Page 1 :
Accredited By NAAC with ‘A’ Grade, Revised Syllabus For, Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) Part III, , Botany, CBCS PATTERN, Syllabus to be implemented from, June, 2020 onwards, Paper –IX, X, XI, XII - (Semester- V), and, Paper –XIII, XIV, XV, XVI - (Semester-VI), , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 1
Page 2 :
A], B], , Ordinance and Regulations: (As applicable to Degree Course), Shivaji University, Kolhapur, Revised Syllabus For Bachelor of Science, , 1. TITLE : Subject- Botany, Optional under the Faculty of Science, 2. YEAR OF IMPLEMENTATION: - Implemented from June 2020 onwards., 3. PREAMBLE:[Note:-The Board of Studies should briefly mention foundation, core and applied components of, the course/paper. The student should get into the prime objectives and expected level of study, with required outcome in terms of basic and advance knowledge at examination level.], 4. GENERAL OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE:, (As applicable to the Degree concerned), Objectives:1) To impart knowledge of Science is the basic objective of education., 2) To develop scientific attitude is the major objective to make the students open, minded, critical, curious., 3) To develop skill in practical work, experiments and laboratory materials and equipments, along with the collection and interpretation of scientific data to contribute the science., 4) To understand scientific terms, concepts, facts, phenomenon and their relationships., 5) To make the students aware of natural resources and environment., 6) To provide practical experience to the students as a part of the course to develop scientific, ability to work in the field of research and other fields of their own interest and to make, them fit for society., 7) To The students are expected to acquire knowledge of plant and related subjects so as to, understand natural phenomenon, manipulation of nature and environment in the benefit of, human beings., 8) To develop ability for the application of the acquired knowledge to improve agriculture, and other related fields to make the country self reliant and sufficient., 9) To create the interest of the society in the subject and scientific hobbies, exhibitions and, other similar activities., 5. DURATION, The course shall be a full time course., 6. PATTERN:Pattern of Examination will be Semester., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 2
Page 3 :
7., , FEE STRUCTURE :As per Government /University rules., 1. Refer brochure and prospectus of concern affiliated college/institute to, Shivaji University, Kolhapur., 2. Other fee will be applicable as per rules and norms of Shivaji University,, Kolhapur., , 8., , ELIGIBILITY FOR ADMISSION:, As per guidelines obtained from Shivaji University, Kolhapur by following rules and, regarding reservations by Govt. of Maharashtra., , 9., , MEDIUM OF INSTRUCTION:, The medium of instruction shall be in English., STRUCTURE OF COURSE- B. Sc. III Botany (Optional), , 10., , THIRD YEAR (SEMESTER V/VI) (NUMBER OF PAPERS VIII), Sr.No., , Subjects/Papers, , Theory Internal, , Total, Marks, , 1., , Paper-IX, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 2., , Paper- X, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 3., , Paper -XI, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 4., , Paper- XII, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 5., , Paper- XIII, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 6., , Paper-XIV, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 7., , Paper-XV, , 40, , 10, , 50, , 8., , Paper-XVI, , 40, , 10, , 50, , Practical -I, , 50, , Practical- II, , 50, , Practical- III, , 50, , Practical -IV, , 50, , Total, , 600, , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 3
Page 4 :
11., , Structure of B. Sc. III P Semester V and VI, SEMESTER V, TEACHING SCHEME, , Sr., No., , Subject Title, , 1, , Credits, , No. of, Lectures, , Hours, , DSE-E, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , 2, , DSE-E, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , 3, , DSE-E, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , 4, , DSE-E, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , TOTAL, , 10, , 16, , 12.8, , PRACTICAL, Cred No. of, its Lectures, , Hours, , 8, , 20, , 16, , 8, , 20, , 16, , 8, , 20, , 16, , SEMESTER VI, 1, , DSE-F, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , 2, , DSE-F, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , 3, , DSE-F, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , 4, , DSE-F, , 2, , 3, , 2.4, , TOTAL, , 10, , 16, , 12.8, , 8, , 20, , 16, , 20, , 32, , 25.6, , 16, , 40, , 32, , GRAND TOTAL, 12., , SCHEME OF EXAMINATION :•, •, •, •, , 13., , The examination shall be conducted at the end of each term for semester pattern., The Theory paper shall carry 40 marks., The evaluation of the performance of the students in theory papers shall be on the basis of, Semester Examination of 40 + 10 marks., Question Paper will be set in the view of the /in accordance with the entire Syllabus and, preferably covering each unit of syllabi., , STANDARD OF PASSING:As Prescribed under rules & regulation for each degree., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 4
Page 5 :
14., , NATURE OF QUESTION PAPER AND SCHEME OF MARKING:, (Unit wise weightage of marks should also be mentioned), Q. 1. Multiple choices questions (8-questions) ---, , 08 Marks, , Q.2. Attempt any two of the following., (Essay type/Broad answer questions) ---Q.3. Write short notes (any four) ---, , 16 Marks, 16 Marks, , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 5
Page 6 :
15., , EQUIVALENCE IN ACCORDANCE WITH TITLES AND CONTENTS OF PAPERS(FOR REVISED SYLLABUS), (Introduced from June 2020 onwards), , Old Syllabus, (Semester pattern), Paper Title of Old Paper, No., IX, Biology of Non Vascular Plants, and Paleobotany, X, Genetics and Analytical, Techniques in Plant Science, , Sem., No, V, , Revised Syllabus, (Semester pattern), Paper No., Title of New Paper, , DSE –E25 Genetics and Plant Breeding, DSE –E26 Microbiology, Plant, Pathology and Mushroom, Culture Technology, Cytology and Research, Techniques in Biology, , XI, , Fundamentals of Plant, Physiology and Ecology, , DSE –E27, , XII, , Plant Biochemistry, , DSE –E28, , Horticulture and Gardening, , XIII, , Biology of Vascular Plants, , DSE –F25, , Plant Biochemistry and, Molecular Biology, , XIV, , Microbiology and Plant, Pathology, Plant Breeding, Biostatistics,, Ethnobotany and Horticulture, Molecular Biology and, Biotechnology, , DSE –F26, , Bioinformatics, Biostatistics, and Economic Botany, Plant Biotechnology and, Paleobotany, Bio fertilizers and Herbal, Drug Technology, , XV, XVI, , VI, , DSE –F27, DSE –F28, , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 6
Page 7 :
SEMESTER V, B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK, MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- IX DSE –E25, Genetics and Plant Breeding, Unit 1: Mendelism:, , 10, , 1.1 Introduction, Definition and Basic terminologies in genetics., 1.2 Principles of inheritance a) Law of Dominance b) Law of Segregation c) Law of independent assortment., 1.3 Gene Interaction-a) Complementary gene interaction b) Supplementary gene interaction., , Unit 2 : Linkage and Recombination, , 10, , 2.1 Linkage: Definition, Linkage group, Types, Coupling and Repulsion phase, Significance., 2.2 Recombination (Crossing over): Definition, Types , Mechanism of crossing over, Significance, 2.3 Mutation – Definition, Spontaneous and Induced mutation. Types of mutagen Physical and Chemical,, Significance., , Unit 3: Chromosomes structure and Variation, 3.1 Chromosome structure - Introduction, types (based on position of centromere), , 13, , 3.2 Multiple allelism: Introduction, Definition, Self-incompatibility in plants, 3.3 Quantitative inheritance: a) Polygene inheritance- Concept, examples- Kernel colour in wheat,, b) Population genetics- Hardy-Weinberg’s law., 3.4 Maternal inheritance- Mendelian versus cytoplasmic inheritance, Plastid inheritance in, Mirabilis jalappa., 3.5 Alternation in genetic make-up and its significancea) Change in chromosome structure- Deletion, Duplication, Inversion and Translocation., b) Change in chromosome number- Euploidy and Aneuploidy., Unit 4: Plant Breeding, , 12, , 4.1 Introduction, Definition of plant breeding., 4.2 Aims and objectives of plant breeding, 4.3 Methods of plant breedinga) Introduction and acclimatization, b) Selection- i) Mass selection ii) Pure line selection iii) Clonal selection, c) Hybridization techniques in self and cross pollinated crops., d) Male sterility and its significance, e) Mutation breeding- Gamma garden, Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 7
Page 8 :
B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK , MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XDSE –E26, Microbiology, Plant Pathology and Mushroom Culture Technology, Unit 1: Microbiology, , 10, , 1.1 Micro organisms in biological world, characteristic features of different groups:, Phytoplasma and Actinomycetes, 1.2 Methods in Microbiology: Staining for microbes: Bacteria, Sterilization Methods,, Culture Media, Pure Culture Techniques, 1.3 Recombination in Bacteria: Transformation and Transduction, Unit 2: Industrial Microbiology, , 10, , 2.1 Applications of micro-organisms with reference to Synthesis of, Antibiotics (Penicillin), Organic Acids (Lactic Acid), Alcohol (Ethyl Alcohol), 2.2 Bio-pesticides- Concept, Types and Significance, Unit 3: Plant Pathology, , 15, , 3.1 Classification of Plant Diseases: on the basis of Pathogens and Symptoms, 3.2 Transmission of Pathogen- Air borne, Seed borne and Soil borne, 3.3 Prevention and Control: Physical, Chemical and Biological Control, Role of Quarantine, 3.4 Study of Plant Diseasesi), , Grassy Shoot of Sugarcane (Phytoplasma),, , ii), , Citrus Canker (Bacterial),, , iii), , Yellow Vein Mosaic of Bhendi (Viral),, , iv), , White Rust of Crucifers and Tikka Disease of ground nut (Fungal), , Unit 4: Mushroom Technology, , 10, , 4.1. History, Types of Mushrooms: Edible (Non poisonous) and inedible (Poisonous)., 4.2 Cultivation Technology:, Pure culture: Medium, Sterilization, Preparation of spawn, Multiplication, Mushroom bed preparation,, factors affecting the mushroom bed preparation and composting technology in mushroom production., 4.3 Storage: Short Term (Refrigeration), Long Term Storage (Canning, Pickles, Papads), Drying, in Salt Solutions, 4.4 Values of Mushroom: Nutrition - Proteins - amino acids, mineral elements nutrition Carbohydrates, Crude fibre content - Vitamins., Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 8
Page 9 :
B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK , MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XI DSE –E27, Cytology and Research Techniques in Biology, Unit 1: Cell as a unit of life, , 10, , I.1 Introduction, The Cell Theory, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells,, 1.2 Cell cycle and Apoptosis., 1.3 Cell division: Mitosis and Meiosis with their significance., Unit 2: Cell Organelles, , 12, , 2.1 Nucleus: Ultra structure, Nuclear envelope, Nuclear pore complex, DNA packaging in, Eukaryotes., 2.2 Mitochondria: Ultrastructure, semiautonomous body and Role., 2.3 Chloroplasts: Ultrastructure, semiautonomous body and Role., 2.4 Ribosomes: Structure and Functions of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ribosome., Unit 3: Sub Cellular Structures and Cell Membrane, , 10, , 3.1. ER, Golgi body and Lysosomes: Structure and Role,, 3.2 Peroxisomes and Glyoxysomes: Structure and Role., 3.3 Cell membrane: Structure, Fluid Mosaic Model, Role., 3.4Types of membranes as per permeability., Unit 4: Research Techniques in Biology, , 13, , 4.1 Principles of microscopy, Light, Fluorescence and Electron microscopy (EM)Scanning EM., 4.2 Colorimetry, Spectrophotometry, Micrometry, Photomicrography,, 4.3 Intellectual property right (IPR) – Concept and Importance., 4.4 Patents – Objectives, Procedure and Working, , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020, , Page 9
Page 10 :
B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK, MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XII DSE–E28, Horticulture and Gardening, Unit 1: Importance and divisions of Horticulture, , 5, , 1.1: Introduction and importance of horticulture, 1.2: Divisions of Horticulture – Pomology, Olericulture, Floriculture, Landscape gardening,, Unit 2: Horticultural Produce and Management of Pest and diseases, , 10, , 2.1: Floriculture: a) Introduction, Cultivation of important cut flowers and management of important, pests and diseases: Rose, Gerbera and Marigold., b) Flower arrangements, Packing and Marketing of cut flowers., 2.2: Fruit preservation technology:, a) Physical - Drying, freezing, heat,, b) Chemical - sugar, salt, chemical preservatives., Unit 3: Nursery, , 15, , 3.1: Definition, objectives and scope, Infrastructure for nursery, 3.2: Propagation Practices: Sexual and Asexual, a) Sexual: Seed: Sowing of seed, Transplanting of seedling, Advantages and Disadvantages., b) Vegetative: i) Cutting – Definition, Stem cutting (Hard wood stem and soft wood stem),Use, of PGR’s for rooting, ii) Layering –Definition, Simple layering, Air layering, iii) Grafting – Definition, Whip grafting, Approach grafting, iv) Budding: Definition, T-budding, Patch budding, c) By specialized vegetative structure – Bulbs, Corms, Tubers, Rhizomes, Unit 4: Landscape Gardening, , 15, , 4.1 Definition, scope and objectives, 4.2 Indoor Garden – Indoor plants, bottle garden, dish garden, hanging basket, Bonsai,, Vertical Garden, 3.3 Outdoor Garden – Lawns, Preparation of lawn, lawn types, Rockery, Terrace garden, Water, garden, green house and polyhouse, 3.4 Important aesthetic Gardens of India: i) Mughal garden, Delhi, ii) Brindavan garden, Mysore., Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 10
Page 11 :
SEMESTER- VI, B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK, MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XIII DSE –F25, Plant Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Unit 1: Carbohydrates, , 12, , 1.1 Introduction and Classification of carbohydrates., 1.2 Structure and Properties of- a) Monosaccharides ( Pentose: Ribose, Hexose: Glucose),, b) Oligosaccharides (Sucrose), c) Polysaccharides (starch)., 1.3 Isomerism: Types of Isomers (Structural and Stereoisomer), 1.4 Significance of carbohydrates, Unit 2 : Lipids, , 12, , 2.1 Introduction, General Structure, properties and classification of Lipids, 2.2 Structure and properties of Saturated Fatty Acids (Stearic and Palmitic acid) and Unsaturated, Fatty Acids (Oleic acid, Linoleic and), 2.3 Significance of Lipids, Unit 3: Proteins, , 11, , 3.1. Introduction, ructure, Properties, Characteristics and classification of Amino acids, 3.2. Brief Outline of biosynthesis of Amino acid: Proline, 3.3. General Structure, Classification of Protein, 3.4. Protein Biosynthesis in Eukaryotes: Transcription and translation, Unit 4: Nucleic Acids, , 10, , 4.1 Introduction, Composition and Structure, 4.2 DNA: Watson and Crick Model, Forms of DNA (A, B and Z), 4.3 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes, 4.4 RNA: Types, structure and role of RNA’s, 4.5 Regulation of Gene expression- Lac Operon, Tryptophan Operon, , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 11
Page 12 :
B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK, MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XIV DSE –F26, Bioinformatics, Biostatistics and Economic Botany, Unit 1: Bioinformatics, , 14, , 1.1 Introduction, Aim, Scope and Branches of Bioinformatics, 1.2 Biological Databases: Classification Format and Retrieval system of Biological Database,, National Center for Biotechnological Information (NCBI), Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, (BLAST), 1.3Protein Information Resource (PIR) - Concept, Resources, Databases and Data Retrieval, 1.5 Applications of Bioinformatics- Molecular Phylogeny (Concept, Methods, Analysis and, Consistency), Unit 2: Biostatistics, , 11, , 2.1 Introduction, definition, terminology., 2.2 Collection and presentation of data: Types of data, techniques of data collection- Census, method, sampling method- simple random, stratified and systematic sampling., Classification, tabulation, graphical representation- Histogram and polygon., 2.3 Measures of central tendency and Dispersion: Arithmetic mean, Mode, Median, Range,, Deviation, Mean deviation, Standard Deviation, Coefficient of Variation., 2.4 Statistical methods for testing the hypothesis’) Students’ T-test ii) Chi-square test., Unit 3: Economic Botany: Cereals, Legumes and Oils, , 10, , 3.1 Origin of Cultivated Plants - Concept of centers of origin, their importance with reference to, Vavilov’s work., 3.2 Cereals: Origin, Botanical Name, Morphology, Sources and Economic importance of Wheat., 3.3 Legumes: Origin, Botanical Name, Morphology, Sources and Economic importance of, Gram and Soybean., 3.4 Oils and Fats: Origin, Botanical Name, Morphology, Parts used and uses of Ground nut., Unit 4: Economic Botany: Spices, Beverages and Fibers, , 10, , 4.1 Spices and Condiments - Origin, Botanical Name, Morphology, Parts used and, Uses of Clove and Black pepper., 4.2 Beverages – Origin, Botanical Name, Morphology, Parts used and uses of Tea., 4.3 Fibre yielding Plants - Origin, Botanical Name, Morphology, Parts used and uses of, Cotton., Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 12
Page 13 :
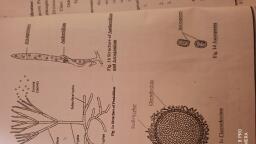
B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK, MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XV DSE –F27, Plant Biotechnology and Paleobotany, Unit 1: Plant Biotechnology, , 03, , 1.1 History, Definition, Scope and Importance (Areas of application), 1.2 Biotechnology in India, Unit 2: Recombinant DNA Technology, , 15, , 2.1. Introduction, Principles and enzymes involved in DNA technology.., 2.2. Cloning Vectors: a) Prokaryotic- Plasmid, Lambda phage and Cosmid., (Brief idea) b) Eukaryotic-YAC (Yeast Artificial Chromosomes)., 2.3Southern blotting and Northern blotting techniques and its applications, Molecular Probes, 2.4. DNA Fingerprinting, Molecular DNA Markers (RAPD, RFLP), 2.5 PCR, DNA sequencing and Concept of Gene bank., Unit 3: Plant Tissue Culture, , 15, , 3.1 Principles and Terminologies, Laboratory Requirement (Conditions and Instruments),, Culture Media, Totipotency and Cellular Differentiation,, 3.2 Micro propagation: Stages of Micro propagation- Callus formation, Root Initiation, Shoot, Initiation, Primary and Secondary Hardening, Advantages and disadvantages, 3.3 Embryogenesis: Protoplast culture, Cybrid, 3.4 Somaclonal Variations, Unit 4: Paleobotany, , 12, , 4.1 General account, Geological time scale, process of fossilization, Types of fossils., 4.2 Study of following form genera with reference to systematic position, external morphology, and affinities: a) Lyginopteris b) Enigmocarpon., 4.3 Application of paleobotany: Role of microfossil in oil and coal exploration., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 13
Page 14 :
B.Sc. Part- III Botany, CREDITS: 2, LECTURE PERIOD: 3 PER WEEK, MARKS: 40+10, , Paper- XVI DSE –F28, Bio fertilizers and Herbal Drug Technology, Unit 1: Biofertilizers, , 11, , 1.1 Introduction, Importance, types and study of –, a) Bacterial fertilizers: Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Azospirillum, b) Blue green Algal:, Cyanobacteria (BGA): Nostoc, Anabaena., c) Mycorrhizal association: VAM, d) Fungal: Trichoderma, 1.2 Organic manures –, a) Farm Yard Manure, Green manure, Compost, b) Vermicomposting and Vermi-wash, Unit 2: Herbal Medicines, , 11, , 2.1 Definition, Importance of herbal medicines, 2.2 Classification of crude drugs: Taxonomical, Morphological and Chemical, 2.3 Identification, authentication, collection, processing and storage of medicinal plants., 2.4 Introduction to general methods of extraction, isolation and purification of, Phyto constituents., Unit 3: Herbal cosmetology, , 11, , 3.1 Applications of herbs in cosmetics: Shampoo (Sapindus laurifolius, Acacia concinna), hair, dye (Lawsonia inermis), 3.2 Facemask (Santalum album), bath oil (Rosa indica), perfume (Jasminum sambac)., Unit 4: Pharmacognosy, , 12, , 4.1 Pharmacognosy: Introduction And, Definition, 4.2 Medicinal uses of Tulsi, Ginger, Methi, Avala., 4.3 Adulteration of drugs of natural origin: Evaluation by morphological, Microscopic,, Chemical, Physical, Chromatographical, Spectrophotometric., 4.4 Plant antioxidants: Properties of Antioxidants, Vitamins (C and E), , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 14
Page 15 :
Shivaji University, Kolhapur, B.Sc. III Botany (CBCS Syllabus), Practical-I (Based on Paper No. X and XV), 1, , Preparation of culture media –PDA (slants and Plates) and sterilization., , 2, , Methods of inoculation- on slants and plates, , 3, , Isolation of soil fungi by serial dilution method., , 4, , Study of different types of stains in biological studies., , 5, , Method of control of seed borne diseases (Dipping/Seed dressing), , 6 and 7, , Plant diseases as per theory, , 8 and 9, , Demonstration of Mushroom Cultivation and Harvesting, , 10, , Isolation of plant genomic DNA and its spooling., , 11, , Calorimetric estimation of DNA using di-phenyl amine., , 12, , Preparation of plant tissue culture medium (M.S.)., , 13, , Demonstration of techniques of In Vitro culture using suitable ex-plant., , 14, , Demonstration of inoculation of explants on suitable medium (M.S.), , 15, , Isolation of Protoplast., , 16, , Study of steps in genetic engineering for the production of Golden rice with the help, of photographs., , 18, , Identification of types of fossils – i) Impression ii) Compression iii) Petrification, IV) Coal., Identification of – i) Lyginopteris, , 19, , Identification of Enigmocarpon, , 20, , Submission of plant diseases, , 17, , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 15
Page 16 :
Shivaji University, Kolhapur, B.Sc. III Botany ( CBCS Syllabus ), Practical-II (Based on Paper No. IX and XIV), 1., , Genetic examples on Linkage., , 2, , Genetic examples on Crossing over, , 3, , Genetic examples on Polygene inheritance, , 4, , Determination of chromosome count in PMCs in Allium / Cynoetis., , 5, , Detection of meiotic anomalies in chromosomes in Rhoeo., , 6, , Preparation of karyotypes – idiograms by using photographs., , 7, , Methods of emasculation, , 8, , Breeding techniques in a) Malvaceae b) Fabaceae c) Poaceae, , 9, , Mounting of floral parts., , 10, , Study of World map to show Vavilov’s centers of origin of cultivated plants., , 11, , Study of Botanical Name. Morphology, Parts used and Economic importance of Wheat., , 12, , Study of Botanical Name. Morphology, Parts used and Economic importance of Gram, and Soybean., , 13, , Study of Botanical Name. Morphology, Parts used and Economic importance of Clove, and Black pepper., , 14, , Study of Botanical Name. Morphology, Parts used and Economic importance of, Ground nut., , 15, , Study of Botanical Name. Morphology, Parts used and Economic importance of Cotton., , 16, , Measures of central tendency of given data., , 17, , Study of frequency distribution and its graphical representation, , 18, , Determination of Standard deviation of the given data., , 19, , Submission of PPT on the basis gene transfer method., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 16
Page 18 :
Shivaji University, Kolhapur, B.Sc. III Botany ( CBCS Syllabus ), Practical-IV (Based on Paper No. XII and XIII), , 1., , Study of budding technique – Patch and T-budding, , 2, , Study of Layering technique – Air layering, , 3, , Study of Grafting technique – Whip and Approach, , 4, , Technique of Potting and Repotting, , 5, , Demonstration of Bonsai, , 6, , Demonstration of Bottle garden and hanging baskets., , 7, , Floral arrangement – Flower pot, Floral bouquet, Floral Rangoli, , 8, , Garden implements (Any five) – Garden shear, sickle, cutter, shovel, budding knife,, secateur, water can, pruning scissors, sprayer, spade, , 9, , Study of ornamental plants – Rose, Gerbera, Marigold, , 10, , Study of hedge and edge plants., , 11, , Study of indoor plants., , 12, , Qualitative test for sugar in plant material, , 13, , Qualitative tests for starch and cellulose in plant material, , 14, , Qualitative test for proteins., , 15, , Qualitative test for lipids., , 16, , Identification of sugars by ascending paper chromatography., , 17, , Determination of fatty acid value of oil sample., , 18, , Separation and identification of amino acids by TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography)., , 19, , Determination of iso-eletric point of plant protein., , 20., , Visit to nursery/ Aesthetic garden / Exhibition / Food industry (Separate handwritten, report to be submitted by student), , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 18
Page 19 :
List of Books Recommended for B. Sc. III Botany, Cytology and Genetics --1. Cell Biology - S. C. Rastogi (1992), 2. Cell Biology - C. B. Powar (2000), 3. Cell Biology, Genetics, Evolution and Ecology – P S. Verma, V K. Agarwal (2001), 4. Cell Biology - R. Dowben (1971), 5. Cell and Molecular Biology – P. K. Gupta (1999), 6. Cell and Molecular Biology (2001) – E. D. P De Robertis& E. M. F De Robertis (Jr.), 7. Cell Physiology - A C. Giese (1979), 8. Cellular Energy Metabolism and Its Regulation - Atkinson, D. E. (1977), 9. Genetics - P. K Gupta (1997)Rastogi Publications. Shivaji Road, Meerut., 10. Gene Action - Hartman alldSuskind (1968), 11. Cytology and Genetics.--Dnyansagar(T. Magrewith& Co.), 12. Plant Chromosomes: Laboratory Methods--Fukui. K. and Nakayama S. 1996. CRC Press,, Boca Raton, Florida., 13. Plant Chromosomes: AnalysisManipulation and Engineering. Sharma A.K. and Sharma A., 1999. Hawood Academic Publishing, Australia., 14. Fundamentals of Cytology --L. W. Sharp., 15. Principles of Genetics -Snustad. D. P. and Simmons. M.J. 2000. (2nd Edition).John Wiley, & Sons Inc., USA., 16. Cytogenetics and Plant Breeding-- S N. Chandrashekharan and S. V. ParthaSarathy., 17. The Science of Genetics.-Atherly. A.G., Girton. J.R. and McDonald. 1999. Saunders College, Publishing Co., Fort Worth USA., 18. Principles of Genetics- Gardener. J., Simmons. H.J. and Snustad. D.P. 1991. (8th Edition)., John Wiley & Sons, New York., 19. Genetics: Principles and Analysis--Hartl.D.L.andJones.E.W. 1998. (4thEdition) Jones &, Barlett Publishers. Massachusetts. USA., 20. Genetics (5th Edition).-Russel. P.J. 1998. The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co., Inc.,, USA., 21. MolecularBiology of Cell. Alberts B., Bray D., Lewis, J., Raff, M. Roberts, K. and Wastson,, J.D. 1999.Garland Publishing Co., Inc., New York USA., 22.Karp, G. 2010. Cell and Molecular Biology: Concepts and Experiments. 6th Edition., John Wiley & Sons. Inc., 23 De Robertis, E.D.P. and De Robertis, E.M.F. 2006. Cell and Molecular Biology. 8th edition. Lippincott Williams, and Wilkins, Philadelphia., 24. Becker, W.M., Kleinsmith, L.J., Hardin. J. and Bertoni, G. P. 2009. The World of the Cell. 7th edition. Pearson, Benjamin Cummings Publishing, San Francisco., 25. Molecular biology (principles and practices) Dr. priyanka Siwach and Dr. Namita singh laxmi publication., ISBN 9788131807476., 26. Molecular biology , N Arumugam , Saras Publication . ISBN 9789382459835, 27. Molecular biology , Dr. P.S. Verma , Dr. V.K. Agrawal, P.Chand Publication, 28. Molecular biology Concepts for Inquiry Jenifer A Hackett., 29. Esential cell biology 4th edition Bruce alberts, Dennis bray,Karen Hopkin, AlexanderD, Jahnson., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 19
Page 20 :
Economic Botany:, 1. Kocchar, S. L. 1998. Economic Botany in Tropics, 2nd edition. MacmillanIndia Ltd., New, Delhi., 2. A Textbook ofEconomic Botany--Sambamurthy, A. V. S. S. and Subramanyam, N. S. 1989., Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi., 3. Hill's Economic Botany. -- Sharma, O. P. 1996. Tata McGraw Hill PublishingCompany Ltd.,, New Delhi., 4. Economic Botany - Plants inOur World. Simpson, B. B. and Conner-Ogorzaly, M. 1986., McGraw Hill, New York., , Horticulture and Gardening:, I. Gardening in India. -- Perey Lancaster (1997) Oxford & I B H Publishing Co.Pvt.Ltd,New, Delhi., 2. Floriculture: Fundamentals & Practices. - Alex Laurie and Ries V.C. (2003), 3. Percy Lancaster's Gardening in India.- Bose, T.K. and Mukherjee, D. (1997) (Ed.)Oxford and, IBH Publ. (P.) Ltd,, New Delhi, India., 4. A Art of Miniature Plant Culture. - Day, S.C. (2003)Agrobias. Jodhpur, India., 5. Complete Home Gardening. -Dej, S.C. (2003) Agrobias, Jodhpur, India., 6. Principles and Techniques for Plant Scientists. -Dhopte, A.M. (2003) Agrobios,Jodhpur,, India., 7. Horticulture and Gardening.- Khan, M.R. (1995) NiraliPrakashan, Pune. India., 8. Gardening for every one- PramilaMehra. Hind pocket book private limited, NewDehli., 9. Kumarsen V. Horticulture ,Saras Publication, 10.Bose T.K. & Mukherjee, D., 1972, Gardening in India, Oxford & IBH PublishingCo., New Delhi., 11. Sandhu, M.K., 1989, Plant Propagation, Wile Eastern Ltd., Bangalore, Madras., 12.Kumar, N., 1997, Introduction to Horticulture, Rajalakshmi Publications, Nagercoil., 13.Edmond Musser & Andres, Fundamentals of Horticulture, McGraw Hill Book Co.,New Delhi., 14.Agrawal, P.K. 1993, Hand Book of Seed Technology, Dept. of Agriculture andCooperation,, National _Seed Corporation Ltd., New Delhi., 15.Janick Jules. 1979. Horticultural Science. (3rd Ed.), W.H. Freeman and Co., SanFrancisco, USA., 16.Randhawa, G.S. and Mukhopadhyay, A. 1986. Floriculture in India. Allied Publishers., , Microbiology and Plant Pathology, 1), 2), 3), 4), , Microbiology- P.D.Sharma; Rastogi Publications, Plant Pathology- Mehrotra, Plant Diseases- R.S. Singh, Plant Diseases- Rangaswamy, , Biochemistry, 1) Fundamentals of Biochemistry- J.L.Jain, Sunjay Jain, Nitin Jain; S. Chand & Company Ltd., 2) Cell Biology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Evolution and Ecology- P. S. Verma, V. K., Agarwal; S. Chand & Company Ltd., Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 20
Page 21 :
Bioinformatics, 1) Introduction to Bioinformatics – S. Sundara Rajan, R. Balaji; Himalaya Publishing House., Plant Biotechnology, 1. Elements Of Biotechnology- P. K. Gupta (Second Edition); Rastogi Publications, 2., , Plant Tissue Culture - Kalyan Kumar De; New Central Book Agency (P) Ltd., , 3. Introduction to Plant Tissue Culture - M. K. Razdan (Second Edition); Oxford & IBH Publishing, Co. Pvt. Ltd., 4. Practical Biotechnology and Plant Tissue Culture - Prof. Santosh Nagar, Dr. Madhuri Adhav;, S. Chand & Co. Ltd., 5. Arnold C.A.1972. An Introduction to PalaeobotanyTata McGraw-Hill,, 6. Andrews H.N. Studies in Palaeobotany 1961. John Wiley & Sons Canada, Limited,, 7. Shukla A.C. and S.P . Mishra. Essentials of Palaeobotany., 8. Wilson, N. S. and Rothwell,G.W.1983. Palaeobotany and the Evolution of Plants, (2ndEdition).Cambridge University Press U.K., 9. Dubey, R.C., 2005 A Text book of Biotechnology S.Chand& Co, New Delhi., 10. Kumaresan, V. 2005, Biotechnology, Saras Publications, New Delhi., 11. John JothiPrakash, E. 2004. Outlines of Plant Biotechnology. Emkay ¬Publication, NewDelhi., Biofertilizers and Herbal Technology, , 1. Sathe, T.V. 2004 Vermiculture and Organic Farming. Daya publishers., 2. SubhaRao, N.S. 2000, Soil Microbiology, Oxford & IBH Publishers, New ¬Delhi., 3. Vayas,S.C, Vayas, S. and Modi, H.A. 1998 Bio-fertilizers and organic ¬Farming Akta, Prakashan, Nadiad, 4. Chopra R.N., S.L.Nayar and I.C.Chopra, 1956.Glossary of Indian medicinal plants, C.S.I.R, New Delhi., 5. Dey and Raj Bahadur,1984. The indigenous drugs of India, Kanny, Lall,., International Book Distributors., , Details of Practical Examination, A) Every candidate must produce a certificate from Head of the Dept. in his /her college, stating that he /, she has completed practical course in satisfactory manner as per guidelines laid down by Academic Council, on the recommendations of Board of Studies in Botany. The student should record his / her observations, and report of each experiment should be written in the journal. The journal is to be signed periodically by, teacher in charge and certified by the Head of the Department at the end of year. Candidates have to, produce their certificated journal and tour report at the time of practical examination. Candidate is not, "allowed to appear" for the practical examination without a certified journal / a certificate from Head of the, Botany Dept. regarding the same., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 21
Page 22 :
B) Practical Examination shall be of Five hours duration and shall test a candidate in respect of the, following., 1. Practical study of external and internal structures of different plant types and their classification., Making temporary stained preparations and identification., 2. Identification and setting of experiments as per syllabus., 4. Spotting of the specimens as per syllabus., , Botanical Excursions, One teacher along with a batch not more than 20 students be taken for botanical excursion to places, of Botanical interest, one in each term. If there are female students in a batch of 20 students, one additional, lady teacher is permissible for excursion. Each excursion will not be more than SEVEN days during college, working days. T.A. and D.A. for teachers and non-teaching staff participating in excursions should be paid, as per rules. Tour report duly certified by tour in charge teacher and Head of the Department should be, submitted at the time of practical examination. For every study tour take the prior permission of the head of, the department and Principal., , Practical Course, B. Sc. III Botany Practical course covered in four practical numbers (Practical no.1 , Practical no.2,, practical no.3 and practical no. 4 with total 80 practicals). These practicals are to be performed by the, students. Each practical is to be supplemented by permanent slides, preserved / fresh specimens / materials,, charts, herbarium sheets, etc. wherever necessary., , C] OTHER FEATURES:, 1., , INTAKE CAPACITY / NUMBER OF STUDENTS:As per university rules., , 2., , TEACHERS QUALIFICATIONS:•, •, , 2, , As prescribed by norms., However required number of core faculty should be given for particular course along with paper, wise and Specialization wise work load allocation., • Work load details should be as per Apex body/UGC/State Govt./University norms., The Board of studies should clearly mention the required Books, Journals and specific, Equipments necessary for the Course., , (A), , LIBRARY: Library be equipped with the required Reference and Text Books, Journals and, Periodicals for higher and advanced studies as per stated in revised syllabus and approved by, BOS., , (B), , SPECIFIC EQUIPMENTS:, T.V., V.C.R. V.C.P., L.C.D., Overhead Projector, Computers and necessary software, and operating systems etc. are necessary to run the course., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 22
Page 23 :
(C), , LABORATORY SAFETY EQUIPMENTS, i)Fire extinguishers at least two sets in each laboratory of 600 sq.ft. Area., ii) Leakage of gases be avoided., iii) First aid kit be made available., iv) Sugar / Glucose –500gm pack- a pinch of sugar and a cup of drinking, water in hypoglycemic condition or in extreme weakness of student or, a person concerned, , B) GENERAL SAFETY RULES FOR LABORATORY WORK, 1) List of equipments needed for Laboratory Safety:1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., , 2), , Fire extinguisher, First Aid Kit, Good earthing and insulated wirings for electrical supply., Emergency exit, Apron and goggles wherever necessary, Fuming Chambers, Masks flows and shoes while handling hazardous chemicals & gases (Good valves,, manometers and regulators for gas supply), 8. Operational manuals for instruments (handling to be made as suggested.), 9. Rules of animals and blanks ethics., 10. Leakage of gases to be avoided., 11. Cylinders or flow pipes to handle Acids., 12. No weighings for NaOH and hygroscopic substances., 13. Stabilized supply in the laboratory., There Is No Substitute for Safety, , 1., , Any injury no matter how small, it must be reported to teacher immediately., , 2., , a) In case any chemical enters your eyes go immediately to eye- wash facility, and flush your eyes and face with large amount of water., b) For acid or phenol split, do not use water instead put some bicarbonate., , 3., , In case of fire, immediately switch of all gas connections in the laboratory and pour sand on the, source of fire or cover it with asbestos or cement sheet., , 4., , While leaving laboratory, make sure that gas, water taps and electricity are switched off., , 5., , Remove your lab coat. Gloves and clean your hands before leaving laboratory., , 6., , Make your workplace clean before leaving the laboratory., , 7., , Keep your hands away from your face, while working in laboratory., , 8., , Each laboratory must have a first aid box., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 23
Page 24 :
9., , Know what to do in case of emergency - e.g., (a) Know the place of fire extinguisher and first aid box., , 10., , Don't use cell phones in the laboratory., (a) Remember important phone numbers, , 3), , DO's, , 1., , Always wear lab coat, shoes in the laboratory. Every student must have their weight box, a, napkin etc., , 2., , Maintain separate record book for each subject., , 3., , Keep your belongings at the place allotted for the same., , 4., , Maintain silence, order, cleanliness and discipline in the laboratory., , 5., , Work at the place allotted to you or specially used for certain operations., , 6., , Keep the working table clean., , 7., , Handle the laboratory equipments, glassware and chemical with great care., , 8., , Use only required quantities of material and apparatus of essential size., , 9., , Perform the test in their proper order., , 10., , Know the location of eye wash fountain and water shower., , 11., , Minimize your exposure to organic solvents., , 12., , The Metal like sodium should be kept under kerosene or liquid paraffin layer in a vessel with a, cork stopper., , 13., , Sodium metal should be cut on dry filter paper. The cut off pieces of sodium should be, immediately collected in a vessel containing kerosene or liquid paraffin., , 14., , Always pour acid into water when diluting and stir slightly., , 15., , All operations involving poisonous flammable gases and vapours should be carried out in the, flame chamber (with exhaust facility), , 16., , Ladies should avoid wearing saree. If it is there, apron is essential., , 4), , DON’T, , 1., , Don’t work alone in the laboratory, , 2., , Don’t leave the glass wares unwashed., , 3., , Don’t take apparatus, chemicals out of lab., , 4., , Don’t leave any substance in a vessel or bottle without label., , 5., , Don’t weigh the reagent directly on the balance pan., , 6., , Don’t throw the cut off pieces of sodium metal in sink or water. Transfer it immediately in its, container., , 7., , Don’t take sodium metal with hands. Use forceps., , 8., , Don’t panic and run in case of fire. Use the fire extinguishers or sand buckets., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 24
Page 25 :
9., , Don’t breathe the vapours of organic solvents., , 10., , Don’t pour any unused reagent back in its stock bottle., , 11., , Don’t eat or drink any food in laboratory., , 12., , Don’t use inflammable solvents like benzene, ether, chloroform, acetone and alcohol around, flame., , 13., , Don’t distill to dryness., , 14., , Don’t exchange stoppers of flasks and bottles containing different reagents., , 15., , Don’t leave reagent bottle lying on the table., , 16., , Don’t disturb the order of reagent bottles in which they are placed., , 17., , Don’t bring reagent on your working table from the general shelf., , 18., , Don’t throw burning matchstick into dustbin., , 19., , Don’t leave the laboratory without permission., , 5), , LABORATORY / FIELD WORK CARE AND SAFTY FOR BOTANY STUDENTS, , 1., , Unnecessary wastage of plant material during practical should be avoided., , 2., , During study tour / personal collection, more emphasis be given on study of plants in nature and, collection of wild plants should not be carried out., , 3., , If at all the collection of the plant material in needed, it should be carried out under supervision, of concerned teacher. Collection of poisonous plants / poisonous mushrooms should be, avoided., , 4., , Oral intake of unknown plant material, out of curiosity, during practical or collection tour is, strictly prohibited., , 5., , If there is any allergic reaction while handling the plants / plant parts / pollen grains / fungal, specimens it should be immediately brought to the notice of the concerned teacher and reported, to the registered medical purloiner., , 6., , Wearing of hand gloves (and mask) is essential while handling poisonous plants / herbarium, sheets / toxic and hazardous chemicals / reagents / strong acids / strong alkalis during the, experiment should be made with vacuum pipette / auto pipette / burette under the supervision of, concerned teacher / lab assistant., , 7., , Highly inflammable organic solvents (alcohol, acetone etc.) should not be kept in vicinity of, spirit lamp., , 8., , The laboratory safety measures adopted for handling of hazardous chemicals in chemistry, practicals should be followed for conducting practicals in plant biochemistry / microbiology., , 9., , Operational manuals for equipments such or centrifuge, autoclave, spectrophotometer should be, followed., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 25
Page 26 :
10., , In case of minor injuries, preliminary treatment should be undertaken with the help of first aid, kit available in the laboratory. In case of serious injury, concerned teacher should be, immediately contacted for consultation to the physician., , 11., , The instruction report for breeding, experimentation will be submitted in a week period., (Which are laid down by Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment and Ministry of, Environment and Forests, Govt. of India)., Course outcomes, 1. Students are acquainted with basic as well as recent knowledge in the field of molecular, biology, biotechnology and bioinformatics, 2. Acquiring the basic procedure in the field of microbiology and plant pathology., 3. To develop skills in of horticulture including nursery, landscaping, gardening, floriculture, and polomology, 4. Students will be able to demonstrate their knowledge, skills and attributes to be successful, contributing members o the horticulture profession., 5. Acquaint the student with the comprehensive knowledge in the bio fertilizers, herbal drug, technology and paleobotany, 6. Students will able to demonstrate their understanding of relevant course theories and concepts, Students able to Mendelian and Neo-mendelian genetics, 7. Students become familiar with the Organic manures, Herbal Medicines, Herbal cosmetology, and Pharmacognosy., 8. Understand the methods of Plant Biotechnology, Protoplast culture and Recombinant DNA, Technology., 9. Acquainted the scope of paleobotany in the present scenario and understand the fossil genera, , 10. Aware about the Spices, Beverages and Fibers, Cereals, Legumes and Oils., 11. Understand the of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, 12. Understand the techniques of plant breeding, 13. Understand the techniques of mushroom cultivation., 14. Acquainted the techniques of micrometry, chromatography and other laboratory techniques, used in the field of life science., , Shivaji University, Kolhapur. B.Sc. III Botany CBCS Syllabus implemented from June 2020 Page 26