Page 1 :
Module 1: Introduction to Economics, Introduction to Economics:, Economics is a social science that analyses production, distribution and, consumption of goods and services. Economic analysis is applied throughout, society in business, finance, government, education, the family, health, law,, politics, religion, social institutions, war, science etc., Meaning of Economics:, Economics is the science that deals with the productions, allocation and use of, goods & services. It is important to study how resources can best be distributed, to meet the needs of the greatest number of people., In simple economics studies decision making in view of many wants against, scarcity means., Definition of Economics:, According to “Adam Smith” Economics is an Inquire into the Nature and Causes, of the wealth of Nations., According to “Paul Samuelson” defines Economics as” the study of how a, person or society meets its unlimited needs and wants through the effective, allocation of resources”., Branches of Economics:, I., II., , Micro Economics, Macro Economics, , I MICRO ECONOMICS:, It is a branch of economics that studies the behaviour of how the individual,, modern household and firm make decisions to allocate limited resources., It applies to markets where goods or services are being bought and sold . Micro, economics examines how these decisions and behaviours affect the supply and, demand for goods & services., II MACRO ECONOMICS:, It is the sub division of economics that studies the behaviour and performance of, an economy as a whole. It focuses on the aggregate changes in the economy such, as unemployment, growth rate, gross domestic product and inflation., Concepts of Macro Economics:, 1. Output & income, , 4. Economic growth, , 2. Unemployment, , 5. Business cycle, , 3. Inflation &deflation, , Page. 1, , 6. International economics., , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 2 :
Differences between Micro Economics and Macro Economics:, , Macro Economics and its interface with business and industry: or, The significance or Importance of Macro Economics:, 1. Functioning of an economic system., 2. Formulation of Economic policies., 3. Understanding micro economics., 4. Understanding and controlling Economic Fluctuation., 5. Analysis of Inflation and Deflation., 6. Study of National Income., 7. Study of Economic development., 8. It helps to understand the problems faced by the various countries., 9. It helps in understanding the importance of savings., 10.It assists in dealing with problem of allocation of goods and services., 11.It helps in understanding the business cycle., 12.It helps to formulate monetary and fiscal policies., 13.It helps to analyse the GDP and economic growth of any nation., Macroeconomics is interfaced with business because business is affected by the, factors that constitute macroeconomics. Macroeconomics is a branch of, economics that deals with issues relating to factors that affect the areas like the, rate of unemployment, inflations, business cycles and Gross domestic product, [GDP]. Entrepreneurs and other people related to business must take such factors, into consideration as part of their market analysis., Page. 2, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 3 :
Managerial Economics:, Introduction to Managerial Economics:, Managerial economics is concerned with the application of business principles, and methodologies to the decision making process within the firm or organization, under the conditions of uncertainty. It seeks to establish rules and principles to, facilitate the attainment of the desired economic aim of management. These, economic aims relate to costs, revenue and profits and are important within both, business and non-business institutions., Meaning of Managerial Economics:, Managerial economics is a specialized discipline of management studies which, deals with application of economic theory and techniques to business, management., Definition of Managerial Economics:, According to Joel Dean “The purpose of Managerial Economics is to show how, economic analysis can be used in formulating business policies”., Nature of Managerial Economics:, 1) Managerial Economics is a science: Managerial economic requires lot of, logical thinking and creative skill for decision making for problem solving. It, is considered as a stream of science by some economist because it involves, the different economic principle technical and methods to solve business, problems., 2) Managerial Economics is an art: Individual should have a lot of utilising his, capability knowledge and understand to achieve the organisational objective., Managerial economics should have an art to put in practice is theoretical, knowledge regarding elements of economic environment., 3) Managerial economics has components of microeconomics: In managerial, economics managers generally deal with the problems relating to particular, organisation instead of whole economy. Here are some of the concepts of, microeconomics such as demand forecasting theory, revenue cost theory,, supply and production theory., 4) Managerial economics has the components of macroeconomics: Here the, business function is external environment. Itself the market which is a part of, economy as a whole. It is essential for the managers to understand the factor, of macroeconomics such as market condition, economic reforms, government, policies, unemployment their impact on the organisation., 5) Multi-disciplinary: It use of many tools and principles belonging to various, disciplines such as accounting, finance, statistics, mathematics, production ,, operation research and psychology., 6) Prescriptive or normative disciplines: It aims to goals achievement and, deals with the practical situation or problems by implementing corrective, measures., 7) Pragmatic: It is a practical and logical approach towards the day-to-day, business problems, Page. 3, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 4 :
8) Managerial Economics for administration of organisations: Managerial, economics helps in decision making. It helps in decisions are based on the, economic rational or valid in the existing economic environment., 9) Managerial Economics is helpful in optimum resource allocation:, Resources are scarce, with alternative uses managers need to use the limited, resources optimal. Teach resources and several uses he should decide which, is preeminent use of the resources., 10) Managerial Economics is dynamic in nature: Managerial economics, deals with the human resources. The nature and attitude differs from person to, person so managerial economics change itself over a period of time., , Scope or Uses of Managerial Economics:, The scope of managerial economics is very wide because it includes theory,, models and methods that help business firms in decision-making and future, planning. It includes the following–, 1) Demand analysis and forecasting: The demand for product would changes, in response to change in price, customers’ income, his tastes, which are, determinants of demand. Demand analysis is the process of making estimation, about future customer demand using historical data and other information a, study of the determinants of demand is necessary for forecasting future, demand of the product., 2) Cost analysis: Estimation of cost is an essential part of the managerial, problems. The factors causing variations of cost must be found out and, allowed for it management to arrive at cost estimates. This will help for more, effective planning profit planning control and sound pricing practice., 3) Pricing decision: The firm’s aim to profit which depends upon the, correctness of pricing decisions. The pricing is an important area of, managerial problems. Theories regarding price fixation helps the firm to solve, the price fixation problems., 4) Profit analysis: Business firms working for profit and it is important, measures of success. But the firms are working under conditions of, uncertainty. Profit planning becomes necessary under the conditions of, uncertainty future environment is unpredictable., 5) Capital budgeting: The managers have to take every important decisions, relating to firm’s capital investment will help the manager as to calculate the, correctly the profitability of investment and the properly allocation the capital., Success of the firm depend upon the proper analysis of capital project and, select the best one., 6) Production analysis: Production analysis is a narrower in scope than cost, analysis. Production analysis frequently proceeds in physical terms while cost, analysis proceeds in monetary terms. Production analysis mainly deals with, different production functions and their managerial uses., , Page. 4, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 5 :
7) Supply analysis: Supply analysis deals with various aspects of supply of an, commodity. Certain important aspects of supply analysis are supply schedule,, Law of supply and increase in price result in an increase in quantity supplied., 8) Theory of Consumption: Managerial economics studies the behaviour of the, consumer and its related aspects like law of demand, elasticity of demand,, cardinal and ordinal approach to utility., 9) Theory of Distribution: Managerial economics studies factor pricing and the, share of the factor in national income. Profit planning is the main area of, managerial economics., 10) Economic Policies: Government policy such as monetary, fiscal,, industrial, trade and labour policies influence the decision of a firm. The firm, has to plan the allocation of resources in different alternative uses., 11) Sales Promotion: A business manager has to pay proper attention for, adopting sales advertisement costs. He has to determine the quality of the, product, sales expenditure; trademark and size which are the main area of, managerial economics., , Objectives of the Firm:, Meaning of firm: Firm is an organisation of individual or a group of individuals, or commercial enterprises that buying and selling product or services to, consumers with the aim of making a profit., , Main objectives of Firm, 1) Profit maximization: Usually in Economics profit maximization is the short, run or long run process by which a firm maintain the price input and output, levels that leads to the highest profit. More profit can be used to finance, research and development. Higher profit enables higher salaries for workers., 2) Sales maximization: Main objective of firm which involves selling more unit, of a goods or services as possible. Without making a loss it means sacrificing, some short-term profit with a view to achieving a long term gain., 3) Social or environmental concerns: A firm maintain to choose product with, doesn't harm the environment or products not effected on animals., Example: local community charitable concerns sometimes may adopt, social and environmental concerns as part of their branding. (TOYOTA), 4) Profit satisfying: Profit satisfying behaviour is an alternative business, objective to maximizing profit. In this situation where there is a separation of, ownership and control in a firm., Shareholders or owners which do not maximize profit, Manager and workers don’t feel the same incentive., 5) Co – operative: It is a different objectives of a firm and exist in every sector, of the economy and cooperative range from very small local business to large, multinational corporations. And it is run to maximize the Welfare of all, stakeholders of the business., 6) Growth maximization: One of the main objective of the firm is measured in, terms of sales, number of employees, number of parties, number of branches,, and variety of products and services., Page. 5, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 6 :
7) Functional Objective:, Better management of raw materials supply., Example: transfer of raw material or product from one country to, another country at lower price., Successful marketing strategy to raise brand awareness and increase, sales., Uniqueness of its markets (product price, securities, and insurance, to customers), 8) Increase market share / market dominance: It is measure of the strength of, a brand, product service or relative to competitive offerings exemplified by, controlling a large proportion of the power in particular market., Companies increased market share through innovation,, strengthening customer relationship, smart hiring practices and, acquiring competitors., It controls the total market for its products and services., 9) Economic objectives: The economic objectives focus on sales maximization,, growth maximization and managerial utility maximization., 10) Survival: It is the long term goal of the firm. Survival in the long run, depends on creating goodwill in the minds of the consumer by producing good, quality products and services., 11) Welfare of employees: It includes good working conditions, fair wages,, medical care, housing etc., , Managerial theories of firm, Various types of managerial theories of firm are as follows:, 1) Baumol’s Theory of Sales Revenue Maximisation:, Prof.Baumol, book Business between value and growth has propounded a theory, of sales maximization. Main aim of firm is to maximise sales. By sales increases, total revenue earned by the sale of goods. That is why this goal is also referred to, has sales maximization goals. According to this theory once profit reach, acceptable levels the goal of the firm become maximization of profits., In the words of Baumol, “The sales maximisation goal says that managers of, firm seek to maximise their sales revenue subject to the constraint of earning a, satisfactory profit”, The above definition maintains that when the profit of firms reach a level, considered satisfactory by the shareholders then the efforts of the managers are, directed to maximize revenue for promoting sales instead of maximizing profit., While studying this theory one must be kept in view that firms do not ignore profit, all together., , Page. 6, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 7 :
2) Marris Growth maximization model:, Working on the principle of segregation of managers from owners, Marris, proposed that owners (shareholders) payment profits and market share ,whereas, manager aim at better salary, job security and growth. These two sets of goals can, be achieved by maximizing balanced growth of the firm (G), which is dependent, on the growth rate of demand for the firm’s products (GD) and growth rate of, capital supply of the firm (GC). Hence growth rate of the firm is balanced when, the demand for its products and the capital supply of the firm grow at the same, rate., Marris further said that firms face to constant in the objective of maximization, of balanced growth which are explained below:, Managerial constraint, Among managerial constraints, Marris stressed on the importance of the, role of human resources in achieving organisational objectives. According to him, skills, expertise, efficiency and sincerity of team managers or vital to the growth, of the firm. Non-availability of Managerial skill sets in required size create, constraints for growth Organisation on their high levels of growth may face, constraint of skill ceiling among the existing employees. New recruitments may, be used to increase the size of the managerial pool with the desired skills have a, new recruits’ lack experience to make quick decisions which may pose as another, constraint., Financial Constraint, This relates to the prudence needed in managing financial resources. Marris, suggested that a prudent financial policy will be based on at least three financial, ratios, which in turn set the limit for the growth of the firm. In order to prove their, discretion managers will normally create a trade-off and prefer a moderate debt, equity ratio (r1), moderate liquidity ratio (r2) and moderate retained profit ratio, (r3)., a) Debt equity ratio (r1) : This is the ratio between borrowed capital and, owner’s capital . High value of debt equity ratio may cause insolvency;, hence a low value of this ratio is usually preferred by managers to avoid, insolvency. However, a low ratio may create a constraint to the growth, of the firm in terms of dependence on high cost capital that is equity., b) Liquidity Ratio (r2): This is the ratio between current assets and, current liabilities and is an indicator of coverage provided by current, assets to current liabilities. According to Marris,a manager would try to, operate in a region where there is sufficient liquidity and safety and, hence would prefer a high liquidity ratio., c) Retention ratio(r3) : This is the ratio between retained profits and total, profits. In other words, it is the inverse of dividend pay out ratio,i.e, the, retained profits for that portion of net profit which is not distributed, among shareholders. A high retention ratio is good for growth, as a, retained profit provide internal source of funds., Page. 7, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 8 :
Behavioural Theories of Firm, The Behavioral theory of the firm first appeared in the 1963 book A Behavioral, theory of the firm by Richard M.Cyert and James G.March. The work on the, behavioural theory started in 1952 when march, a political scientist , joined, carnegiemellon university .where cyert was an economist., Definition: An examination of the inner motives and direction of firms, using a, range of model and different assumptions about Those who work in a firm., In Classical economics the theory of firm is based on the assumption that they, will seek profit maximization. However, in the real world managers and owners, may be quite different., Behavioral theories of the firm’s include:, o Size of a firm/ prestige, o Profit satisfying, o Co-operative/ ethical concern, o Human emotion /bias., , Economic System:, Economic system means some total of the arrangement for the production and, distribution of goods and services in society., An economic system is a mechanism with the help of which the government, plans and allocate assessable service resources and commodities across the, country economic system manage elements of production combining Wealth, labour physical resources and business people and economic system incorporates, many companies it and models as well as for deciding procedures., There are three types of economic system:, 1. Capitalist Economy (Free Market), 2. Socialist Economy, 3. Mixed Economy, 1. Capitalistic economy:, It’s a system of economic organization in which the factors of production are, owned, manage and control by private individual and product takes place for, private profit., Every individual is free to start any business are choose any occupation with the, limits of law., Eg: USA, Canada, France, US, UK, Germany, Spain, Mexico…, Features of Capitalist Economy:, 1) Economic freedom, 2) Consumer Sovereignty, 3) Limited government, 4) Finance sector, 5) Profit motive, Page. 8, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 9 :
6) Market forces, 7) Flexible labour markets, 8) Private property, 9) Law of inheritance, 10), No social welfare, Merits of Capitalist Economy:, 1) Optimum utilization of resources, 2) Variety of products, 3) Efficient production of goods and services, 4) Economic freedom, 5) Consumer sovergenity, 6) Right to have private property, 7) Technological development, 8) Higher standard of living, 9) Higher rate of economic growth, Demerits of Capitalist Economy:, 1) Inequality in distribution of income and wealth, 2) Monopoly market, 3) Class conflict, 4) No social welfare, 5) Labour exploitation, 6) Wasteful competition, 7) Creates unemployment, 8) Misallocation of resources., 1. Socialistic Economy :, Under socialistic economy the factor of production that is land, labour, money,, organization has owned manage, control by state / government. They carried, business for social welfare. E.g.: China, Socialist Economy is run by government with motive of social welfare. This, economic system acknowledges the three enquiries in a different way in a, socialist society the government determines what products are to be manufactured, in accordance with the requirement of society. It is believed that the government, understands what is appropriate for the citizen of the country., Features of Socialistic Economy:, 1) Collective ownership, 2) Economic social and political equality, 3) Economic planning, 4) No competition, 5) Positive role of government, 6) Work and wages according to ability and needs, 7) Maximum social welfare., Page. 9, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 10 :
Merits of Socialistic Economy:, 1) Equal distribution of income and wealth, 2) Social welfare, 3) Absence of exploitation, 4) Optimum utilization of resources, 5) Wastages avoided, 6) Absence of trade cycle, Demerits of Socialistic Economy:, 1) Absence of consumer sovergenity, 2) No occupation freedom, 3) Administration burden, 4) Reduction in efficiency of state entrepreneur, 5) Loss of Liberty, 6) Wastage of resources., 3. Mixed economy:, It refers to the all the factors of production like land, labour, money, organization, are owned, managed, and controlled by both private individuals and government., Business carried over for profit and social welfare., It is a system which includes the features of both capitalistic and socialistic, economy. E.g.: India., Features of mixed economy, 1) Coexistence of the private and public sector, 2) Existence of joint sector, 3) Regulation of private sector, 4) Planned economy, 5) Private property, 6) Provision of social security, 7) Motive of business concern, 8) Reduction of inequalities of income and wealth, 9) Complete economic freedom., Merits of Mixed Economy:, 1) Efficiency, 2) Reduce inequality, 3) Systematic plan, 4) Consumer Sovereignty, 5) Promotion of social welfare, 6) Rights of individuals, 7) Optimum utilization of resources, 8) Variety of products, 9) Technological development, 10), Higher standard of living, 11), Higher rate of economic growth, Page. 10, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 11 :
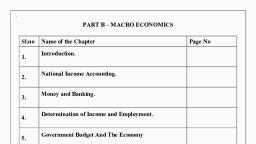
Demerits of Mixed Economy:, 1) Unhealthy competition, 2) No freedom to private sector, 3) Inefficient public sector, 4) Unemployment and uncertainty, 5) Threat of nationalisation, 6) Lack of co-ordination, 7) Government interference, 8) Corruption., , National Income:, National income is the total net value of all goods and services produced within, a nation over a specified period of time. It represents sum of wages, profits, rents,, interests and pension payments of citizens of a nation., Concepts of National Income, 1) Gross Domestic Product (GDP), 2) Gross National Product (GNP), 3) Net National Product ( NNP), 4) Personal income, 5) Disposable income, 6) Per capital Income, 1) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) :, Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final goods and, services produced within a country in a year. It does not include income earned, from abroad., GDP = P×Q, Where P: price of goods and service, Q: quantity of goods and services, or, GDP= C+I+ G+(X-M), Where C = consumption, I = Investment, G = Government expenditure, (X-M) = Exports minus Imports., 2) Gross National Product (GNP):, Gross National product (GNP) is the total market value of all final goods and, services produced within a country in a year plus(+) net factor income earned, from abroad., GNP = C + I + G + (X-M) + NFIA, NFIA = Net factor income from abroad, or, GNP = GDP + NFIA, Page. 11, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 12 :
Hence , GNP includes the following, Consumer goods and services, Gross private domestic investment in capital goods, Government expenditure, Net exports (export - imports), Net factor income from abroad., 3) Net National Product (NNP):, NNP is the market value of goods and services produced within a country, and net factor income from abroad minus Depreciation., a) NNP at market price: NNP is the market value of all final goods and, services of the providing for depreciation., NNP = GNP – Depreciation, or, NNP = C+I+G(X-M)+NFIA-Dep., b) NNP at factor cost (National Income): NNP at factor cost or national, income is the sum of wages, rent, interest and profit paid to factors for, their contribution to the production of goods and services in a year., NNP = NNP at Market price – Indirect taxes + Subsidies., 4) Personal income (PI):, PI is the sum of all incomes actually earned by the individuals and households in, a country during one year. It is the amount available to them for spending, paying, taxes, and saving purpose., PI = NI –Corporate Income taxes – Undistributed corporate profits- social, security contribution + transfer payments., 5) Disposable Income (DPI):, The income left after the payment of direct taxes from personal income is called, disposable income, DPI = Consumption expenditure + savings, or, DPI = PI – Personal direct taxes., 6) Per Capital Income:, Per capital income refers to the average income per head of population. It is, calculated by dividing national income by total population., Per capital income = National Income / Total Population, , Methods of Measuring or Computation of National Income:, 1) Output or Production Method, 2) Income Method, 3) Expenditure Method., Page. 12, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 13 :
1) Output or Production Method:, In this method, only value added by each producing unit at various stages of, production is taken into account for the estimation of national income. This, method is also called the value added method., This method approaches national income from the output side under this method, the economy is divided into different sectors such as agriculture, fishing, mining,, construction, manufacturing and other services, then the growth product is found, out by adding up the net values of all the production that has taken place in the, sector's during a given year., 2) Income Method:, According to this method national income obtained by adding up of incomes of, all individuals in the country. It is also known as this distribution share method., National income is calculated by adding all the incomes earned in the form of, rent, wages, salaries, interest on capital, profit from business, income of selfemployed people., In India this method is used in service sectors like:, a. Transport, communication, b. Electricity, gas and water supply, c. Banking. Finance and insurance, d. Real estate, e. Public administration and defence., 3) Expenditure Method:, In this method National income is calculated by adding up of all the expenditure, made on goods and services during a year., If we add the total expenditure incurred by all individuals, households, business, units and the government in a year then we get total national income of the, country., The following expenditures to be added to calculate National income, a. Expenditure by individuals and households on goods and services denoted by, C, b. Expenditure by private business peoples on capital goods denoted by I, c. Government expenditure i.e. government purchase denoted by G, d. Expenditure made by foreigners on goods and services denoted by (X-M), Y = C + I + G + (X-M)., , Problems or Difficulties in computation of National Income:, 1. Difficulty in defining the Nation: National income of a country does not mean, only income earned within a country. It also includes the income earned from, abroad., 2. Lack of statistical data: The up to date, accurate, adequate and reliable data, regarding the value and volume of goods and services produced are not available, in backward countries., Page. 13, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara
Page 14 :
3. Absence of proper records: Many people due to illiteracy, ignorance and, indifferent attitudes do not have the habit of keeping proper accounting data on, production, income and expenditures., 4. Existence of non-monetary transactions: The national income must be, calculated in monetary terms. There are certain non -monetary transactions which, are not included in the value of a product for e, g, unpaid personal service of, House wife., 5. Absence of occupational specialization: Many people are engaged in more, than one occupation for earning their livelihood. Many people work as part time, workers and such they do not give complete information about sources of their, income., 6. Danger of double counting: While calculating National income we have to, take into account the value of final goods and services but many times the value, of intermediate goods is included in the national income. For e.g. the value of oil, or oil seeds taken into account and not the value of both., 7. Existence of illegal earnings: There is huge volume of incomes earned, through illegal activities like gambling, smuggling, black marketing, adulteration, etc.. but these items cannot be included in calculation of national income., 8. Treatment of profits from foreign firms: Profit from foreign firms is treated, as income of parent country or income of Host country., 9. Imperfect instrument to measure national income: Value of goods and, services measured in terms of money. But the values of money itself change due, to inflation or deflation., 10. Incomes earned through lottery, dowry, pensions, unemployment relief,, etc should be excluded from the calculation of national income because the above, items are gratis., 11.Goods kept for self-consumption: The values of these goods are to be, included in the calculation of national income., 12.Existence of non-market transactions: Many people stitch their own, clothes, grow vegetables in their own gardens the value of such activities does, not enter the market transactions and hence are not included in the national, income estimates., 13. Existence of different methods to calculate depreciation charges:, 14.Coverage of commodities and services: Value of all unpaid work on account, of love, affection, mercy, kindness friendship etc. should be excluded in the, calculation of national income., 15.Valuation of inventory., 16.Production for self-consumption, 17.Valuation of government services, 18.Illiteracy and ignorance., Page. 14, , Prepared by Prakash.K Assistant Professor, GFGC Ramanagara