Page 1 :
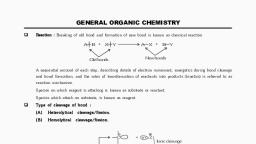
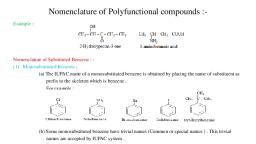
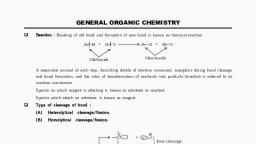
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME ASIC PRENCIFLES AND TECHNIQUES ast, , portion of the molecule (a positive reactive site), ‘e.g. an atom with incomplete electron shell or, the positive end of the dipole in the molecule. If, the attacking species is electron rich. attacks,, these sites, If attacking species 1s electron, deficient, the reactive ste for its that part ofthe, substrate molecule which can supply electrons,, ‘©. & electrons in a double bond., , ‘Areagent that brings an electron pair tothe, reactive site is called a nucleophile (Nix) Le.., ‘nucleus seeking and the reaction is then called, nucleophilic. A reagent that takes away an, electron pair from reactive site 1s called, ‘electrophile (EL... electron seeking and the, reaction ts called electrophilic., , During a polar organic reaction. a, nucleophile attacks an electrophilic centre of, the substrate which is that specific atom or part, Of the substrate which is electron deficient., Similarly, the electrophiles attack at, nucleophilic centre, which is the electron, rich centre of the substrate. Thus, the, clectrophiles receive electron pair from the, substrate when the two undergo bonding., interaction. A curved-arrow notation is used, toshow the movement of an electron pait from, the nucleophile to the electrophile, Some, ‘examples of nucleophiles are the negatively, ‘charged tons with lone pair of electrons such, as hydroxide (HO"}, cyanide (NC) tons and, , }. Neutral molecules such, RNH ete. can also act as, nucleophiles due to the presence of lone pair, of electrons, Examples of eleetrophiles, include carbocations (GH, ) and neutral, molecules having functional groups like, carbonyl group (>C*0) oF alkyl halides, (R,C-X. where X is-a halogen atom). The, carbon atom in earbocations has sextet, ‘configuration; hence. itis electron deficient, land can receive a pair of electrons from the, nucleophiles, In neutral molecules such as, alkyl halides, due to the polarity of the C-X, bond a partial positive charge is generated, ‘onthe earbon atom and hence the carbon atom, becomes an electrophilic centre at which a, nucleophile can attack., , , , , , , , , , , , ‘Problem 12.11, Using curved-arrow notation, show the, Oe Raney coment uae oe orge, heterolytic cleavage., , (a) CH,-SCH,,(6) CHEN, () CH,-Cu, Solution, , w cn, Scn,—> én, + Seu,, w cH, Ltn —» on, + ew, , @ & You = an +d,, , , , c¥S.CHO (CHL), NHN:, have unshared pate of, which can be donated and, © Btectrophites: 8, Cia, -6=0NO,., premade nlite, lect can ace ean, Problem 12.18, Identify electrophilic centre in the, following: CH,CH=0, CH,CN, CHI., Solution, cHNd=0, H,céeN, and, ‘I, the starred carbon atoms are, electrophilic centers as they will have, ‘partial positive charge due to polarity of, the bond., , , , 12.7.3 Electron Movement in Organic, Reactions, , ‘The movement of electrons tn reactions, , ‘ean be shown by curved-arrow notation. It
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic





















































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









