Page 1 :
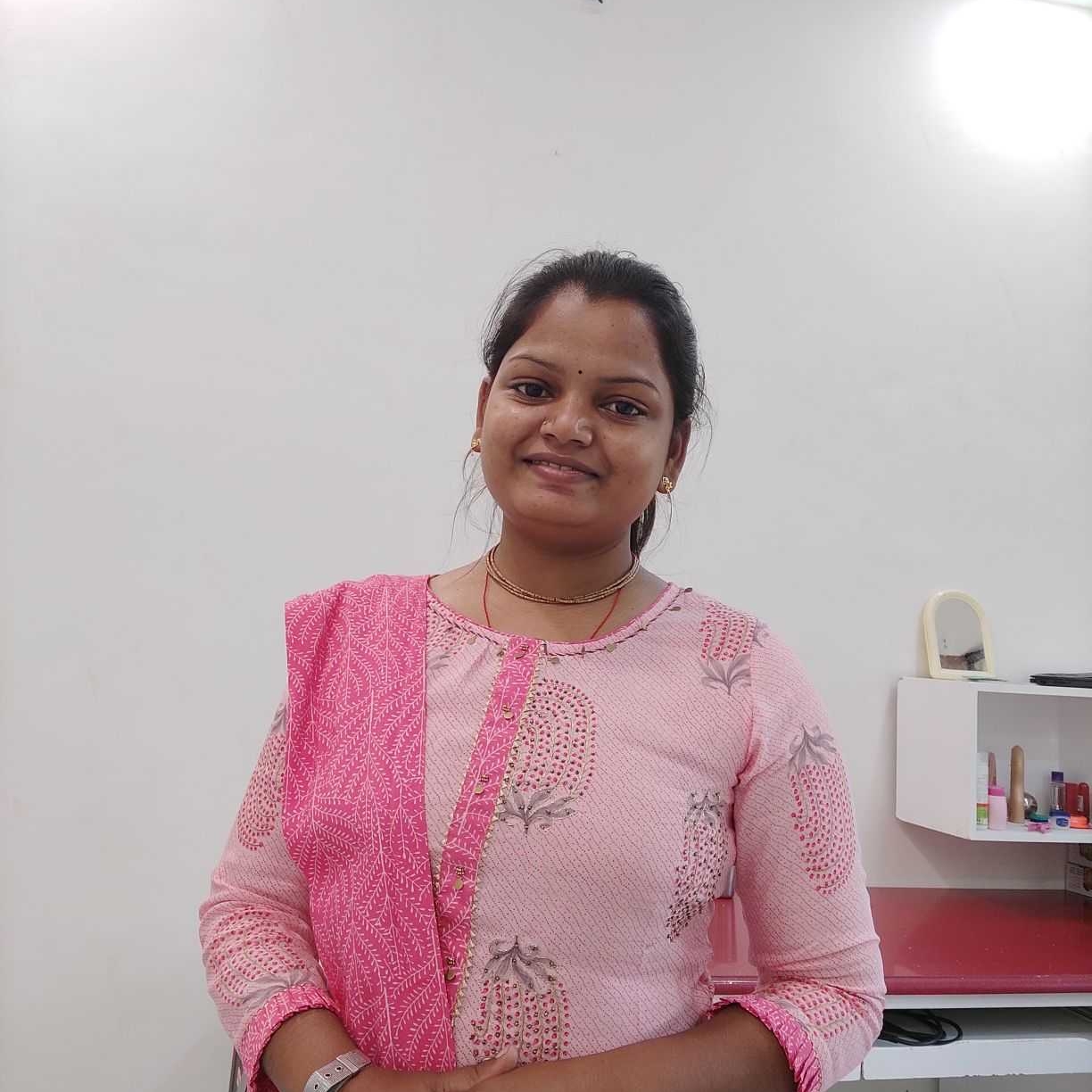
menjas eee NOL DE pardliei (0 Cee PO, , 4 - because the rate of substitution in different IC, ~ schedules need not necessarily be equal. Usually they vs, , are found different (Fig- 7): eb, 47 Straight line ICs indicate that the two goods are perfect iz by, substitutes (see Fig. 8). on, 3, ICs will be rectangular in case the two goods are non- aa 2, x substitutable (see Fig. 9)- 0 Nols X, &. A consumer has generally not one indifference curve Fig. 7, , but a set of indifference curves{A set of indifference, , curves is known as Indifference Map)It may contain any number of indifference curves,, ranked in the order of consumer’s preferences(A higher indifference curve represents a, higher level of satisfaction) Indifference map is shown in Fig. 10., , Ae, , , , vy, Y, 4, 2 E, = —_, fo, O, Apple rep 20 Apple x, f ., | Fig. 8 Fig.9, , | \ Applications or Importance of Indifference Curve Analysis, , The ordinal approach of consumer behaviour is very useful in every walk of life. It is, useful not only for consumption but also for production, exchange, distribution, investment, choice, taxation etc. Indifference curve analysis is an important tool for decision making., Following are the uses of indifference curve analysis; |, , LY Helpful in production function: It is useful in production function. The production, equilibrium of a firm will be decided on the basis of Iso-quants. Iso-quants give same, level of production from various combinations of two factors of production in the same, manner as indifference curves give same level of satisfaction from various combinations, of two commodities.In short, the IC is used to find out the producer's equilibrium., , 2 Helpful in exchange: It is useful in exchange between two individuals for the commodities, possessed by each of them.