Page 1 :
6, , Sample Paper, Time : 90 Minutes, , Max. Marks : 50, , General Instructions, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , The Question Paper contains three sections., Section A has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions., Section B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions., Section C has 12 questions. Attempt any 10 questions., All questions carry equal marks., There is no negative marking, SECTION-A, , DIRECTION: This section consists of 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from this section. The first attempted 20 questions, would be evaluated., 1., , The type of cells under going meiosis in the flowers are, (a) micro spore and mega spore mother cell, (b) ovule & stamen, (c) tapetal cells, (d) placental cell, , 2., , D, , B, C, F, A, E, , 3., , 4., , In the diagram given above, parts labelled as ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’, ‘E’ and ‘F’ are respectively identified as:, (a) synergids, polar nuclei, central cell, antipodals, filiform apparatus and egg, (b) polar nuclei, egg, antipodals, central cell, filiform apparatus and synergids, (c) egg, synergids, central cell, filiform apparatus, antipodals and polar nuclei, (d) central cell, polar nuclei, filiform apparatus, antipodals, synergids and egg, Which of the following condition of angiospermic embryo sac is seen at maturity?, (a) 7 celled, 8 nucleate, (b) 7 celled, 7 nucleate, (c) 8 celled, 8 nucleate, (d) 8 celled, 7 nucleate, Select the incorrect pair of type of pollination and the corresponding pollinating agency., (a) Anemophily, –, Wind, (b) Hydrophily, –, Water, (c) Ornithophily, –, Birds, (d) Chiropterophily, –, Insects
Page 3 :
Sample Paper-6, 11., , 12., 13., , 14., , 15., , 16., 17., , 18., , 19., 20., , 21., , 22., , 23., , SP-53, , Generally the pollen grains of monocots are ________ and dicots are respectively., (a) uniporate and biporate, (b) biporate and trip orate, (c) uniporate and triporate, (d) triporate and tetraporate, Person having genotype Ia Ib would show the blood group as AB. This is because of, (a) Pleiotropy, (b) Codominance, (c) Segregation, (d) Incomplete dominance, Which one of the followings is correctly matched with their chromosomal condition?, (a) Sickle cell anaemia – Heterozygous condition of Hbs gene, (b) Down’s syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 22, (c) Turner’s syndrome – XO condition, (d) Klinefelter’s syndrome – failure of cytokinesis after telophase, If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only same of the male progeny, the, disease is, (a) Autosomal dominant (b) autosomal recessive (c) sex-linked dominant, (d) sex-linked recessive, Across between two tall plants resulted in offspring having few dwarf plants. What would be the genotypes of both the, parents ?, (a) TT and Tt, (b) Tt and Tt, (c) TT and TT, (d) Tt and tt, In his classic experiments on pea plants, Mendel did not use, (a) Pod length, (b) Seed shape, (c) Flower position, (d) Seed colour, Down’s syndrome in humans is due to, (a) Two ‘Y’ chromosomes, (b) Three ‘X’ chromosomes, (c) Three copies of chromosome 21, (d) Monosomy, Lactose operon produces enzymes, (a) -galactosidase, permease and glycogen synthetase., (b) -galactosidase, permease and transacetylase., (c) Permease, glycogen synthetase and transacetylase., (d) -galactosidase, permease and phosphoglucose isomerase., Genes that are involved in turning on or off the transcription of a set of structural genes are called, (a) Operator genes, (b) Redundant genes, (c) Regulator genes, (d) Polymorphic genes, Reverse transcriptase is, (a) RNA dependent RNA polymerase, (b) DNA dependent RNA polymerase, (c) DNA dependent DNA polymerase, (d) RNA dependent DNA polymerase, One gene-one enzyme relationship was established for the first time in, (a) Salmonella typhimurium, (b) Escherichia coli, (c) Diplococcus pneumoniae, (d) Neurospora crassa, In the DNA molecule, (a) the total amount of purine nucleotides and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal, (b) there are two strands which run parallel in the 5' 3' direction, (c) the proportion of adenine in relation to thymine varies with the organism, (d) there are two strands which run anti-parallel one in 5' 3' direction and other in 3' 5', The figure given below depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of all female reproductive system of humans. Which of the, following option represent III, IV and V part?, , I, II, , 24., , (a) (I) Perimetrium, (II) Myometrium, (III) Fallopian tube, (b) (II) Endometrium, (III) Infundibulum, (IV) Fimbriae, (c) (III) Infundibulum, (IV) Fimbriae, (V) Cervix, (d) (IV) Oviducal funnel, (V) Uterus, In a DNA strand the nucleotides are linked together by, (a) glycosidic bonds, (b) phosphodiester bonds (c), , III, V IV, , peptide bonds, , (d), , hydrogen bonds
Page 4 :
EBD_7332, Biology, , SP-54, , SECTION-B, DIRECTION: This section consists of 24 questions (Sl. No.25 to 48). Attempt any 20 questions from this section. The first, attempted 20 questions would be evaluated., Question No. 25 to 28: Consist of two statements Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate, option given below:, (a) If both Assertion and Reason are True and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion., (b) If both Assertion and Reason are True but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion., (c) If the Assertion is True but Reason is False., (d) If both Assertion and Reason are False., 25. Assertion: In very rare cases, a surrogate mother may have to be used to bring up in vitro fertilised ovum to maturity., Reason: Success rate of test tube baby is more than 90%., 26. Assertion: The Mendalian factors are also called unit factor which are known as genes., Reason: Chemically, a gene is a linear segment of DNA called cistron., 27. Assertion: The flower colour of sweet pea shows the inheritance of complementary genes., Reason: The ratio obtained for complementary genes is 9:7., 28. Assertion: Mendel was born on 22nd july, 1822 to a farmers family in the Austria., Reason: Mendel died due to heart attack in the year 1901., 29. The given diagram refers to T.S. of testis showing sectionl view of a few semniferous tubules. Identify the parts labelled A-D, and select the correct option., , D, A, B, C, , 30., , 31., , 32., , 33., , 34., , (a) A-Sertoli cell, B-Spermatozoa, C -Interstitial cell, D-Sperms, (b) A-Sertoli cell, B-Secondary spermatocyte, C -Interstitial cell, D-Sperms, (c) A-Interstitial cell, B-Spermatogonia, C -Sertoli cells, D-Sperms, (d) A-Sertoli cells, B-Spermatogonia, C -Interstitial cells, D-Sperms, The main function of the fimbriae of the Fallopian tube in females is to, (a) release to ovum from the Graafian follicle, (b) make necessary changes in the endometrium for implantation, (c) help in the development of corpus luteum, (d) help in the collection of the ovum after ovulation, A particular species of plant produces light, non-sticky pollen in large numbers and its stigmas are long and feathery. These, modifications facilitate pollination by, (a) insects, (b) water, (c) wind, (d) animals, At the time of fertilization sperm head enters in the egg from, (a) Any where, (b) Animal pole, (c) Vegetal pole, (d) Lateral side of egg, Copper-T is a device that prevents, (a) implantation of blastocyst & fertilization, (b) ovulation, (c) decrease phagocytosis of sperm, (d) egg maturation, The diaphragm, cervical cap and vaults are, (a) disposable contraceptive devices, (b) reusable contraceptives, (c) IUDs, (d) Implants
Page 5 :
Sample Paper-6, 35., 36., 37., , 38., , 39., , SP-55, , The point at which funiculus touches the ovule is, (a) chalaza, (b) hilum, (c) raphe, (d) endothelium, A man with blood group ‘A’ marries a woman with blood group ‘B’. What are all the possible blood groups of their offsprings?, (a) A, B and AB only, (b) A, B, AB and O, (c) O only, (d) A and B only, Which of the following characteristics represent ‘Inheritance of blood groups’ in humans?, A. Dominance, B. Co-dominance, C. Multiple allele, D. Incomplete dominance, E. Polygenic inheritance, (a) B, C and E, (b) A, B and C, (c) A, C and E, (d) B, D and E, When two unrelated individuals or lines are crossed, the performance of F1 hybrid is often superior to both parents. This, phenomenon is called:, (a) heterosis, (b) transformation, (c) splicing, (d) metamorphosis, In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio it denotes that, P generation, Round yellow, RR YY, , Wrinkled green, rr, yy, , Gametes, , Round yellow, Rr Yy, Selfing, , F1 generation, , RY, , RY, Gametes, , rY, Ry, , ry, , RrYY, , RrYy, , RrYy, , F2 generation, , rrYy, , Ry, , RrYY, rrYy, , RRYy, , Gametes, , rY, , RRYY, , ry, , RRYy, RrYy, , RRyy, , RrYy, rrYy, , Rryy, , Rryy, rryy, , 40., , (a) the alleles of two genes are interacting with each other., (b) it is a multigenic inheritance., (c) it is a case of multiple allelism., (d) the alleles of two genes are segregating independently., In our society women are blamed for producing female children. Choose the correct answer for the sex-determination in humans, (a) Due to some defect in the women, (b) Due to some defect like aspermia in man, (c) Due to the genetic make up of the particular sperm which fertilizes the egg, (d) Due to the genetic make up of the egg
Page 6 :
EBD_7332, Biology, , SP-56, , 41., 42., , 43., , 44., , Which of the following is sex linked disorder ?, (a) Sickle-cell anaemia (b) Albinism, In prokaryotes, gene regulation occurs at the level of, (a) transcription, (c) post-transcription, Telomerase is an enzyme which is a, (a) simple protein, (c) ribonucleoprotein, During oogenesis, each diploid cell produces:, , (c), , Haemophilia, , (b), (d), , translation, post-translation, , (b), (d), , RNA, repetitive DNA, , (d), , Phenylketonuria, , Oogenesis, Oogonium, , Primary oocyte, Meiosis, I, , Secondary oocyte, Meiosis, II, , Ovum, , Polar body, , Polar body, , Mature egg cell, Process of oogenesis, , 45., , 46., , 47., , 48., , (a) Four functional eggs, (b) Two functional eggs and two polar bodies, (c) One functional eggs and three polar bodies, (d) Four functional bodies., Mendel’s rules do not correctly predict patterns of inheritance for tightly linked genes or the inheritance of alleles that show, incomplete dominance or epistasis. Does this mean that his hypothesis are incorrect ?, (a) Yes, because they are relevant to only a small number of organisms and traits., (b) Yes, because not all data support his hypothesis., (c) No, because he was not aware of meiosis or the chromosome theory of inheritance., (d) No, it just means that his hypothesis are limited to certain conditions., Termination of polypeptide chain is brought about by, (a) UUG, UAG and UCG, (b) UAA, UAG and UGA, (c) UUG, UGC and UCA, (d) UCG, GCG and ACC, Nucleotide arrangement in DNA can be seen by, (a) X-ray crystallography, (b) electron microscope, (c) ultracentrifuge, (d) light microscope, A pedigree is shown below for a disease that is autosomal dominant. The genetic made up of the first generation is, , Generation I, Generation II, Generation III, (a) AA, Aa, , (b), , Aa, aa, , (c), , Aa, AA, , (d), , Aa, Aa
Page 7 :
Sample Paper-6, , SP-57, , SECTION-C, DIRECTION: This section consists of one case followed by 6 questions linked to this case (Q.No.49 to 54). Besides this, 6 more, questions are given. Attempt any 10 questions in this section. The first attempted 10 questions would be evaluated., Case : Refer the diagram given below of human sperm and answer the questions that followsPlasma membrane, Acrosome, Head, , Nucleus containing, chromosomal material, Neck, Middle piece, Mitochondria, (energy source for swimming), Tail, , 49., 50., , 51., , 52., , 53., 54., 55., , 56., , The body of sperm is covered by _______, (a) head, (b) cell membrane, (c) cell wall, (d) cytoplasm, Egg is covered by a tough sheet of tissue that protects it from desiccation and infection by pathogens. But the same tissue, also prevents sperm nuclei from encountering the egg nuclei. However, a part of sperm is known to release enzymes that, digest this tough sheet. What part of sperm is it?, (a) Tail end, (b) Mitochondria, (c) Acrosome, (d) Sperm nuclei, Rakesh and Reshma have difficulty conceiving a baby. They consulted a sex therapist. Sperm count of Rakesh was normal, but the doctor observed that the motility of his sperm was less. What part of sperm do you think has the issue?, (a) Tail, (b) Nucleus, (c) Mitochondria, (d) Acrosome, The major constituents of semen are _____ and _____, (a) Sperms and RBCs, (b) Sperms and Blood plasma, (c) Sperms and seminal plasma, (d) Sperms and WBCs, Which of the following is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male?, (a) Sperm count, (b) Sperm motility, (c) Sperm height, (d) Sperm production rate, What part of sperm holds the haploid chromatin?, (a) Acrosome, (b) Head, (c) Tail, (d) Neck, Study the pedigree chart of a certain family given below and select the correct conclusion which can be drawn for the character., , (a) The female parent is heterozygous., (b) The parents could not have had a normal daughter for this character., (c) The trait under study could not be colourblindness., (d) The male parent is homozygous dominant., Which of the following figure of contraceptives contains progesterone alone or in combination with estrogen and used as, injection or implants by females?, , (a), , (b), , (c), , (d)
Page 8 :
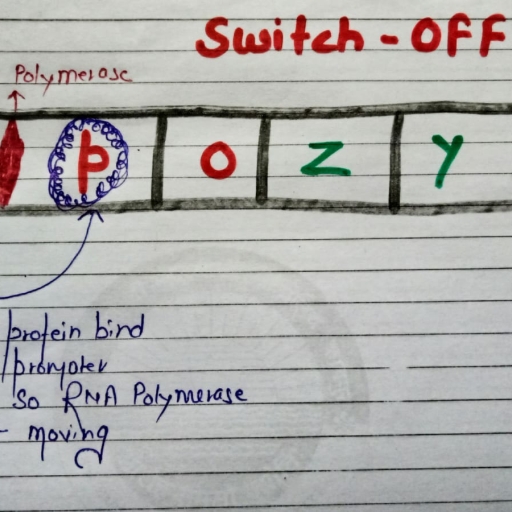
EBD_7332, Biology, , SP-58, , 57., , Refer the figure of mammary gland with few structure marked as A, B, C and D. Which structure contains clusters of milk, secreting cells?, A, , D, , 58., , B, C, , (a) A, (b) B, (c), Female gametophyte of angiosperms is represented by, , C, , Mitosis, , (d), , D, , Mitosis, , Flower-meiosis, occurs here, , Seed, Fertilised, nucleus, of egg cell, = embryo, Fertilisation, , Pollination, , Nucleus of egg, cell in magnified, part of flower, , 59., , (a) ovule, (b) megaspore mother cell (c) embryo sac, (d) nucellus, In Meselson and stahl's experiments, heavy DNA was distinguished from normal DNA by centrifugation in, Generation I, 15, , N-DNA, , 15, , Generation II, , 14, , N-DNA, , 14, , N-DNA, , N-DNA, , 15, , N-DNA, , 40 min, , 20 min, , 14, , N-DNA, , Gravitational force, , 14, , N-DNA, , 14 14, N15N, N N 14N15N, Light, Hybrid, Hybrid, Meselson and Stahl’s experiment, 14, , 15 15, , N N, Heavy, , 60., , (a) CsOH gradient, (b) 14NH4CL, In the figure, strand A and B represent respectively, , (c), , Transcription, start single, Promoter, , 3', 5', (a) A-Coding strand, B-Template strand, (c) Both (a) & (b), , A, B, , (b), (d), , 15NH Cl, 4, , (d), , CsCl gradient, , Terminator, , 5', 3', A-Template strand, B-Coding strand, None of them
Page 9 :
6, , Sample Paper, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, , 1., 4., 5., 8., , 9., , 10., 11., , 12., , (a), (a), (a), (d), (c), (a), , 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, , (b), (c), (a), (b), (c), (b), , 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, , (c), (d), (b), (a), (c), (b), , 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, , (a), (d), (d), (d), (c), (b), , ANSWER KEYS, (c) 31 (c), 25, (b) 32 (b), 26, (a) 33 (a), 27, (c) 34 (b), 28, (d) 35 (b), 29, (d) 36 (b), 30, , (a) 2. (a) 3. (a), (d) Chiropterophily is pollination by bats., (c) 6. (a) 7. (b), (c) Considering the female reproductive endocrinology,, ovulation is the process of the monthly release of the viable, oocyte from the ovary between the time of menarche and, menopause. During this time, there is a surge in the, production of LH and FSH, termed as gonadotropins,, thereby initiating estradiol and progesterone secretion from, the ovary. Both these hormones are very important for the, menstrual cycle., (a) The corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine structure, involved in ovulation and early pregnancy. The main, secretory product of corpus luteum is progesterone, which, is required for the establishment and maintenance of, pregnancy., (b), (c) Pollen grains are mostly uniporate (with single germ, pore) in monocots and trip orate (with three germ pores) in, dicots., (b) The example of codominance is ABO blood grouping in humans. ABO blood groups are controlled by gene I., Gene I consists three alleles IA, IB and IA and IB are the, dominant alleles. When IA and IB are present together,, both express equally and produce the surface antigens A, and B, whereas i is the recessive allele and does not produce any antigen., The genetic effect of a single gene on multiple phenotypic traits is pleiotropy. Incomplete dominance a genetic, term in which does not completely dominate another allele., The separation of allele during the process of gametogenesis is known as Segregation. This is the basis of reappearance of recessive character in F2-generation., , 13., 14., , 15., , 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, , (c), (c), (d), (b), (a), (b), , (b), (c), (a), (c), (c), (b), , 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, , 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, , (a), (d), (a), (c), (d), (b), , (c), (d) Most sex-linked (X-linked) conditions are recessive., This means that person having two X-chromosomes (females), both copies of a gene (i,e., one on each X-chromosome), must have a change or mutation whereas in a, person with one X- chromosomes (males), only one copy, or a gene must have a mutation., A female with a mutation in one copy of a gene on the Xchromosme is said to be a ‘carrier’ for an X- linked condition., For X-linked recessive disorders, and unaffected carrier, mother who has a mutation in a gene on the X-chromosome can transfer either the X- chromosome with this mutation or a normal X-chromosome to her children., The pattern of inheritance of a condition directly or indirectly due to a dominant faulty gene located on autosome, is known as autosomal dominant inheritance., The condition caused directly or indirectly due to a recessive faulty gene copy on autosome is known as autosomal recessive inheritance., Rare trait that is caused by single abnormal gene on the, X-chromosome is called sex-linked dominant., (b) The F1 plants of genotype Tt are self-pollinated., (both tall (T) but with dwarf (t) alleles)., T, , 16., , (b), (a), (d), (c), (c), (a), , 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, , t, , ×, , T, , t, , Selfing, , F -generation, Tt tt 2, Tt, TT, Phenotypic ratio = Tall : Dwarf, 3: 1, Genotypic ratio = Pure tall : Hybrid : Pure dwarf, 1 :, 2 :, 3, (a) Mendel did not use pod length for his experiment.
Page 10 :
EBD_7332, Biology, , S- 14, , 17., , 18., 19., 20., 21., , 22., , 23., 24., , 25., 26., , 27., 28., 29., 33., 34., 36., , (c) Down’s syndrome is the chromosomal disorders due, to the presence of an additional copy of the chromosome, number 21 (trisomy of 21). The affected individual is short, statured with small round head, furrowed tongue and, partially open mouth and mental development is retarted., (b), (a) Operator gene allows the functioning of the operon., (d), (d) It was given by Geneticists George W. Beadle and E., L. Tatum which states that each gene in an organism, controls the production of a specific enzyme. It is these, enzymes that catalyze the reactions that lead to the, phenotype of the organism., (d) In the DNA molecule, there are two strands which, run anti-parallel one is 5’ - 3’ direction and other in 3’ -5’, direction, the two chains are held together by hydrogen, bonds between their bases. Adenine (A), a purine of one, chain is exactly opposite thymine (T), a pyramidine of the, other chain. Similarly, cytosine (C), a pyrimidine lies, opposite guanine (G), a purine. This allows a sort of lock, & key arrangement between large sized purine & small, sized pyrimidine. It is strengthened by the appearance of, hydrogen bonds between the two., (c), (b) In a DNA strand the nucleotides are linked together, by 3’–5’ phosphodiester linkage (bonds) to form a, dinucleotide. To form a polynucleotide chain, more, nucleotides can be joined., (c) Assertion is true but Reason is false., Success rate of test tube baby is less than 20%., (b) Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a, correct explanation of Assertion., Gene is the unit of inheritance which passes from one, generation to the other through the gamete., (a) Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a, correct explanation of Assertion., 9 purple and 7 white flowers are obtained in sweet pea., (c) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect., Mendel died due to kidney disorder in the year 1884 in the, age of 61., (d) 30. (d) 31. (c) 32. (b), (a) Copper ‘T’ is an intrauterine device which prevents, the fertilized egg becoming implanted in the wall of the, womb., (b) 35. (b), (b) Possible, × Possible, genotype, genotype, of man with blood, of woman with, group A, blood group B, IA IA, IA IO, × IB IB, IB IO, , 37., , 38., 39., 40., , 41., 43., , 44., 50., 55., , 56., , 57., , 58., , If the genotype is, IA IO, × IB IO, The possibility of resultant blood group may be A, B, AB, and O., (b) IAIO, IBIO - Dominant-recessive, relationship, IAIB - Codominance, IA, IB & I O - Three different allelic forms of a gene, (multiple allelism), (a) Heterosis or hybrid vigor occurs when two unrelated, individuals or lines are crossed, the performance of F1, hybrid, which is often superior to both is parents., (d), (c) In case of humans, the sex determining mechanism is, XY type. Out of 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 pairs are, exactly same in both males and females called autosomes., A pair of X-chromosomes present in the female, whereas, the presence of an X and Y chromosome are determinant, of male characteristic. In case the ovum fertilises with, a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops, into a female (XX) and the fertilisation of ovum with, Y-chromosome carrying sperm results into a male offspring., (c) 42. (a), (c) Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein which synthesize, the rich strand of telomeres in DNA. Telomerase is an, enzyme that adds specific DNA sequence repeats, (“TTAGGG” in all vertebrates) to the 3’ end of DNA, strands in the telomere regions, which are found at the, ends of eukaryotic chromosomes., (c) 45. (d) 46. (b) 47. (a) 48. (b) 49. (b), (c) 51. (a) 52. (c) 53. (c) 54. (b), (a) On the basis of the given pedigree chart of a certain, family, it can be concluded that the female parent (shown, by blank circle) is heterozygous where one gene is, dominant and other gene is recessive., (d) The implant is inserted under the skin of upper arm to, prevent pregnancy. The implant releases hormones that, keep ovaries from releasing eggs and thicken cervical, mucus, which helps to block sperm from getting to the egg, in the first place., (a) The structures marked in the figure of mammary gland, are A–mammary lobe, B–mammary duct, C–ampulla, and, D–lactiferous duct. The mammary gland is a gland located, in the breasts of females that is responsible for lactation., Mammary glands only produce milk after childbirth., Mammary lobe (A) contains clusters of cells called alveoli, which secrete milk which is stored in the cavities of alveoli., (c) 59. (d) 60. (b)