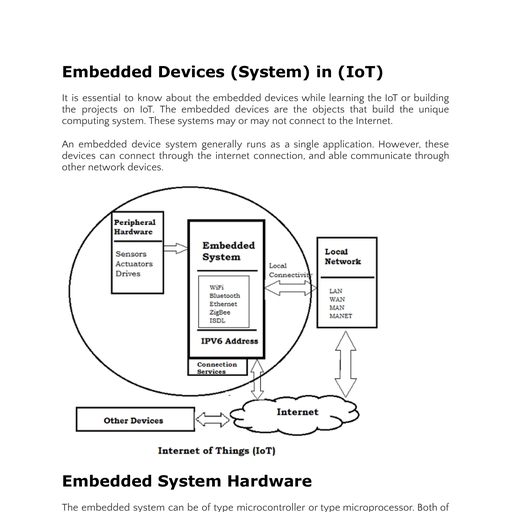
Page 1 :
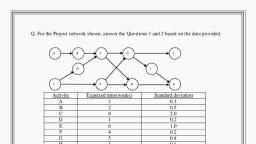
4) Critical Path: Path 1-3-5-7-8-10 with project duration of 22 weeks is the critical path., , 5.2.11.6. Floats and Slacks bunts —, , There are many activities where the maximum time available to finish the activity 1S more than, uired to complete it, i.e., its duration. The difference between the two ", , that activity. So there are two terms used in network analysis for calculation of project, , |) Floats, 2) Slack, , t, , 52.11.61. Float ri:, , Float indicates the free time associated with an event- It is the time available for an activity in ad, , {aration time. So, float or slack is the length of time an activity can be delayed de!, ‘ect. When activities have no slack time, this means that none of them can Pe J, , $-3=2 eT ., a ie -7-19 11:54
Page 2 :
‘, , Lx — Es = Tail slack Lp — Es = Head slack, 5-3=2 9-6=3, , , , , , , , , , , of Floats, There are four types of floats as shown in figure below:, , , , , , Type of Floats, , , , , , , , , , , , Total Float Interfering Float, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Free Float Independent Float, , , , , , , , , , 1) Total Float: The total float of an activity represents the amount of time by which it can, delaying the project completion date. In other words, it refers to the amount of free ti, activity which can be used before, during or after the performance of this a, difference between the total time available for the performance of an activity and, , performance. a
Page 3 :
For any activity, i-j, the total float can be calculated as follows:, Total Float = latest finish time — earliest finish time, , , , , , , , = latest start time — earliest start time, = latest finish time — earliest start time — duration of the activity, , Conclusion Drawn from Total Float Values ;, The value of total float for any activity is useful for drawing the following conclusions:, , , , Bee Value, |, hastens Zero i, Resources are not adequate and Resources are just sufficient to oure are, activity may not finish in time complete the activity or say the : ~ <p, v activity cannot be delayed, 4, Induct extra resources or Say critical One has the freedom, path needs crashing in order to the resources ba ac, reduce the negative float delayed by so m, . sae . a, 2) Interfering Float: Utilization of the float of an activit, , seco y may, and is likely to, Pda. fae, Other activities in the network. That part of the total float *ihigh gee a ae the float times., Successor activities is called interfering float. z F chon. in; the float, , ee a, ea <j
Page 4 :
2) Interfering Float: Utilization of the float of an activity may, and is likely to, affect the float f wea es |, , 3), , 4), , , , , , , , , , , other activities in the network. That-part of the total float which causes a reduction in, , successor activities is called interfering float., , Formulated as the difference between the latest finish time of the activity in question, starting time of the following activity, or zero, whichever is larger; it indicates the po, float which cannot be consumed without affecting adversely the float of the sub, , activities., Free Float: The free float is that part of the total float which can be used without, succeeding activities. Thus, it is that value of the float which is consumable when the, , (of the activity in question) are started at their earliest starting times., , , , Alternately, free float may be computed as follows. If the slack of float of an e, difference between the earliest and latest event times, we can calculate the slack, , of the tail event in respect of any activity. In that case,, Free float = Total float >Head slack, 5, , Independent Float: The independent float time of an activity is the amount of float time y, , without affecting either the head or the tail events.
Page 5 :
ee, , , , 4) Independent Float: The independent float time of an activity is the amount 0, without affecting either the head or the tail events., , f float time which, , , , , , , , It represents the amount of float time available for an activity when its preceding activities, their latest and its succeeding activities begin at their earliest time-leaving the minimum, , its performance. Any excess of this minimum time over the duration of the, independent float associated with it. The value of independent float is taken as foll, , Independent Float of an Activity = (Ty of the head event) — (Ty of the tail ev, activity), , Alternatively,, Independent Float = Free Float - Tail Slack, Characteristics of Floats, 1) Independent float < Free float < Total float. sail, 2) Only independent can be negative, the rest two floats are always positive or, 3) Activities with all floats is equal to zero, are critical activities.