Page 1 :
ANGIOSPERMS, B. Angiospermae (Angios : enclosed : Sperma : seed), 1.Angiosperms are the flowering plants., 2. The seeds are enclosed within the fruit i.e .ovary., 3.Angiosperms is a group of highly evolved plants., 4.They vary in size., 5. They show heteromorphic alternation of generation., 6.The sporophyte is diploid, dominant, autotrophic and independent., 7.The gametophytes (male or female) are reduced, haploid and, concealled., 8. Angiosperms are heterosporous., 9. Microspores (commonly called pollens) are formed in, microsporangia (or anthers). They develop in highly specialized, microsporophyll or stamens ., 10. Megaspores are formed in megasporangia (or ovules) borne on, highly specialized megasporophyll called carpel., 11.The essential whorls of microsporophylls (Androecium) and, megasporophylls (Gynoecium)., 12. The accessory whorls namely calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals), arranged together to form flowers., Angiosperms are subdivided into two classes:, a)Dicotyledonae :, 1. These plants have two cotyledons in their seed., 2.They have a tap root system ., 3.The stem is branched., 4. Leaves show reticulate venation., 5.The flowers show tetra or pentamerous symmetry., 6.Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and open type. Cambium is, present between Xylem and Phloem for secondary growth., 7. In Dicots secondary growth is commonly found., e.g. Helianthus annuus (sunflower), Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (China, rose)., b). Monocotyledonae :, 1.These plants have single cotyledon in their seed., 2They have adventitious root system., 3.The stem is unbranched.
Page 2 :
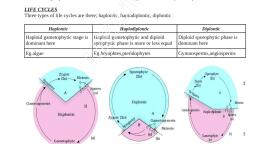
4. Leaves show parallel venation., 5. The flowers are trimerous., 6.The vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed type., 7. In Monocots, except few plants secondary growth is absent., e.g. Zea mays (Maize), Sorghum vulgare (Jowar)., 3.4 Plant life cycle and alternation of generations:, 1. Life cycle of a plant includes two phases.(distinct generations), namely sporophyte (diploid : 2n) and gametophyte (haploid : n)., 2. Diploid cells of sporophyte divide by meiosis to produce haploid, cells. These haploid cells divide mitotically to give rise haploid, gametophyte., 3. The gametophyte produces male and female gametes by mitosis., which fuse during fertilization to produce diploid zygote. It divides by, mitosis to form diploid sporophyte., 4.The sporophytic and gametophytic generations occur alternately in, the life cycle of a plant. This phenomenon is called alternation of, generations., 5.Distinct alternation of these two generations is observed in, Bryophytes and Pteridophytes., 6.In Gymnosperms and Angiosperms, gametophyte is much reduced, and exists within sporophyte., 7. In algae, based upon the nature of dominant phase in life cycle, it is, called haplontic, diplontic or haplodiplontic life cycle., 8.In Bryophytes gametophyte is dominant. It is photosynthetic,, independent thalloid or erect phase. Sporophyte is short lived,, multicellular and depends totally or partially on gametophyte for, nutrition and anchorage., 9. In Pteridophytes, sporophyte is dominant, independent and vascular, plant body.Haploid multicellular gametophyte is generally autotrophic, and short lived. It alternates with Sporophyte.