Page 2 :
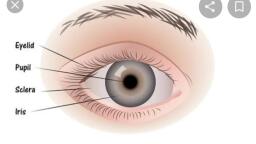
External ocular appearance
Page 3 :
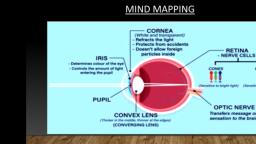
Key Eye Functions, • Transmits and refracts, light from the front to, the back of the eye, • Transparent light path, • Includes structures, that bend light, (refract), • Converts light energy, into action potentials, transmitted to brain
Page 4 :
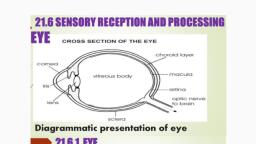
Layers and chambers of the eye, Anterior Chamber, Posterior Chamber, , Vitreous Chamber, , Fibrous Tunic, Vascular Tunic, Nervous Tunic
Page 5 :
Defining ocular segments, Anterior, segment:, Structures in, front of, vitreous:, Cornea,, iris,, ciliary body,, and lens, , Posterior, segment:, Vitreous,, retina,, choroid,, optic nerve
Page 6 :
Tear film layers and functions, • Oil layer:, • Meibomian glands, , • Prevents evaporation, , • Water layer:, • Lacrimal glands, •, •, •, •, , Lubricates, Allows blinking, Washes away debris, Forms smooth surface, , • Mucin layer:, • Goblet cells of conjunctiva, • Attaches tear film to eye, • Spreads water evenly
Page 7 :
Cornea functions, •, , Transmits light, transparent, • Collagen and matrix, • Aligned, • Spacing, • Relative dehydration is, maintained by endothelial, cells, • No blood vessels, , •, , Refracts light +40-44 dioptres, • Curvature, • Has different refractive index, from air
Page 8 :
Corneal anatomy, Epithelium:, Barrier to fluid loss and pathogen, penetration, Stroma:, Collagen, ECM, keratocytes, Endothelium:, Maintains relative dehydration, Dense innervation:, Most sensitive organ in the body, Immune privilege, Rapid tearing reflex, The cornea:, Transmits light, Refracts lights, Protects ocular interior
Page 9 :
Structure of the crystalline lens
Page 10 :
Crystalline Lens: Structure and function, • Composed of α, β, and γ crystallins, (water soluble proteins), , • Transmission of light, • Refraction of light. +17 dioptres, • Variable refraction of light accommodation, , Cornea 2/3rd and lens 1/3rd refracting power
Page 11 :
Accommodation, Far objects:, Ciliary muscle relaxed, (↑ diameter), Zonules tight, Lens flatter i.e., distance, , Near objects:, Ciliary muscle contracts, (↓ diameter), Zonules relaxed, Lens increases in convexity, ‘accommodation’ i.e. near
Page 14 :
Retinal Function, , • Photoreceptors: conversion of light into action potentials, • Cones. 6 million. High threshold to light. High acuity. Light adapted (photopic), vision. Colour vision- 3 types of cones: blue, green, red., • Rods. 120 million. Low threshold to light. Sensitive to movement. Dark adapted, (scotopic) vision. No colour. Low resolution., • Synapse with bipolar cells Retinal ganglion cells Axons form the optic nerve., 1 million fibres.
Page 16 :
RETINAL MICRO-STRUCTURE
Page 17 :
RETINAL MICRO-STRUCTURE
Page 20 :
Temporal, , Nasal
Page 21 :
Superior, Retinal, Detachment
Page 25 :
Name, these, ocular, structures
Page 26 :
The Uveal Tract, The eye’s vascular and immunological pool, Iris, Variable size of pupil (iris diaphragm) with light, level with nearness of fixation, , Ciliary Body, Aqueous, accommodation, zonule, , Choroid, Nutrition of retina and sclera, , The most vascular tissue in the body
Page 27 :
Eyelids and conjunctiva, 1. Skin, 2. Muscles, Meibomian glands, , 3. Tarsal plate - mechanical, stability & Meibomian glands, – oil layer of tear, 4. Conjunctiva, Attach eyeball to orbit & lids, & permits rotation, , Functions: Distribute tears, clear debris, cover eyes, during sleep & prevent evaporation, protect from, foreign bodies via the blink reflex
Page 28 :
Eyelids, and, conjunctiva
Page 33 :
Innervation of extraocular muscles, Lateral Rectus Muscle , “Abducts” Innvervated by, Abducens nerve, = Cranial nerve 6, Superior Oblique Muscle , Passes through the, “trochlea” , Innervated by Trochlear, nerve = Cranial nerve 4, The other 4 muscles , Produce “ocular movements”, Innervated by Oculomotor, nerve = Cranial nerve 3
Page 37 :
Visual Pathway, , Optic nerve, Optic chiasm, Optic tract, Lateral geniculate, nucleus, Optic radiation, , Primary visual cortex
Page 38 :
Injuries to Visual Pathway, , ON, OT, LGN, OR, 1° Visual cortex
Page 40 :
Cataract of the crystalline lens, Age of onset, Congenital, Age-related, , Location, , Nuclear sclerotic, Cortical, Posterior, Subcapsular, , Cause, , Age-related, Traumatic, Diabetic
Page 44 :
Long thought extinct, living takahē were, rediscovered in an, expedition led, by Invercargill based, ophthalmologist & ENT, physician Dr Geoffrey, Orbell near Lake Te, Anau in the Murchison, Mountains, in 1948.
Page 45 :
The End, Material contained in this lecture presentation, is copyright of The Department of, Ophthalmology, New Zealand National Eye, Centre, University of Auckland, and should not, be reproduced without first obtaining written, permission