Page 1 :
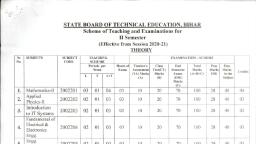
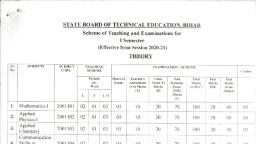
¥ Scheme, , , , Program Name: Mechanical and Civil Engineering Program Group, : AE/CE/FG/ME/PT/PG, , : Second, , Program Code, Semester, Course Title, , Course Code, , : Applied Science (Physics & Chemistry), + 22202, , 1. RATIONALE, , Diploma engineers have to deal with various materials and machines. The study of concepts, and principles of science like elasticity. viscosity, surface tension, mction, thermo couples,, photo-sensors, LASERs, X-Rays, metals, alloys, cement, lime. refractory materials water, treatment and analysis. fuel and combustion will help the student to select and use relevant, materials and methods which will be economical and eco-friendly, , 2, COMPETENCY, This aim of this course is to help the student to attain the following industry identified, competency through various teaching learning experiences:, * Solve broad-based engineering problems using principles of advanced physics, and chemistry., , 3. COURSE OUTCOMES (COs), , The theory, practical experiences and relevant soft skills associated with this course are to be, taught and implemented, so that the student demonstrates the following industry oriented, COs associated with the above mentioned competency:, , Select relevant material in industry by analyzing its physical properties, , Apply laws of motion in various applications., , Use LASERs, X-Rays and photo electric sensors., , Select the relevant metallurgical process related to industrial applications., , Use relevant water treatment process to solve industrial problems, , Use relevant fuel in relevant applications., , meacgs, , 4. TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Examination Scheme, Credit Theory | Practical, uf) e|*™ Ease pa [Tara Se [_Pa Toa —|, Hes. [Max |Min| Max [Min | Max | Min) Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min, | 15* | 00 25@ 10 23 10 50 20, 4 8 20 70%# | 28. 100 | 40 = |, Min [15* | 00 23@| 1 | 25 | 1 | 30 | 20, , , , , , , , , , , , , , (*): Under the theory PA. Out of 30 marks, 10 marks are for micro-project assessment (5, marks each for Physics and Chemistry) to facilitate integration of COs and the remaining 20, marks is the average of 2 tests to be taken during the semester for the assessment of the, cognitive domain UOs required for the attainment of the COs., , Legends: L-Lecture; T - Tutorial/Teacher Guided Theory Practice: P - Practical: C — Credit, ESE - End Semester Examination: PA - Progressive Assessment, , Note: Practical of Chemistry and Physics will be conducted in alternate weeks for eac, batch,, , , , , , , , , MSBTE,, , , , inal Copy dt. 30.10.2017 Page 1 of 10, , Applicd Seienes HY Scheie, , 5. COURSE MAP with sample COs, PrCs, UOs. ADOs and topics), , This course map illustrates an overview of the flow and linkages of the topics at various levels, of outcomes (details in subsequent sections) to be attained by the student by the end of the, course, in all domains of learning in terms of the industry/employer identified competency, depicted at the centre of this map., , a, (GaN, , wen nerd, , Prakaie, elas eb, ‘wee, , , , , , Figure 1 - Course Map, , 6. SUGGESTED PRACTICALS/ EXERCISES, The practicals in this seotion are PrOs (i.e. sub-components of the COs) to be devéloped and, assessed in the student for the attainment of the competency., , ... Practical Outcomes (PrOs), , , , Physics, Use Searle’s method to determine the Young's modulus of given, , , , u, , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017 Page 2 of 10
Page 2 :
Applica Science 1 Scheme Avplied Seance Ste, , § Unit APPFOS. ] S.No Performance Indicators Weightage in %, , Ne a Practical Outcomes (PrOs) No. Hrs. 3 Safety measures _ | 10, , o LS | Required 4 Observations and Recording 10, wire T 3 Interpretation of result and Conclusion 20, , 2 Apply Archimedes” principle to determine the buoyancy force on I a 6 Answer to sample questions 10, a solid immersed in liquid. - | 7 Submission of report in time 10, , 3. Determine the coefficient of viscosity of given liquid by Stoke's 1 02 [ Total 100, , method, , 4 Find the downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a I @ The above PrOs also comprise of the following social skills/attitudes which are Affective, , roller due to gravity and its relationship with the angle of Domain Outcomes (ADOs) that are best developed through the laboratory/field based, inclination, experiences:, , 5 Predict the range of the projectile trom the initial launch speed 1 02* a. Follow safe practices., , and angle. b. Practice good housekeeping, 6 i) Find the dependence of the stopping potential on the ui 2 © Practice energy conservation, frequency of light source in photo electric effect experiment d, Demonstrate working as a leader/a team member, ii) Find the dependence of the stopping potential on the intensity e. Follow ethical Practices,, of light source in photo electric effect experiment,, , 7__ [Determine the I-V characteristics of photoelectric cell and LDR | Ill oF | The ADOs are not specitic to any one PrO. but are embedded in many PrOs. Hence, the, [3 Decteninine the eivermenae oF liger beam Ti a] acquisition of the ADOs takes place gradually in the student when s/he undertakes a series of, ' = Cheniisthy t / practical experiences over a period of time, Moreover, the level of achievement of the ADOs, , S| Seana ualion OTRO So aos ins aT a = secorting to Krathwohl’s “Affective Domain Taxonomy” should gradually increase as planned, , and Determine the percentage of iron present in given Hematite TOW “Valuing Level” in 1* year, ore by KMn0O, solution AE SN a UE, 10 Determine the percentage of copper in given copper ore Vv 02 : cee oe me year, 11 | Determine total hardness, temporary hardness and permanent Vv 02* aracicrsing. Level "in3! year, : f TA, as af wat semple bs ED’ meshes 7 a 7. MAJOR EQUIPMENT/ INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED, —— ie aa e Elven wat a fe —— i a The major equipment with broad specification mentioned here will usher in uniformity in, cae ecfurpislity OF given water sample iby Nephelometric| conduct of experiments, as well as aid to procure equipment by administrators., |, 14 Determine the moisture and ash content in given coal sample | VI 02* = =, __using proximate analysis L a Equipment Name with Broad Specifications —, 15 Determine the calorific value of given solid fuel using Bomb vi 02 |_| Sova Te TS cai 16 Se percentage of Sulphur in given coal sample by VI 2 Z SS oo 3, timate analysis.(Gi tric analysis; t i - R, ultimate analysis.(Gravimet ysis) Tee 4 | Stoke’s apparatus (glass tube, viscous liquid, spherical balls of varying sizes) 3, EE 5_| Stop watch 45, 1A suggestive list of PrOs is given in the above table. More such PrOs can be added to | $ Photo transcucer i, attain the COs and competency. A judicial mix of minimum 12 or more practical need to be : mae Sa :, performed. out of which, the practicals marked as ‘*’ are compulsory, so that the student | § —Guceuls motion detector _, reaches the ‘Precision Level’ of Dave's “Psychomotor Domain Taxonomy’ as generally 4 role sects fleet apparatus sacs oF GRIGG SST ‘, required by the industry. | 10 _ Experimental setup for characteristics of photoelectric ce _|, , ii, The ‘Process’ and ‘Product’ related skills associated with each PrO is to be assessed 11 Experimental setup for characteristics of LDR z, , according to a suggested sample given below. SS OF TEC 12 Laser Source ( He Ne, diode laser) 8, Oe We | 13 Electronic balance, with the scale range of 0.001g to 500g. pan size l0umm, Ail, hi f A 2 response time 3-5 sec.: power requirement 90-250 V_ 10 watt, , Eto. Performance Indicators Weightage in % e/ = SS \S\ 18 Electric oven inner size 18°x18"x18""; temperature range 100 t0 250" C with | 14,16, , I Preparition of experimental set up 20 7 \e the capacity of 40 It, , 2 Setting and operation _ _ 20, i 15, , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017, , Page 3 of 10, , , , , , , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017 Page 4 of 10
Page 3 :
a sis Scheme, Ss. ; * * i Exp., ce Equipment Name with Broad Specifications | Re, 20 | Mufile fumace, Temperature up to 900°C, digital temperature controller with, , an accuracy of +/- 3°C, , 14,16, , , , , , 21 | Nephelometer ; Auto-ranging from 20-200 NTU,+/- 2% of reading plus 0.1 13, _NTU. power 220 Volts +/- 10% AC 50 Hz, , 8. UNDERPINNING THEORY COMPONENTS, The following topics/subtopics should be taught and assessed in order to develop LOs in, cognitive domain for achieving the COs to attain the identified competeacy, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Unit Unit Outcomes (UOs) Topics and Sub-topics, {in cognitive domain), Physics, Unit—T la, Explain concept of elasticity [1 Deforming Force and Restoring Force,, Properties | and plasticity for the given Elasticity, Plasticity, Rigidity, of matter material 1.2 Stress and Strain aad their types, Elastic, and Non- Ib. Establish relation between limit and Hooke's law, types of moduli, |Destructiv given types of modulii of of elasticity, ¢ Testing elasticity, 1.3 Stress -Strain diagram, Poisson's ratio,, le. Predict the behavior ofthe | _ factors affecting elasticity, given metallic wire., id. Explain pressure-depth 14 Fluid friction, pressure, pressure- depth, relation for the given law relation, Pascal's law, Archimedes’, le. Explain Newton's law of principle, viscosity for the given liquid. 1.5 Viscosity, velocity gradient, Newton's, If. Explain Stokes” law for the law of viscosity., free fall of the body through 1.6 Free fall of spherical body through, the given viscous medium viscous medium and Stokes" law,, derivation of coefficient of viscosity 'y!, by Stokes’ method, effect of temperature, a ____and adulteration on viscosity of liquids, | Ig. Describe the salient features 1.7 Non-desiructive testing (NDT).Various |, of the given NDT method NDT methods used, Criteria for the, | selection of NDT method, merits and, demerits of NDT, [Unit 1 2a, Explain the equations of __2.1 Displacement, velocity, acceleration and, Types of motion for the given body retardation, equations of motion,, Motion moving in the given type of equations of motion under gravity, path 22. Angular displacement, angular velocity,, (2b. Calculate the angular velocity angular acceleration, three equations of, | of the given body. angular motion, (2c, Explain the relevant 23 Momentum, impulse, impulsive force,, Newton’s laws of motion for Newton’s laws of motion and their, the given moving object. Applications, 2d. Calculate the work/power! 2.4 Work, power and energy” potential, energy for the given situation. _ energy, kinetic energy, work -energy, be Calculate the given principle., , , , , , , , , , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017, , Page 5 of 10, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Applied Sicnee 1 Schome, Unit Unit Outcomes (UOs) Topics and Sub-topics, (in cognitive domain), , parameters for the given 2.5. Projectile motion, trajectory, angle of, , projectile in motion projection, time of flight and range of, projectile with formulae |, , \, , Unit- Tl 3a. Explain the concept of the 5.1 Planck’s hypothesis, properties of ], Photoelect given parameters of the given photons, Photo electric effect: threshold, , ricity, X- material., Rays and 3b. Explain the working of the, LASERs given photoelectric device., , frequency, threshold wavelength,, stopping potential, Work function,, characteristics of photoelectric effect,, Einstein's photoelectric equation,, Photoelectric cell and LDR: principle., working and epplications., , , , 3c, Explain the production of X, Rays of the given material, with properties and, applications., , Production of X-rays by modern, Coolidge tube, properties and, applications,, , , , LASER and given colour of, , |, |, 3d. Differentiate between, | light, , I, , examples,, , , , Chemistry, , Be. Explain the given terms with, , Laser: properties, absorption,, spontaneous and stimulated emission,, applications of Laser, , Population inversion, active medium,, optical pumping, three energy level, system, He-Ne Laser., , , , , , Unit-TV 4a. Describe construction and, Metals, working of the given type of, alloys, | famace., , Cement, 4b. Describe the extraction, , 41, , 42, , and process of the given ore with 4.3, , Refractory | chemical reaction, materials 40. Explain purposes and, preparation methods of, making the given alloy., Select the relevant alloy for, the given application stating, the properties with, justification., , Describe the constituents,, hardening and setting, process of the given type of, cement, , 4, , a, , 4, , \4, , =, , for given application stating, the properties with, justification, , Select the relevant refractory, , 44, , 45, 46, , 47, , 48, , 49, , Metallurgy: Mineral, ore, gangue, flux,, slag, , Types of furnace: Mufile furnace, Blast, furnace., , Extraction processes of Haematite,, copper pyrite ores: Crushing,, concentration, reduction, refining., Properties of iron and copper:, Hardness, tensile strength, toughness. |, malleability. ductility, refractoriness,, fatigue resistance. specific gravity., specific heat, brazing. castability,, stiffness,, , Preparation of alloys (Fusion and, compressior. method)., , Ferrous alloys: Low carbon, medium, carbon, high carbon steels, Non-ferrous alloy: Brass, Bronze,, Duralumin, Tinman Solder, Woods, metal, , Cement: Types; Biocement and, Portland cement; constituents, setting, and hardening, applications, , Lime: classification, constituents,, setting and hardening. applications., , , , , , , , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017, , Page 6 of 10, , 2
Page 4 :
Applied Seiene, , , , 1 Scheme, , , , , , , , , , , , , , Unit Unit Outcomes (UOs) Topics and Sub-topics, (in cognitive domain), 4.10 Refractory material: Types, properties, | Unit-V Sa. Describe the given 5.1 Hardness; Classification, Water terminologies related to hard 5.2 Hard water in boilers and prevention:, treatment ‘water and their effects Boiler corrosion, caustic embrittlement,, 5b. Describe the given process priming and foaming, scales and, for softening of the given sludges., water sample, 5.3 Water softening: lime soda process (hot, Se Describe with sketches the lime soda and cold lime soda process),, purification of the given type zeolite process, ion exchange process, of water, (cation exchange and anion exchange)., Sd. Describe the given type of of 54 Potable water treatment: Sedimentation,, waste water treatment coagulation, filtration and sterilization, 5.5 Waste water treatment: sewage, treatment, BOD and COD of sewage, water; Reverse Osmosis, recycling of, | waste water, Unit-VI 6a. Describe salient properties of © 1 Fuel. Calorili and ignition, Fuels and the given type of fuel temperature fication., , , , a, , Combustio 6b, , 6c., |, 6d, , 6, , e, , Explain the given type of 62, analysis of the given type of, , coal, , Calculate the calorific value, , of the given solid fuel using, , Bomb calorimeter. 63, Describe composition., , properties of given gaseous, , fuel with their applications, Calculate the mass and, , volume of air required for 6.4, complete combustion of the, , given fuel, , Solid fuels: Coal, Classification and, composition , proximate analysis, Ultimate analysis, Bomb calorimeter., Carbonization of coke by Otto, Hofmann’s oven, , Liquid flels: Fractional distillation of, crude petroleum, boiling range,, composition, properties. Knocking, cracking. octane number and cetane, number., , Gaseous fuels: Biogas, LPG., Combustion equation of gaseous fuels,, mass and volume of air required for, complete combustion., , , , , , , , and CNG., , , , , , , , , , Note: To atiain the COs and competency, above listed UOs need to be undertaken to achieve, the ‘Application Level’ and above of Bloom's ‘Cognitive Domain Taxonomy, , a SUGGESTED SPECIFICATION TABLE FOR QUESTION PAPER DESIGN, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Unit | Unit Title Teaching | Distribution of Theory Marks, No. | Hours R U A | Total, Level___Level | Level | Marks, | Physics, |_| Properties of matter and NDT 4 03 | 05 | 06 14, [Il] Types of motion 09 02 02 | 06 10, UL | Photoelectricity, X-Ray and LASER. | _09 03 | 04 | 04 |, Chemistry I |, MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017 2, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Applica Science f Sebame, [ Unit | Unit Title ‘Teaching | Distribution of Theory Marks |, No. Hours R U A | Total |, Level_| Level | Level | Marks |, IV_| Metals, alloys, cement, refractory 12 02 ] 04 06 | =12 |, materials | | | |, V_| Water treatment to | 02 03 | 06 ui, VI_| Fuels and combustion 10 | 03 a4 | 05 12, Total 4 | 15 2 | 33_| 70, Legends: R=Remember, U=Understand. A=Apply and above (Bloom's Revised taxonomy), , , , Note: This specification table provides general guidelines to assist student for their learning, and to teachers to teach and assess students with respect to attainment of UOs. The actual, distribution of marks at different taxonomy levels (of R. U and A) in the question paper may, vary from above table., , 10. | SUGGESTED STUDENT ACTIVITIES, Other than the classroom and laboratory learning, following are the suggested student-related, co-curricular activities which can be undertaken to accelerate the atta:nment of the various, outcomes in this course, , a Seminar on any relevant topic, , b. Library survey regarding engineering material used in different industries, , ¢ Prepare power point presentation of animation for showing applications of lasers, , Il. SUGGESTED SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES (if any), These are sample strategies which the teacher can use to accelerate the attainment of the, various leaming outcomes in this course, a Massive open online courses (MOOCs) may be used to teach various topies/sub, topics., b ‘L’ in item No. 4 does not mean only the traditional lecture method. but different, types of teaching methods and media that are to be employed to develop the outcomes, ¢ About 15-20% of the topics/sub-topics which is relatively simaler or descriptive in, nature is to be given to the students for self-directed learning and assess the, development of the COs through classroom presentations (see implementation, guideline for details),, d With respect to item No.1, teachers need to ensure to create opportunities and, provisions for co-curricular activi, ©. Guide student(s) in undertaking micro-projects., , , , 12. | SUGGESTED MICRO-PROJECTS, , Only one micro-project is planned to be undertaken by a student assigned to him/her in the, beginning of the semester. S/he ought to submit it by the end of the semester to develop the, industry oriented COs. Each micro-project should encompass two or more COs which are in, fact, an integration PrOs, UOs and ADOs. The micro-project could be industry application, based, internet-based, workshop-based, laboratory-based or field-based. Each student will, have to maintain dated work diary consisting of individual contribution in the project work, and give a seminar presentation of it before submission, The total duration of the microproject should not be less than 16 (sixteen) student engagement hours during the course, , the first four semesters, the micro-project could be group-based. However, in higher, ‘jSimesters, it should be individually undertaken to build up the skill anc confidence in every, , , , Page 8 of 10 a
Page 5 :
Applied Seienee ¥ Scheme, , student to become problem solver so that s/he contributes to the projects of the industry. A, suggestive list is given here. Similar micro-projects could be added by tae concerned faculty, , a, , , , Elasticity: Prepare working model to demonstrate the stress — strain behavior of, different wires of different thickness and material, , Viscosity: Collect 3 to 5 liquids and prepare a working model to differentiate liquids, on the basis of viscosity and demonstrate their applications, , Motion: Prepare model of ball rolling down on inclined plane to demonstrate the, conservation of energy and motion of an object in inclined plane., , Photo Sensors: Prepare simple photo sensor using LDR, , Properties of Laser: Use Key chain laser to differentiate laser with ordinary light, Water analysis: Collect water samples from different water sources and find the, characteristics like acidity, conductivity, dissolved solids, suspended particles., , Water treatment: Collect 3 to 5 water samples to find the dosage of bleaching, powder required for its sterilization., , Water analysis: Prepare model io find the soap foaming capacity of bore water on, addition of soda ash, , Fuels: Prepare chart showing different types of liquid fuels showing their calorific, values and uses., , Cement: Collect different samples of cement and find their initial and final setting, time., , Refractory materials: Prepare chart showing properties of refractory materials., , Metal properties: Prepare chart showing different industrial application of metal and, relate it with required property or properties using intemet., , Alloy steel: Find the effect of alloying elements like Mn, Cr, Ni, W, V, Co on, properties of steel. Prepare chart of showing percentage composition, properties and, industrial applications of different types of steel based on above alloying elements, using internet., , , , , , , , , , SUGGESTED LEARNING RESOURCES, , , , Title of Book Author Publication, , , , Physics Textbook Part | Narlikar. J. V.: Joshi, | National Council of Education, J and Part - Class XT A. W.: Mathur, Research and Training, New Delhi., Anuradha: ef al 2010, ISBN : 8174505083, , , , Physics Textbook Part | Narlikar. J.V.: Joshi, | National Council of Education, Vand part Il - Class A. W.: Ghatak A.K. ef | Research and Training, New Delhi,, Xi al 2013, ISBN : 8174506314, , , , , , , , [Engineering Physics | Bhattacharya, D.K; | Oxford Publishing, New Delhi,, , | Tandon Poonam ISBN:0199452814, , | Principles of Md. Nazoor Khan and | Cambridge university press, New, Engineering Physics -I_| Simanchela Panigrahi_| Delhi, 2016 ISBN : 9781316635643, Engineering Physics | Palanisamy, P. K SCITECH Publications, Chennai,, ISBN: 9788183711012, , , , Principles of Physics | Walker, J, Halliday, | Wiley Publications, New Delhi, 10", , D; Resnick, R edition ISBN: 9788126552566, , , , , , , , Textbook of, Engineering Physics, , Avadhanulu, M, N.; S. Chand and Co., New Delhi, 2015, Kshirsagar, P.G. ISBN: 9788121908177, , , , , , Engineering, , Agarwal, Shikha Cambridge university press ; New, | Chemistry, , Delhi, 2015 ISBN : 97811074764, , , , , , , , , , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017, , Page 9 of 10 2, , , , Applied Seionee 1 Sehicme, , , , Title of Book Author, , , , , , , , Engineering Dara, S. S.; Umare, Chemistry SS, , Engineering Tain & Jain, Chemistry, , S.Chand and Co, Publication, New, Delhi, 201, ISBN: 8121997658, Dhanpat Rai and sons; New Delhi,, 2015, ISBN ; 9352160002, , , , Engineering, Chemistry, , Vairam, S, Wiley India Pvt, Ltd. New Delhi,, , 2013, ISBN: 9788126543342, , , , , , 10, , Chemistry for, engineers, , Agnihotri, Rajesh Wiley India Pvt.Ltd. New Delhi,, , 2014, ISBN: 9788126550784, , , , =, , vos unease nono ge?, , , , SOFTWARE/LEARNING WEBSITES, hitp://nptel.ac.in/course php?disciplinel, hitp://nptel.ac.in/course.php?disciplinel, http://hperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hph htm!, www. physicsclassroom.com, www.fearofphysics.com, , www sciencejoywagon,com/physicszone, www.science.howstuffivorks.com, hittps://phet,colorado.edu, , www chemistryteaching.com, www.visionlearning.com, , www.chem |.com, , www onlinelibrary.wiley.com, , www rsc.org, , www chemcollective.org, , www. waa.org, , www em-ea.org, , , , , , MSBTE Final Copy dt. 30.10.2017, , Page 10 of 10 2