Page 1 :
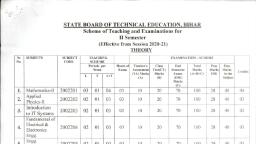
Scheme, , , , , , Program Name _: Electrical Engineering Program Group, Program Code : EE/EP/EU/IE/S, , Semester : Second, , Course Title : Applied Science (Physics & Chemistry), , , , Course Code 322211, , 1. RATIONALE, , Diploma engineers (also called technologists) have to deal with various materials and, machines. The study of concepts and principles of science like capacitance and current, electricity, electromagnetic induction and alternating current, photo-sensors and LASER., water treatment and analysis, electrochemistry and batteries, metals, alloys. insulators and, others will help them in understanding the engineering courses where emphasis is laid on the, applications, This course is developed in the way by which fundamental information will help, the diploma engineers to apply the concepts and principles of advanced science in various, engineering applications to solve broad based problems, , 2. COMPETENCY, The aim of this course is to help the student to attain the following industry identified, competency through various teaching learning experiences:, * Apply principles of advanced physics and chemistry to solve broad based, engineering problems,, , , , 3. COURSE OUTCOMES (COs), ‘The theory. practical experiences and relevant soft skills associated with this course are to be, taught and implemented, so that the student demonstrates the following industry oriented COs, associated with the above mentioned competency, a. Use relevant capacitors in electrical circuits., Use equipment/instruments based on radioactive and ultrasonic principles, Use equipment/instruments based on photoelectric effect, X-Ray and LASER, Select relevant water treatment process for various applications, Use relevant electrolyte in batteries for different applications, Use relevant metals, alloys and insulating materials in various applications., , means, , 4. TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Teacher | Examination Scheme, Credit | Theory Practical, u|t (OO ee ESE PA Total ESE PA Total, Hirx_[Mlax [Ma | stax [Stim] Max] Min] Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min, TFs] g | 2 Irons! op LL von | ap L2S@L 1 | 2s |e | 0 | 20, 2 Min | 15* | 00 23@| 10 | 2 | 10 | so | 20, , , , , , , , , , , , (*): Under the theory PA, Out of 30 marks, 10 marks are for micro-project assessment (5, marks each for Physics and Chemistry) to facilitate integration of COs and the remaining 20, marks is the average of 2 tests to be taken during the semester for the assessment of the, cognitive domain UOs required for the attainment of the COs., , , , MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 1 of 10 2, , , , , Applied Science € Scheme, , Legends: L-Lecture; T — Tutorial/Teacher Guided Theory Practice; P - Practical; C — Credit,, ESE - End Semester Examination; PA - Progressive Assessment, , Note: Practical of Chemistry and Physics will be conducted in alternate weeks for each, batch., , 5. COURSE MAP (with sample COs, PrOs, UOs, ADOs and topics), , This course map illustrates an overview of the flow and linkages of the topics at various levels, of outcomes (details in subsequent sections) to be attained by the student by the end of the, course, in all domains of leaning in terms of the industry/employer identified competency, depicted at the centre of this map., , Compstener, Apply prineipes of, , , , , , , , Figure 1 - Course Map, , 6. SUGGESTED PRACTICALS / EXERCISES, ‘The practicals in this section are PrOs (i.e. sub-components of the COs) to be developed and, assessed in the student for the attainment of the competency, , MSBTE — Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 2 of 10 R
Page 2 :
Applied Seicnee AU Scheme, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , : Tonite | APP FOX., | x Practical Outcomes (PrOs) mae Hes., Leen "Required, i Physics 1 i) Use condensers to increase and decrease the equivalent 1 02, capacity of the circuit, ii) Determine the characteristics of condenser using RC circuit, 2 | i) Use meter bridge to determine the equivalent resistance of the | 1 02, conductors in series and parallel |, ii) Use meter bridge to estimate specitic resistance of a given, wire., 3 | i) Use potentiometer to compare emf of two cells. I 02, ii) Use potentiometer to find internal resistance of a cell, 4 | Use resonance tube to determine velocity of sound. I 02, 5 Use ultrasonic distance — meter to measure distance Mm 02, 6 | i) Use photoelectric cell to see the dependence of photoelect-ic ul 02, current on intensity of light., ii) Use photoclectric cell to see the dependence of photoelectric |, |__| current on piate potential _ __|, 7 | Use LDR to see the dependence of resistance of LDR on intensity III 02, of light _ _ - 8 | Use He Ne LASER to find the divergence of LASER beam with, Ldistance a aa |, Chemistry, 9 | Determine alkalinity of water sample IV |, 10 | Determine total hardness (temporary hardness and permanent Vv 02*, hardness) of water sample by EDTA method., 11 | Determine specific conductance and equivalence conductance of Vv 02, ven salt sample solution., 12 | Determine equivalence point of acetic acid and ammonium Vv 02*, hydroxide using conductivity meter., 13. | Determine chloride contents in a given water sample by Mohr's Vv 02, method |, 14 _| Prepare the Thiokol rubber VI 02, 15 | Separate two miscible liquids like acetone and water using vi 02, distillation technique., 16 | Determine acid value of given resin VI 02*, [ Total 32,, ‘Note, , i A suggestive list of PrOs is given in the above table. More such PrOs can be added to, attain the COs and competency. A judicial mix of minimum 12 or more practisal need to be, performed. out of which, the practicals marked as ‘*’ are compulsory. so that the student, reaches the Precision Level’ of Dave's ‘Psychomotor Domain Taxonomy’ as generally, required by the industry., , The ‘Process’ and ‘Product’ related skills associated with each PrO is to be assessed, according to a suggested sample given below., , | S.No. Performance Indicators, | 1 Preparation of experimental set up, , MSBTE - Fit, , , , | Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 3 of 10, y, , , , , , , , , , , , , , Applied Sense 1 Scheme, S.No. Performance Indicators Weightage in %, , 2 ing and operation _ _ ——| 20, , 3 Safety measures - 10, , 4 Observations and Recording 10, , 5 Interpretation of result and Conclusion 20, , 6 _ Answer to sample questions _ 10, , L Submission of report in time 10, , L Total 100, , , , The above PrOs also comprise of the following social skills/attitudes which are Aflective, Domain Outcomes (ADOs) that are best developed through the laboratory/field based, experiences:, , a. Follow safe practices, , b. Practice good housekeeping, , c. Practice energy conservation., , d. Demonstrate working as a leader/a team member., , Follow ethical practices, , The ADOs are not specific to any one PrO, but are embedded in many PrOs. Hence, the, acquisition of the ADOs takes place gradually in the student when s/he undertakes a series of, practical experiences over a period of time. Moreover, the level of achievement of the ADOs, according to Krathwohl’s “Affective Domain Taxonomy” should gradually increase as planned, below, , © ‘Valuing Level’ in 1" year, , © ‘Organising Level’ in 2"? year, , * ‘Characterising Level’ in 3” year., , t MAJOR EQUIPMENT/ INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED, The major equipment with broad specification mentioned here will usher in uniformity in, conduct of experiments, as well as aid to procure equipment by authorities concerned., , , , , , | Ne Equipment Name with Broad Specifications Hap SiN,, 1 Digital multimeter : 3% digit display, 9999 counts digital multimeter 1.2.3,67, , measures: Voc, Vie ( 1000V max), Age, Anc(10 amp max), Hz, Resistance, (0- 100 MQ), capacitance and Temperature, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , | 2 | Micrometer screw gauge : Range : 0-25mm, Resolution: 0. 01mm 2, Accuracy: +0.02mm or better, 3 _Resistance Box: 4 decade ranges from | ohm to IKQ, accuracy:0.1%-1% | 1,2.3.6.7, (4 Battery - - :, 5__| Meter brid: Jockey a |, 6 Potentiometer 3, _7 Ultrasonic distance meter = _ >|, 8 Resonance tube. tuning fork 4, 9 | Daniel cell and Leelanche cell 2, 10_| LASER kit 8, , , , 11 | Conductivity meter: conductivity range — 0.01 uS/em to 200 mS/em, Cell 11,12, constant ~ digital 0.1 to 2.00; Temp. range - 0 to 100°C, 12 Electronic balance, with the scale range of 0.00 1am to 500gm pan size Ail, , , , , , MSBTE — Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 4 of 10 2
Page 3 :
opti sees 1 Stone, , ee Equipment Name with Broad Specifications Eap.S. Ne, 100 mm: response time 3-5 see.. power requirement 90-250V, 10 watt, , T3_| Simple distillation unit is, , , , , , , , 8. UNDERPINNING THEORY COMPONENTS, 9. The following topics/subtopics are to be taught and assessed in order to develop UOs, for achieving the COs to attain the identified competency,, , , , , , , , Unit Unit Outcomes (UOs) Topics and Sub-topics, (in cognitive domain), Cc _ Physics., Unit 1 ta. Explain working of the given 11 Capacitors and capacitance., | Electricity capacitor 1.2 Parallel plate capacitor, effect of, and Ib. Calculate the equivalent capacity dielectric on capacitance, | Capacitance and energy stored in the given 1.3. Combination of capacitors., , , , Radioaetivit, y and, Ultrasonic, Waves, , combination of capacitors, , lc. Calculate the voltage in various, components of the given electric, cireuit,, , 1d. Calculate the value of the given, resistance using the principle of, Wheatstone’s bridge,, , le. Calculate the emf of the given, cell using potentiometer., , ‘2a. Describe the phenomenon of, , radioactivity for the given, system, 2b. Calculate half-life period of, given radioactive substance, Calculate the value of the period,, frequency and velocity of the, given type of wave., Describe the properties of given, ultrasonic waves., Describe the properties of the, given Piezo-electric material., Explain the production of, ultrasonic waves using the given, equipment, 2g. Describe the Doppler effect for, the given application, , 2c., , 8, , v, 2, , °, , 2, , R, , energy stored in a capacitor., , 1.4 Cells, emf of cell, internal, resistance of cell. Kirchhoff's, laws, Wheatstone’s bridge, , 1.5. Potential gradient, potentiometer, , Radioactivity, a. B and y particles:, , rays and their properties,, , 22 Radioactive decay law, half-life, period, , 2.3 Sound waves, amplitude,, frequency, time - period wavelength and velocity of wave,, telation between velocity,, frequency and time - period of, wave., , 2.4 Ultrasonic waves, properties of, ultrasonic waves., , 2.5 Piezo-electric effect Piezo, materials; Natural: Quartz,, Synthetic: Gallium orthophosphate, , 2.6 Generation of ultrasonic waves, using Piezo electric effect, , 27 Applications of ultrasonic waves, , 2.8 Doppler Effect and its, , applications, , , , Applied Seienee "Scheme, Unit | Unit Outcomes (UOs) Topics and Sub-topies, (in cognitive domain), X-Rays and photoelectric cell and LDR. | wavelength, stopping potential,, LASERs Work function, characteristics of, , wl, , , , Explain the production of, from given material with its, properties and applications., , photoelectric effect,, , Einstein's photoelectric equation, Photoelectric cell and LDR:, principle, working and, applications., Production of X-rays by Modern, Coolidge tube, properties and, applications of X-rays., , , , , , Differentiate between LASER B4, and given colour of light,, , Describe the lasing action of a, , typical LASER system and its 3.5, applications. |, , Laser, properties of laser,, absorption, spontaneous and, stimulated emission., , Population inversion. active, medium. optical pumping, three, energy level system, He-Ne Laser,, applications of Laser., , , , Chemistry, , , , , , Unit-1V 4a., Water, , Describe the hardness in given 4.1, water source, , Hardness: Types of hardness,, soap solution methad, EDTA, , , , , , , , , , , , MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017, , 3a, Explain concept of photoelectric, effect for the given materials, 3b. Explain the working of the given, , Page 5 of 10 2, , 311 Planck's hypothesis, properties of, , photons, photoelectric effect:, threshold frequency. threshold, , , , , , , , , , , , frontiibit |b, Celene ne hardness Gr oat method, and analysis | for the given data 42. Effect of hard water in boilers, 4c, Describe the effects of hard water and prevention: Boiler corrosion,, in the given boilers. caustic embrittlement, priming, 4d. Explain the given type of water and foaming, scales and sludges, | softening process 43 Water softening: Lime soda, |4e. Describe the purification of process (hot lime soda and cold, municipal water for the given lime soda process), zeolite, process process, ion exchange process, 48, Describe the reverse osmosis (cation exchange and anion, process for the given type of exchange), water 4.4. Municipal water treatment:, 4g, Describe the given process of Sedimentation, coagulation,, desalination of water. filtration and sterilization., 45. Waste water: Characteristics,, BOD and COD, Sewage, treatment, recycling of waste, water, 4.6 De-salination process by reverse, osmosis., Unit-V 5a, Differentiate the electrical 3.1 Electrical conductance in metals, Electroche | _conduotance in given metals and and electrolytes, specific, mistry and | electrolytes conductance, equivalent, Batteries 5b. Identify factors affecting conductance. cell constant,, conductivity of the given |52 Conductance: Nature of solute,, nature of solvent, temperature,, , [Se., , solution, Describe construction of given _|, , concentration or dilution, , , , , , MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017, , Page 6 of 10
Page 4 :
Applid Seienee IF Scheme, , , , , , , , , , Unit Unit Outcomes (UOs) ] Topics and Sub-topics, (in cognitive domain), | electrodes. 5.3 Electrodes: Hydrogen electrode,, Sd, Describe the process for calomel electrode and glass, calculation of the strength of | electrode, given acid and base. 5.4 Conductometric Titration:, 5e. Calculate specific and equivalent |5.5 Batteries- Dry cell, alkaline, conductance of given electrolyte battery, lead Acid storage cell and, Sf Describe construction and Ni-Cd battery, H2-O> fuel cell,, working of given type of battery. | Lithium ion battery |, Unit-V1 Gu. Describe the properties of the (6.1 Properties of metals like copper. |, Metals, given metal Aluminium, tungsten, platinum, Alloys and 6b. Select refevant thermocouple nickel, | Insulators alloy for given application 6.2. Thermocouple alloy: Composition, 6c, Describe the properties and uses and characteristics of nickel alloy,, of the given insulators platinum/thodium, tungsten/, 6d. Select reevant insulator for rhenium, chromel-gold/iron., given system 63. Electrical insulators:, 6e, Describe given techniques of unit Classification. Soli¢ - ceramics,, operation mica, asbestos, urea formaldehyde, , resin and glass. Liquid-silicon, fluid, Gaseous-inert gases,, hydrogen and nitrogen gas., 6.4 Types of rubber : Natural and,, synthetic, processing of natural, | rubber. Synthetic rubber :, Properties and applications of, Buna-N, Thiokol, Neoprene, 6.5 Process industry unit operations:, Evaporation, condensation,, Distillation, Energy balance and, mass balance for above processes., 6.6 Nanomaterials: Applications of, Fullerence, Graphene, Note: To attain the COs and competency, above listed UOs need to be undertaken to achieve, the ‘Application Level’ and above of Bloom's ‘Cognitive Domain Taxonomy, , 10. SUGGESTED SPECIFICATION TABLE FOR QUESTION PAPER DESIGN, , , , Unit Unit Title Teachin _ Distribution of Theory Marks, No. g Hours R ul A Total, | Level | Level | Level Marks, Physics, Capacitance and current electricity, H_| Radioactivity and ultrasonic waves., Ill_| Photo-electricity, X-rays and LASER, | Chemistry, IV_| Water treatment and analysis, , , , , , , , , , , , , , 8 02 03 D4, 12 03 | 04 07, 03 04 os, , , , , , , , 8, , 12 02 04 | 06, , , , , , MSBTE ~ Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 7 of 10 2, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Applied Sciense 4° Scheme, Unit Unit Title [Teachin |_Distribution of Theory Marks, No. igHours |) R U A | Total, | Level | Level | Level_| Marks, \_| Electrochemistry and Batteries. 12 03 | 05 | 06 14, VI_| Metals, Alloys, Insulators 08 o2 | 02 | 05 09, Total oa [ is | 2 | 33 | 70, Legends: R=Remember, U= Understand, A=Apply and above (Bloom s Revised taxonomy), , , , Note: This specification table provides general guidelines to assist student for their learning, and to teachers to teach and assess students with respect to attainment of UOs. The actual, distribution of marks at different taxonomy levels (of R. U and A) in the question paper may, vary from above table., 11. SUGGESTED STUDENT ACTIVITIES, Other than the classroom and laboratory learning, following are the suggested student-related, co-curricular activities which can be undertaken to accelerate the attainment of the various, outcomes in this course:, , a. Seminar on any relevant topic., , ©. Library survey regarding Engineering Material used in different industries, , c. Prepare power point presentation or animation for showing applications of lz, , , , , , 12, SUGGESTED SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES (if any), ‘These are sample strategies which the teacher can use to accelerate the attainment of the, various learning outcomes in this course:, a, Massive open online courses (MOOCs) may be used to teach various topics/sub, topics, b. ‘L’ in item No. 4 does not mean only the traditional Jecture method, but di‘Terent, types of teaching methods and media that are to be employed to develop the outcomes, c. About 15-20% of the topics/sub-topics which is relatively simpler or descriptive in, nature is to be given to the students for self-directed learning and assess the, development of the COs through classroom presentations (see implementation, guideline for details), d. With respect to item No.10, teachers need to ensure to create opportunities and, provisions for co-curricular activities, €. Guide student(s) in undertaking micro-projects, , 13. | SUGGESTED MICRO-PROJECTS, , Only one micro-project is planned to be undertaken by a student assigned to him/her in the, beginning of the semester. S/he ought to submit it by the end of the semester to develop the, industry oriented COs, Each micro-project should encompass two or more COs which are in, fact, an integration of PrOs, UOs and ADOs. The micro-project could be industry application, based, internet-based, workshop-based, laboratory-based or field-based. Each student will, have to maintain dated work diary consisting of individual contribution in the project work, and give a seminar presentation of it before submission, The total duration of the microproject should not be less than 16 (sixteen) student engagement hours during the course, , , , , , In the first four semesters, the micro-project could be group-based. However, in higher, semesters, it should be individually undertaken to build up the skill and confidence in every, student to become problem solver so that s/he contributes to the projects of the industry, A, suggestive list is given here, Similar micro-projects could be added by the concerned Luculty, , a. Capacitors: Prepare the models of various types of ¢:, , , , , , , , MSBTE — Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 8 of 10 12
Page 5 :
Appliéd Science F Seheme Applica Seicnee it Sctieme, , b Current electricity: Make one circuit with bulbs/ LED/ connected in parallel or, series., , © Photosensors: Prepare working model of simple photosensor using LED., , d. LASER: Prepare the presentation on the industrial application of LASER, , ¢ Water analysis: Collect water samples from different water sources and determined, the acidity. Conductivity, dissolved solids. suspended particles in the sample., , f Water treatment: Collect 3 to 5 water samples from borewell and determined the, , . http://nptel.ac.in/course.php?disciplineld=104, hitp://hperphysics.phy-astr.gsu edu/hbase/hph. htm!, www physicsclassroom.com, www physics.org, www. fearofphysics.com, www sciencejoywagon.com/physicszone, www chemistryteaching.com, , , , , , se meaoe, , , , , , dosage of bleaching powder required for its sterilization i, wwwvisionlearning.com, g. Water analysis: Determine the soap foaming capacity of bore water on addition of j. www.chem1.com, soda ash k. www onlinelibrary.wiley.com, h Energy sources: Prepare chart showing different types of energy sources with their 1 www.rse.org, advantages m.www.chemcollective.org, i. Electrolytic Cells: Collect fruit and vegetable and prepare working model of cell. n. www.wga.org, j. Electric Insulators: Collect the samples of different insulators and list their industrial o. www.em-ea.org,, , applications ., k. Thermocouple: Prepare chart showing different types of thermocouples with their, characteristics used in electronic and electrical industry, , 14. SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES, , , , , , , , , , , , , , Title of Book Author Publication, 1 | Physics Textbook Part I | Narlikar, J. V.; Joshi, National Council of Education, - Class XI A. W.; Mathur, Research and Training, New Delhi,, Anuradha; ef al 2010, ISBN : 8174505083, 2 | Physics Textbook Part | Narlikar, J. V.; Joshi. | National Council of Education, Il - Class XL A. W.; Mathur, | Research and Training, New Delhi,, | Anuradha; ef al | 2015, ISBN : 8174505660, 3 | Physics Textbook Part I | Narlikar, J.V.; Joshi, [pxational Council of Education, ~ Class X11 A.W, eral Research and Training, New Delhi,, | 2013, ISBN : 8174506314, , , , , , 4 Physics Textbook Part | Narlikar, J.V.; Joshi, | National Council of Education, , , , , , , , , , , , IL Class XII A.W. etal Research and Training, New Delhi,, 2013. ISBN : 8174506713 |, , 3 Engineering Chemistry | Agarwal, Shikha Cambridge university press ; New, Dethi,2015_ISBN :9781 107476417, , 6 | Engineering Chemistry | Dara, S.S. | S.Chand. Publication, New Delhi, |, 2013, ISBN: 8121997658, , 7 | Engineering Chemistry | Jain & Jain Dhanpat Rai and sons; New Delhi., 2015. ISBN :9352160002, , % | Engineering Chemistry | Dr Vairam, S Wiley India Pvt Ltd, New Deihi,, , | 2013, , | ISBN: 9788126543342, 9 | Chemistry for engineers | Agnihotri, Rajesh” Wiley India Pvt Ltd, New Delhi,, 2014, ISBN: 9788126550784, , , , , , , , 15. SOFTWARE/LEARNING WEBSITES, a, http://nptel.ac.in/course php? disciplineld=115, jg, MSBTE - Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 9 of 10 R OS “ay MSBTE — Final Copy Dt. 30.10.2017 Page 10 of 10 2, wine ES