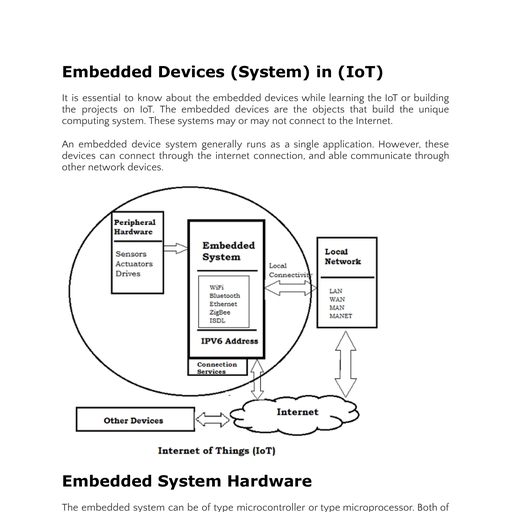
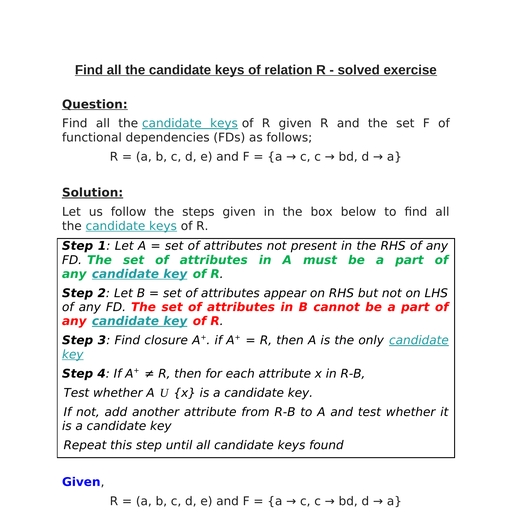
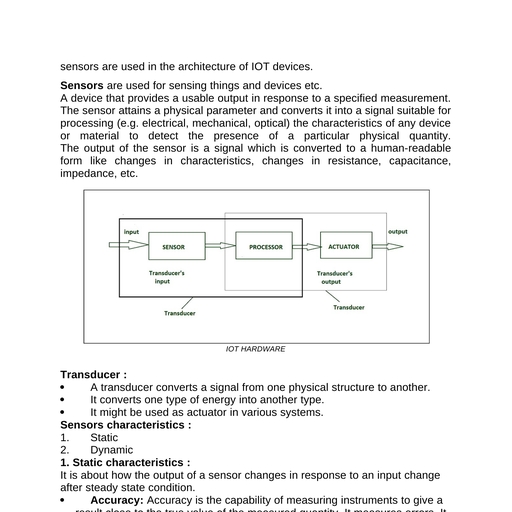
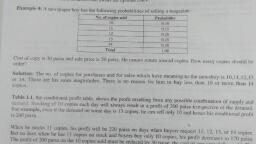
Page 1 :
Decision under Risk –, Making, this type of puoblem arises when the state of., nature s wnknown , but con the basis of objective, au empirical evidence it i possible to asšign, puobabilities to various states of nature., It is passible, and past experience to assign probabilities to, various possible state of nature., on the basis of hietorical dlata, Under, this condition Ihe various states of nature, and the long suun elative, assumed to, can be enumerated, frequency of their occuvrence, be knowon ., The information about the state of nature, ů puobabilistic ie decision maeer cannot, preedict as, a verult of his selecting, course of action., to what outcome will occur as, a particular, Each cowse of action sesults in more than, one outcome, therefore it is not simple to, calculate the exact monetary pay ofts.
Page 3 :
Steps foy calculating EMV, Stepl- Construct a, payoff matrix listing alli, possible courses of action aund state, of nature . -Enter the conditional pay., ff values associated with each poseible, combination, state of nature along with the, probabilities of the occurrence of, each state of 'nature., of cowrse of action and, Step 2- Calculate the EMV to4 each cowrse of, action by multiplying the conditional, pay-offs by the associated poobabi -, lities and add these values, toy each cowrse of action., weighted, Step3-Select the course of action that, yields the optimal EMv., (1) Expected Oppartunity Loss CEOL)-, An alterrative approach to maximizing, Expected Monetary value (EMv) s to, minimize the expected Opportunilg Loss, (EOL), also called Expected Value of, Regret., EOL is defined aus, the highest, state of nature and the actual psofit, obtained foy the, action taken:, the difference blw, psofit Cor payoff) for a, pasuticular course of, 2021-5-24 1