the treatment of mental diseases, B. Answer any two questions from 25 to 27. Each carries 3 scores., 25. How will you bring about the following conversions?, i) Toluene to benzoic acid, ii) Benzoic acid to benzamide, Answer:, , i), , ii), , 26. Explain the following reaction, i) Kolbe’s reaction, Answer:, , ii) Hydroboration, , Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
Page 4 :
i), , Kolbe’s reaction, , ii), , Hydroboration, , 27. Haloarenes are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions, than that of haloalkanes. Give any two reasons., Answer: Due to resonance effect C-X bond in haloarenes has double, bond character and also halogen is attached to more electronegative sp2, carbon atom, , PART IV, A. Answer any three questions from 28 to 31. Each carries 4 scores., 28. Explain the following reactions., i) Sandmeyer’s reaction ii) Aldol condensation, Answer:, i), Sandmeyer’s reaction, , Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
Page 5 :
ii), , Aldol condensation : it is characteristics reaction of aldehydes, containing α-hydrogen atom, 𝑑𝑖𝑙.𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻, 2CH3CHO →, CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO, , 29. Starch is a polysaccharide., a) What are the two components of starch? Which one of them is water, soluble?, b) …….is known as animal starch, Answer:, a) Amylose and amylopectin , amylose is soluble in water, b) Glycogen, 30. Write any four differences between SN1 and SN2 mechanism., Answer:, SN1 Reaction, Proceeds in 2 steps, An intermediate (carbocation) is formed, Order of the reaction is 1, For optically active compounds, the reaction, proceeds through racemisation, The order of reactivity of alkyl halide is 3˚> 2˚> 1˚, , SN2 Reaction, Proceeds in a single step, No intermediate is formed, Order is 2, For optically active compounds, the reaction, proceeds through inversion of configuration., The order of reactivity of alkyl halide is 1˚ > 2˚ > 3˚, , 31. Explain the following with examples, i) Rosenmund’s reduction ii) Wolf kishner reduction, Answer:, , B. Answer any one question from 32 to 33. Each carries 4 scores., 32. Antibiotics are broadly classified into two. Briefly explain this, classification with examples., Answer:, Broad spectrum antibiotics eg: chloramphenicol, Narrow spectrum antibiotics eg: Penicillin G, 33. How ethanal reacts with i) Semicarbazide, ii) Hydrazine, Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com
Page 7 :
c), , 36. Luca's reagent is used to distinguish primary , secondary and tertiary, alcohols, a) What is Lucas reagent?, b) How can you distinguish different alcohols using Lucas reagent?, c) What is picric acid? How it is prepared?, Answer:, a) Mixture of Con. HCl and Anhydrous ZnCl2, b) i) tertiary alcohol react with Luca’s reagent to form turbidity, immediately, ii) secondary alcohol react with Luca's reagent to form turbidity, with in five minutes, iii) primary alcohol do not form turbidity at room temperature., c) 2,4,6-trinitrophenol is called picric acid. It is prepared by The, action of phenol with concentrated nitric acid, , Downloaded from www.hssreporter.com