Page 1 :
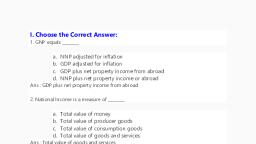
I., , Choose the best answer., , 1. Which of the following has the smallest mass?, a. 6.023 × 1023 atoms of He, b. 1 atom of He, c. 2 g of He, d. 1 mole atoms of He, , 2. Which of the following is a tri-atomic molecule?, a. Glucose b. Helium c. Carbon dioxide d. Hydrogen, , 3. The volume occupied by 4.4 g of CO2 at S.T.P, a. 22.4 litre b. 2.24 litre c. 0.24 litre d. 0.1 litre, , 4. Mass of 1 mole of Nitrogen atom is, a. 28 amu b. 14 amu c. 28 g d. 14 g, , 5. Which of the following represents 1 amu?, a. Mass of a C – 12 atom, b. Mass of a hydrogen atom, c. 1/12th of the mass of a C – 12 atom, d. Mass of O – 16 atom, 6. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
Page 2 :
a. 12 gram of C – 12 contains Avogadro’s number of atoms., b. One mole of oxygen gas contains Avogadro’s number of molecules., c. One mole of hydrogen gas contains Avogadro’s number of atoms., d. One mole of electrons stands for 6.023 × 1023 electrons., , 7. The volume occupied by 1 mole of a diatomic, gas at S.T.P is, a. 11.2 litre b. 5.6 litre c. 22.4 litre d. 44.8 litre, , 8. In the nucleus of 20Ca40, there are, a. 20 protons and 40 neutrons, b. 20 protons and 20 neutrons, c. 20 protons and 40 electrons, d. 40 protons and 20 electrons, , 9. The gram molecular mass of oxygen molecule is, a. 16 g b. 18 g c. 32 g d. 17 g, 10. 1 mole of any substance contains ____ molecules., a. 6.023 × 1023 b. 6.023 × 10-23 c. 3.0115 × 1023 d. 12.046 × 1023, , II. Fill in the blanks, 1. Atoms of different elements having _______ mass number, but ________ atomic
Page 3 :
numbers are called isobars. (same , different), 2. Atoms of different elements having same number of ___________ are called isotones., (neutrons), 3. Atoms of one element can be transmuted into atoms of other element by ________ (artificial, transmutation), 4. The sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons of an atom is called its __________ (mass, number), 5. Relative atomic mass is otherwise known as __________ (standard atomic weight), 6. The average atomic mass of hydrogen is ___________ amu. (1.008 amu), 7. If a molecule is made of similar kind of atoms, then it is called ____________ atomic, molecule. (homo), 8. The number of atoms present in a molecule is called its ____________ (atomicity), 9. One mole of any gas occupies ________ ml at S.T.P (22400), 10 Atomicity of phosphorous is ___________ (4), III. Match the following, 1. 8 g of O2, , -, , 4 moles, , (4), , 2. 4 g of H2, , -, , 0.25 moles, , (1), , 3. 52 g of He, , -, , 2 moles, , (2), , 4. 112 g of N2, , -, , 0.5 moles, , (5), , 5. 35.5 g of Cl2, , -, , 13 moles, , (3), , IV. True or False: (If false give the correct statement), 1. Two elements sometimes can form more than one compound. True, 2. Noble gases are Diatomic (monoatomic). False, 3. The gram atomic mass of an element has no unit. False.
Page 4 :
(The gram atomic mass of an element is expressed in the unit grams), 4. 1 mole of Gold and Silver contain same number of atoms. True, 5. Molar mass of CO2 is 42g (44g). False, V. Assertion and Reason:, Answer the following questions using the, data given below:, i) A and R are correct, R explains the A., ii) A is correct, R is wrong., iii) A is wrong, R is correct., iv) A and R are correct, R doesn’t explains A., 1. Assertion: The Relative Atomic mass of aluminium is 27, Reason: An atom of aluminium is 27 times heavier than 1/12th of the mass of the C – 12 atom., i) A and R are correct, R explains the A., , 2. Assertion: The Relative Molecular Mass of Chlorine is 35.5 a.m.u., Reason: The natural abundance of Chlorine isotopes are not equal., i) A and R are correct, R explains the A., , VI. Short answer questions, 1. Define: Relative atomic mass., Relative atomic mass of an element is the ratio between the average mass of its isotopes, to 1/12th part of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. It is denoted as Ar. It is otherwise called, “Standard Atomic Weight”., Relative Atomic Mass
Page 5 :
(Ar) = Average mass of the isotopes of the element, 1 of the mass of one Carbon-12 atom, 12th, 2. Write the different types of isotopes of oxygen and its percentage abundance., The different types of isotopes of oxygen and its percentage abundance are) %abundance, 16, 15.9949, 99.757, 8O, 17, 16.9991, 0.038, 8O, 18, 17.9992, 0.205, 8O, 3. Define: Atomicity, The number of atoms present in the molecule is called its ‘atomicity’., Atomicity = molecular mass, Atomic mass, 4. Give any two examples for hetero-di-atomic molecules., The examples of hetero – di – atomic molecules are, Hydrogen chloride (HCl), Carbon monoxide (CO), 5. What is Molar volume of a gas?, One mole of any gas occupies 22.4 litre or 22400 ml at S.T.P. This volume is called as molar, volume., 6. Find the percentage of nitrogen in ammonia., Ammonia - NH3, 1 N – 1 x 14 = 14, 3H–3x1 =, , 3, 17, , % of nitrogen in ammonia = 14 x 100 = 82.35 %, 17
Page 6 :
VII. Long answer questions, 4. Give the salient features of “Modern atomic theory”., ‘The main postulates of modern atomic theory’ are as follows:, ·, , An atom is no longer indivisible (after the discovery of the electron,proton, and neutron)., , ·, , Atoms of the same element may have different atomic mass. (discovery of isotopes 17Cl35,, Cl37)., , 17, , ·, , Atoms of different elements may have same atomic masses (discovery of Isobars, 40, 40, 18Ar ,20Ca )., , ·, , Atoms of one element can be transmuted into atoms of other elements. In other words, atom, is no longer indestructible (discovery of artificial transmutation)., , ·, , Atoms may not always combine in a simple whole number ratio (E.g. Glucose C6H12O6,, C:H:O = 6:12:6 or 1:2:1 and Sucrose C12H22O11 C:H:O = 12:22:11)., , ·, , Atom is the smallest particle that takes part in a chemical reaction., , ·, , The mass of an atom can be converted into energy (E = mc2)., , 5. Derive the relationship between Relative molecular mass and Vapour density., , i. Relative molecular mass: (Hydrogen scale), The Relative Molecular Mass of a gas or vapour is the ratio between the mass of one molecule of, the gas or vapour to mass of one atom of Hydrogen., , Relative molecular mass (hydrogen scale) =, Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at STP, Mass of 1 atom of hydrogen
Page 7 :
ii. Vapour Density:, Vapour density is the ratio of the mass of a certain volume of a gas or vapour, to the mass of an, equal volume of hydrogen, measured under the same conditions of temperature and pressure., , Vapour Density (V.D.) = Mass of a given volume of gas or vapour at S.T.P., Mass of the same volume of hydrogen, , According to Avogadro's law, equal volumes of all gases contain equal number of molecules., Thus, let the number of molecules in one volume = n,, then V.D. at S.T.P = Mass of ‘n’ molecules of a gas or vapour at S.T.P., Mass of ‘n’ molecules of hydrogen, Cancelling 'n' which is common,, V.D. = Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at S.T.P., Mass of 1 molecule of hydrogen, However, since hydrogen is diatomic, V.D.= Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at S.T.P., Mass of 2 atoms of hydrogen, When you compare the formula of vapour density with relative molecular mass, they can be, represented as, V.D.= Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at S.T.P., 2 × Mass of 1 atom of hydrogen, , (Eqn 1), , Relative molecular mass (hydrogen scale) =, Mass of 1 molecule of a gas or vapour at STP, Mass of 1 atom of hydrogen, substitute the above equation to an Eqn 1, we get, , (Eqn 2)
Page 8 :
V.D. = Relative molecular mass, 2, Now on cross multiplication, we get, 2 × vapour density = Relative molecular mass of a gas, (Or), Relative molecular mass = 2 × Vapour density