Page 1 :
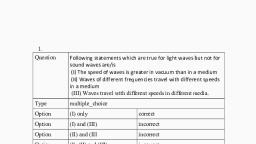
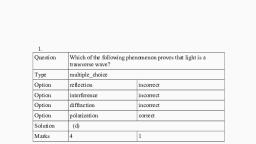
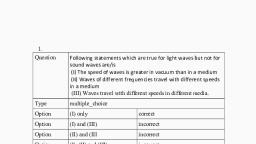
Wave Optics, Single choice questions (LEVEL 0), Wave nature of light, 1. The speed of light depends, (a) on elasticity of the medium only, (b) on inertia of the medium only, (c) on elastically as well as inertia, (d) neither on elastically nor on inertia, 2. The wave function (in S.I. units) for an, electromagnetic wave is given as (x,t) = 103 sin, 4x106x 9x1014t) The speed of the wave is, (a) 9x1014 m/s, (b), 2.25x108, m/s, (c) 3x106 m/s, (d) 3x108 m/s, 3. Which of the following properties show that light, is a transverse wave, (a) reflection, (b) interference, (c) diffraction, (d) polarization, 4. When a ray of light entres a glass slab from air, (a) its wavelength decreases, (b) its wavelength increases, (c) remains the, same, (d) its frequency increases., 5. When light is refracted into a medium, (a) its wavelength and frequency both increase, (b) its wavelength increases but frequency remains, unchanged, (c) its wavelength decreases but frequency remains, unchanged, (d) its wavelength and frequency both decrease, 6. The wavefront of light coming from a distant, source of unknown shape are nearly, (a) plane (b) elliptical (c) cylindrical (d) spherical, 7. The wave emitted by any atom or molecule must, have some finite total length which is known as, the coherence length. For sodium light, this length, is, 2.4 cm. The number of oscillations in this, length will be (Given = 5900 Å), (a) 4.068x105, (b) 4.068x106, 7, (c) 4.068x10, (d) 4.068x108, 8. When a light ray enters from air to a medium of, refractive index n. If the frequency, wavelength, and speed of light ray in air are v, and c, respectively, then these quantities in medium will, be, v c, c, v , (a) , , (b) nv, n, nc (c) v, , (d) , , c, n n n, n n, n n, 9. Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature is, evident by, (a) polarization, (b) interference, (c) reflection, (d) diffraction, 10. A light wave has a frequency of 4 x 1012 Hz and a, wavelength of 5 x 10-7 meters in a medium. The, refractive index of the medium is, (a) 1.5, (b) 1.33, (c) 1.0, (d) 0.66, 11. A glass slab of thickness 4 cm contains the same, number waves as 5 cm of water when both are, , traversed by the same ray of light. The refractive, index of water is 4/3, what is that for glass?, (a) 5/3, (b) 5/4 (c) 16/15, (d) 3/2, 12. The angle of incidence at which reflected light is, totally polarized for reflection from air to glass, (refractive index n), is, (a) tan-1(1/n), (b) sin-1(1/n), -1, (c) sin (n), (d) tan-1(n), 13. A 60 watt bulb is hung over the center of a table, 4 '4 ' at a height of 3'. The ratio of the intensities of, illumination at a point on the centre of the edge, and on the corner of the table is, (a) (17 / 13 )3 / 2, (b) 2 / 1, (c) 17 / 13, (d), 5/4, 14. A monochromatic plane wave of speed c and, all aperture., The diagram illustrates successive wave fronts., After what time will some portion of the, wavefront XY reach P?, X, , P, , Y, , (a), , 3, 2c, , (b), , 2, c, , (c), , 3, c, , (d), , 4, c, , 15. The critical angle of a certain medium is sin1, , 3, the polarizing angle of the medium is:, 5, 4, , , (a) sin-1 5 , , 3, , , (c)tan-1 4 , , 5, , , (b) tan-1 3 , , 4, , , (d)tan-1 3 , , 16. In the case of linearly polarized light, the, magnitude of the electric field vector:, (a) Is parallel to the direction of propagation, (b) Does not change with time, (c) Increases linearly with time, (d) Varies periodically with time, 17. An optically active compound, (a) Rotates the plane of polarized light, (b) Changes the direction of polarized light, (c) Does not allow plane polarized light to pass, through, (d) None of these., 18. At what angle of incidence will the light, reflected from glass, ( 1.5 ) be completely polarized :
Page 2 :
(a) 72.80, (d) 56.30, , (b) 51.60, , (c) 40.30, , 26., interfere. Find the ratio, , young's experiment: Interference, 19. Two beams of light having intensities I and 4I, interfere to produce a fringe pattern on a screen., The phase difference between the beams is at, 2, , point A and at point B. Then the difference, between the resultant intensities at A and B is, (a) 2I, (b) 4I, (c) 5I, (d) 7I, 20. Two identical sources emitted waves which, produces intensity of k unit at a point on screen, where path difference is . What will be intensity, at a point on screen at which path difference is /4, (a), 21., , k, 4, , (b), , k, 2, , (c) k, , (a), 27., , 28., , (c) 1.54 103 m, (d) 1.44 103 m, 22. The two slits are 1mn apart from each of other, and illuminated with a light of wavelength, , 30., , interfere, , at, , a, , 31., , 32., , point, the, , amplitude of the resulting wave will be about, (a) 7, (b) 6, (c) 5, (d) 3., 24., , In interference if, , I max, 144, , then what will be, I min, 81, , 33., , the ratio of amplitudes of the interfering wave, (a), 25., , 144, 81, , (b), , 7, 1, , (c), , 1, 7, , (d), , 12, 9, , If one of the two slits of a Young's double slit, experiment is painted over so that it transmits half, the light intensity of the other, then –, (a) The fringe system would disappear, (b) The bright fringes will be more bright & dark, fringes will be more dark, (c) The dark fringes would be bright and bright, fringes would be darker, (d) Bright as well as dark fringes would be darker, , 1 , , (b), , 2, 1 , , (c), , 1, 1, , (d), , , 1 , , In young's double slit experiment, let A and B be, the two slits. A thin films of thickness t and, , , , , 29., , , , y 2 3 sin t , 3, , , 2 , , fringe width. The central maxima will shift by-, , In a double slit experiment using light of, wavelength 600 nm, the angular width of a fringe, on a distant screen; is 0.10. The spacing between, the two slits is :, (a) 3.44 104 m, (b) 1.54 104 m, , the slits, then the distance between third dark, fringe and fifth bright fringe is:, (a) 1.2 mm (b) 0.75 mm(c) 1.25 mm(d) 0.625 mm, 23. If two waves represented by y1 4 sin t and, , in the, , interference pattern –, , (d) Zero, , 5 107 m. If the distance of the screen is 1m from, , I max I min, I max I min, , 34., , 35., , 36., , t, , , , , (c), , t, , , (d) None, , In young's experiment total number of maxima, that can be obtained over screen with light of, wavelength 5000Å and d = 15000Å, (a) 3, (b) 7, (c) 5, (d) 6, In YDSE, the wavelength of light used is 6000Å., If path difference between waves reaching at a, point P on screen is 1.5 microns, then at point P –, (a) Second bright exist, (b) Second dark exist, (c) Third dark exist, (d) Third bright exist, YDSE is made in a liquid. The 10th bright fringe, in the liquid lies where 6th dark lies in vacuum., The refractive index of liquid is approximately –, (a) 1.8, (b) 1.54, (c) 1.67, (d) 2, In YDSE, the ratio of maximum and minimum, intensities of fringe system is 4 : 1. The amplitudes, of the coherent sources are in the ratio of –, (a) 1 : 1, (b) 3 : 1, (c) 1 : 4, (d) 5 : 1, The slits in Young’s double slit experiment have, equal width and the source is placed symmetrically, with respect to the slits. The intensity at the central, fringe is Io. If one of the slits is closed, the, intensity at this point will be, (a) Io, (b) Io/4, (c) Io/2, (d) 4Io, Interference fringes were produces in Young’s, double slit experiment using light of wavelength, 5000Å. When a thin film of material 2.5x103 cm, thickness is placed over one of the slits, the fringe, pattern shifted by a distance equal to 20 fringe, widths. The refractive index of the material of the, film is, (a) 1.25, (b) 1.33, (c) 1.4, (d) 1.5, The amplitude of the light waves emerging from, two slits in Young’s experiment is in the ratio of, 2:3. The intensity of the minima to that of the, consecutive maxima on the screen will be in the, ratio of:, (a) 2:3 (b) 4:9 (c) 1:9 (d) none of the above, In a Young’s set up for interference of light, Imax:Imin = 16:9. The ratio of the amplitude of the, two interfering sources is:, (a) 4:3, (b) 3:4 (c) 7:1 (d) 5:7, In Young’s double slit experiment the slits S1 and, S2 are illuminated by light of wavelength . P is a
Page 3 :
point on the screen. If there is no initial phase, difference between S1 and S2 and P corresponds to, fifth minima, then path difference S2P S1P is, equal to, (a) 10/2 (b) 11/2, (c) 9/2, (d) 5/2, 37. If the individual intensities of the two interfering, beams is Young’s double slit experiment are I1 and, I2, then the contrast between the maximum and, minimum intensity on the screen is good when:, (a) I1 is much greater than I2, (b) I1 is much smaller than I2, (c) I1 = I2, (d) Either I1 = 0 or I2 = 0, 38. In Young’s double slit experiment interference is, produced due to slits distance d metre apart. The, fringe pattern is observed on a screen distant D, metre from the slits. If in metre, denotes, the, wavelength of light, the number of fringes per, metre of the screen is, (a) D/d, (b) d/D, (c) d/D, (d) D/d, 39. In Young’s double-slit experiment, the separation, between the slits is halved and the distance between, the slits and the screen is doubled. The fringe width, is, (a) unchanged., (b) halved., (c) doubled, (d) quadrupled, 40. Two coherent monochromatic light beams of, intensities I and 4 I are superposed. The maximum, and minimum possible intensities in the resulting, beam are, (a) 5I and I (b) 5I and 3I (c) 9I and I (d) 9I and 3I, 41. In Young’s double slit experiment intensity at a, point is (1/4) of the maximum intensity. Angular, position of this point is:, (a) sin–1 (λ/d), (b) sin–1 (λ/2d), –1, (c) sin (λ /3d), (d) sin–1 (λ /4d), 42. In a Young’s double slit experiment, 12 fringes are, observed to be formed in a certain segment of the, screen when light of wavelength 600nm is used. If, the wavelength of light is changed to 400nm,, number of fringes observed in the same segment of, the screen is given by:, (a) 12, (b) 18, (c) 24, (d) 30, 43. In a Young’s double slit experiment the intensity at, a, , point where the path difference is, , , (λ being the, 6, , wavelength of light used) is I. If I0 denotes the, maximum intensity,, (a), , 3, 4, , (b), , 1, 2, , 3, 2, , To make the central fringe at the centre O, a, mica sheet of refractive index 1.5 is introduced., Choose the correct statement –, , , , , , , , , , (a) The thickness of sheet is 2 2 1 d in front of, S1, , (b) The thickness of sheet is 2 2 1 d in front of, S2, (c) The thickness of sheet is 2 2 d in front of S1, , , , , , (d) The thickness of sheet is 2 2 1 d in front, of S1, 46. A two-slit Young's interference experiment is, arranged as illustrated (Fig.); = 5000 Å. When a, thin film of a transparent material is put behind, one of the slits, the zero order fringe moves to the, position previously occupied by the 4th order, bright fringe. The index of refraction of the film is, n = 1.2. Calculate the thickness of the film., , (a) 5 µm, , (b) 8 µm, , (c) 10 µm, , (d) 12 µm, , single slit diffraction, 47. A slit of width a is illuminated by white light . For, 0, , red light ( 6500 A) , the first minima is, obtained at 300 .Then the value of a will be, 0, , (a) 3250 A, (c) 1.3microns, , I, is equal to, I0, (c), , 45., , (b) 6.5 10 4, (d) 2.6 10 4 cm, 0, , (d), , 1, 2, , 44. To demonstrate the phenomenon of interference, we require two soruces which emit radiation of, (a) of nearly the same frequency, (b) of the same frequency, (c) of different wavelength, (d) of the same frequency and having a definite, phase relationship., , 48. The light of wavelength 6328 A is incident on a, slit of width 0.2 mm perpendicularly , the angular, width of central maxima will be, (a) 0.360, (b) 0.180, (c) 0.720 (d) 0.090, 49. The penetration of light into the region of, geometrical shadow is called, (a) Polarisation, (b) Interference, (c) Diffraction, (d) Refraction, 50. A slit of size 0.15 cm is placed at 2.1 m from a, screen. On illuminated it by a light of wavelength, 5 10 5 cm . The width of central maxima will be, (a) 70mm (b) 0.14mm (c) 1.4mm (d) 0.o14cm
Page 4 :
51. A diffraction is obtained by using a beam of red, light .What will happen if the red light is replaced, by the blue light, (a) Bands will narrower and crowd full together, (b) Bands become broader and further apart, (c) No change will take place, (d) Bands disappear, 52. What will be the angle of diffracting for the first, minimum due to Fraunhoffer diffraction with, sources of light of wave length 550nm and slit of, width 0.55mm, (a) 0.001 rad (b) 0.01 rad (c) 1 rad (d) 0.1 rad, 53. Angular width ( ) of central maximum of, diffraction pattern on a single slit does not depend, upon, (a) Distance between slit and source, (b) Wavelength of light used, (c) Width of the slit, (d) Frequency of light, used, 54. If we observe the single slit Fraunhoffer, diffraction with wavelength and slit width e, the, width of the central maxima is 2 . On decreasing, the slit width for the same , (a) increase, (b) remains unchanged, (c) decrease, (d) increase or decrease depending on the, intensity of light, 55. A beam of light of wavelength 600 nm from a, distant source falls on a single slit 1 mm wide and, the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a, screen 2 m away . The distance between the first, dark fringes on either side of the central bright, fringe is, (a) 1.2 mm (b) 1.2 cm (c) 2.4 cm (d) 2.4 mm, 56. The condition for observing Fraunhofer diffraction, from a single slit is that the light wavefront, incident on the slit should be, (a) Spherical (b) Cylindrical (c) Plane (d), Elliptical, 57. Consider Fraunhoffer diffraction pattern obtained, with a single slit illuminated at normal incidence., At the angular position of the first diffraction, minimum the phase difference (in radians), between the wavelets from the opposite edges of, the slit is, (a) π / 4, (b) π / 2, (c) 2 π, (d) π, 58. A parallel monochromatic beam of light is incident, normally on a narrow slit. A diffraction pattern is, formed on a screen placed perpendicular to the, direction of the incident beam. At the first, minimum of the diffraction pattern, the phase, difference between the rays coming from the two, edges of the slit is:, (a) 0, (b) /2, (c) , (d) 2, 59. In an experiment, electrons are made to pass, through a narrow, slit of width ‘d’, comparable to, d, y=0, their de Broglie, wavelength. They, are detected on a, D, , screen at a distance ‘D’ from the slit (see figure), 60. Which of the following graphs can be expected to, represent the number of electrons ‘N’ detected as a, function of the detector position ‘y’ (y = 0, corresponds to the middle of the slit), y, , y, , (a), , (b), , N, , d, , N, , y, , y, , (c), N, , d, , (d), d, , N, , d, , 61. A beam of light of wave length 600 nm from a, distance source falls on a single slit 1 mm wide and, a resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a, screen 2m away. The distance between the first dark, fringes n either side of central bright fringe is, (a) 1.2 cm (b) 1.2 mm (c) 2.4 cm (d) 2.4 mm, 62. The diameter of the pupil of human eye id about, 2 mm. Human eyes is most sensitive to the, wavelength of 555 nm. the limit of resolution of, human eye is :, (a) 1.2min (b) 2.4 min (c) 0.6 min (d) 0.3 min, 63. Two points separated by distance of 0.1 mm can, just be inspected in a microscope when light of, wavelength 6000Å is used. If the light of, wavelength 4800Å is used then limit of resolution, will become :, (a) 0.8 mm (b) 0.12 mm (c) 0.1 mm (d) 0.08 mm