Page 2 :
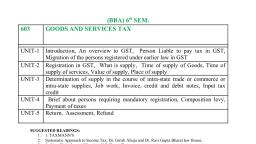
B.COM, , TH, 5, , SEMESTER, , GOODS AND, SERVICEs TAX
Page 3 :
INDIRECT TAX, Indirect taxes are those whose burden can be shifted to others so that those who pay these taxes to, , the government do not bear the whole burden but pass it on wholly or partly to others., Indirect taxes are levied on production and sale of commodities and services and small or a large, part of the burden of indirect taxes are passed on to the consumers ., , FEATURES OF INDIRECT TAX, Important source of revenue, Wider Tax-base, Check on Potential Increase in Consumption, Minimisation of Inequalities in Consumption Standard, Mobilisation of Resources for Capital Formation, Diversification of Resources
Page 4 :
Indirect Tax Structure in India, Central Taxes, , State Taxes, , •, •, •, , •, •, •, •, , •, •, •, , Central Excise duty, Additional duties of excise, Excise duty levied under, Medicinal, & Toilet Preparation Act, Additional duties of customs, (CVD & SAD), Service Tax, Surcharges & Cesses, , •, •, •, •, , GST, 4, , State VAT / Sales Tax, Central Sales Tax, Purchase Tax, Entertainment Tax (other than, those levied by local bodies), Luxury Tax, Entry Tax (All forms), Taxes on lottery, betting & gambling, Surcharges & Cesses
Page 5 :
GST IN INDIA, The, Constitution, (122nd, Amendment) Bill was introduced in, the Lok Sabha, , 2006, , 2011, , Announcement of GST by the Union, Finance Minister, during budget of 2006-07, that it would introduced from 1 April 2010, , May 2017, , All states, except J&K, passed their, SGST, , GST Council, recommends, all the rules, , 2014, Aug 2016, , March 2017, , Sep 2016, , GST Council Recommends, the CGST, SGST, IGST,, UTGST and Compensation, Cess Act, , 1st GST Council, Meeting, , April 2017, CGST, IGST, UTGST and, Compensation Cess Acts, passed, , The constitution, (101st, amendment) act, was enacted, , 30th June 2017, 1st July 2017, , GST Launched, , 5, , Constitution (115th Amendment) Bill introduced, and subsequently lapsed, , 8th July 2017, , SGST Act passed by J&K; CGST and IGST, Ordinances promulgated to extend GST to J&K, , Journey continues...
Page 6 :
GOODS AND SERVICES TAX IN INDIA, , , Goods and Services tax (GST) has been conferred by Article 246 A of the Constitution, which was introduced by the Constitution(101st amendment) Act 2016., , S.No, , Definition, , Article, , 1., , Goods, , 366(12), , 2., , Service, , 3., , State, , 4., , Goods, And, Services, Tax, , Definition, , Includes all materials, commodities, and articles ., , 366 (26A) Anything other than goods., 366(26B) With reference to articles 246A, 268, 269,269A and Article 279A, includes a Union territory with Legislature., 366(12A), , “Goods and services tax” means any tax on supply of goods, or, services or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for, human consumption.
Page 7 :
FEATURES OF THE GST, 1., , Applicable on supply of goods or services, , 2., , Destination based consumption taxation, , 3., , Dual GST in India, , 4., , Levy & collection of GST by the Centre (CGST) and the States (SGST). Centre to levy and collect, IGST on supplies in the course of inter- State supplies & imports, , 5., , HSN( Harmonised System of Nomenclature) is used for classifying goods and services, , 6., , All transactions and processes only through electronic mode – Non- intrusive administration, , 7., , PAN Based Registration, , 8., , Composition scheme for providing benefit to small businesses, , 9., , Seamless flow of credit.
Page 8 :
BENEFITS OF GST, 1. Elimination of cascading effect, 2. Self-Regulating Tax System, , 3. Benefits to Small Taxpayers, 4. Common National Market, 5. Reduction in Multiplicity of Taxes, 6. Overall Reduction in Prices, 7. Consumption Based Tax, , 8. Non-Intrusive Electronic Tax System, 9. Simplified Tax Regime, , 10. Protection of Domestic Industries
Page 9 :
GST –RELEVANT DEFINITIONS, ❖ Section 7 Supply includes all forms of supply of goods and/or services such as sale, transfer, barter,, , exchange, license, rental, lease, or disposal made or agreed to be made for a consideration by a person in, the course of business and also includes import of services for a consideration whether or not in the course, of business, ❖ Section 2(6) Aggregate turnover: means the total value of all taxable supplies, exempt supplies,, exports of goods and/or services, and interstate supplies of a person having the same PAN, computed on, the pan-India basis and excluding taxes. However, the value of inward supplies on which taxation is based, on reverse-charge mechanism shall not be admitted., ❖ Appropriate government refers to the Central Government for IGST, UTGST and CGST, and the State, Government for SGST., ❖ Section 2(74) Mixed supply means two or more individual supplies of goods and/or services made, together by a taxable person for a single price where such supply does not form a composite supply, ❖ Section 2(30) Composite supply means a supply consisting of two or more goods and/or services,, which are naturally bundled and provided together, one being a principal supply, ❖ Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) is a non-profit, public-private partnership company. Its, main purpose is to provide IT infrastructure and services to Central and State Governments, taxpayers, and, other stakeholders to facilitate the implementation of GST., ❖ Input tax credit means the credit of input tax
Page 10 :
GST –RELEVANT DEFINITIONS, ❖ Section 2(84) Person includes:, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , An individual, A Hindu undivided family, A company, A firm, A Limited Liability Partnership, An association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, in India or outside India, Any corporation set up by or under any Central, State, or Provincial Act or a government company as, defined in section 2(45) of the Companies Act, 2013 (18 of 2013), A body corporate incorporated by or under the laws of a country outside India, A cooperative society registered under any law relating to cooperative societies, A local authority, Central government or a State government., Society as defined under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 (21 of 1860), A trust, Every artificial juridical person, not falling within any of the preceding sub-clauses
Page 11 :
GST –RELEVANT DEFINITIONS, Section 2(17) “Business includes –, Any trade, commerce, manufacture, profession, vocation or any other similar activity, whether or not it is for a pecuniary, , , , , , , , , , benefit;, Any activity or transaction in connection with or incidental or ancillary to (a) above;, Any activity or transaction in the nature of (a) above, whether or not there is volume, frequency, continuity or regularity, of such transaction;, Supply or acquisition of goods including capital assets and services in connection with commencement or closure of, business;, Provision by a club, association, society, or any such body (for a subscription or any other consideration) of the facilities or, benefits to its members, as the case may be;, admission, for a consideration, of persons to any premises; and, services supplied by a person as the holder of an office which has been accepted by him in the course or furtherance of his, trade, profession or vocation;, Activities of race club including by way of totalistor or license to book maker or activities of a licensed book maker in such, club, Any activity or transaction undertaken by central government , state government or local authority in which they are, engaged as public authorities
Page 12 :
TYPES OF GST, • CGST(Central, Goods and, Service, Tax)levied and, collected by, Central, Government, , • UTGST(Union, Territory goods &, service Tax) levied, and collected by, Union Territory, , • SGST(State Goods, and Service, Tax)levied and, collected by State, Government, , CGST, , SGST, , UTGST, , IGST, • IGST(Integrated, goods and service, tax) is levied by, Central, government on, inter state supplies
Page 13 :
REGISTRATION UNDER GST, SECTIONS, , PARTICULARS, , SECTION 22, , PERSON LIABLE FOR REGISTRATION, , SECTION 23, , PERSON NOT LIABLE TO REGISTERATION, , SECTION 24, , COMPULSORY REGISTRATION WITHOUT THRESHOLD LIMIT, , SECTION 25, , PROCEDURE FOR REGISTRATION, , SECTION 26, , DEEMED REGISTRATION, , SECTION 27, , REGISTRATION BY NON- RESIDENT TAXABLE PERSON, , SECTION 28, , AMENDMENT OF REGISTRATION, , SECTION 29, , CANCELLATION OR SURRENDER OF GST REGISTRATION, , SECTION 30, , REVOCATION OF CANCELLATION OF REGISTRATION
Page 14 :
PERSON LIABLE FOR REGISTRATION (SECTION 22), A person is liable for registration:, 1. whose aggregate turnover will be 20 lakh rupees, 2. In case of special category states: 10 lakh, , CBIC has notified the increase in, threshold turnover from Rs 20 lakhs, to Rs 40 lakhs. The notification will, come into effect from 1st April 2019, , A person who on the day immediately preceding the appointed day, is registered, , under existing law, shall be liable to be registered with the effect from appointed, day., In case of transfer/succession of business or other reason , the transferee/successor, will be the person to get registered from the date of transfer., Registration is only required for a place of business from where taxable supply takes, place.
Page 15 :
COMPULSORY REGISTRATION –SECTION 24, Compulsory registration is required by :, 1. Person making any inter state taxable supply, Casual taxable person making taxable supply, 3. Person who are required for required to pay tax under reverse charge, 4. Electronic Commerce Operator, 5. Non-resident taxable persons making taxable supply, 6. Persons who are required to deduct tax under section 51, whether or not separately registered under this, Act, 7. Persons who make taxable supply of goods or services or both on behalf of other taxable persons whether, as an agent or otherwise, 8. Input Service Distributor, 9. Every person supplying online information and data base access or retrieval services from a place outside, India to a person in India, other than a registered person, 10. Such other person or class of persons as may be notified by the Government on the recommendations of, the Council., 2.
Page 16 :
PROCEDURE OF REGISTRATION (SECTION 25), Section 25(1), PARTICULARS, , WHERE TO APPLY, , Person registered under section 22 and, 24, , Casual taxable person/non resident, taxable person, , WHEN TO APPLY, , Within 30 days from the date when he, becomes liable for registration, In every state or UT in which he is, liable, , Atleast 5 days before the, commencement of the business, , Section 25(2) -State wise registration, Section 25(3) -Voluntary registration, Section 25(4)and (5) -Distinct person as per, section 25(6) -PAN is must for registration and section 25(7)- for non resident taxable person, any other document as may be prescribed, Section 25(8) SUO MOTO registration, Section 25(9)and (10) -Unique identity number(UIN), , , ,
Page 17 :
PROCEDURE OF REGISTRATION
Page 18 :
PROCEDURE OF REGISTRATION
Page 19 :
REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM, , , Section 2(98) Reverse Charge: Normally, the supplier of goods or services pays the tax, on supply. In the case of Reverse Charge, the receiver becomes liable to pay the tax, i.e., the, chargeability gets reversed
Page 20 :
REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM, WHEN IS REVERSE CHARGE APPLICABLE, 1. Supply from an Unregistered dealer to a Registered dealer, 2. Services through an e-commerce operator, 3. Supply of certain goods and services specified by CBEC, REGISTRATION UNDER REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM, Under Reverse Charge Mechanism who is liable to register is a person who pays taxes under, reverse charge is required to register under GST irrespective of the threshold and annual, threshold Limit is 20 lakhs (10 lakhs in case of Hill states and North Eastern State), THE MANNER OF PAYMENT OF GST UNDER THE REVERSE CHARGE, MECHANISM, As per section 49(4) of CGST Act’2017, ITC can be used for payment of output tax only., Therefore tax under reverse charge can be paid through cash only without availing the, benefit of ITC. The supplier must mention in his tax invoice whether the tax is payable on, reverse charge.
Page 21 :
SECTION 10 - COMPOSITION SCHEME, The Composition levy scheme is for small taxpayers. It is a voluntary and optional scheme., BENEFITS OF COMPOSITION SCHEME, 1. very simple, hassle free compliance scheme, 2. Simple Quarterly Return, 3. Quarterly payment of tax, TURNOVER LIMIT FOR COMPOSITION SCHEME, a registered taxable person, whose aggregate turnover(sum of value of all outward supplies), does not exceed Rs. 1.5 crores (Rs. 75 lakhs for special category States except J & K and, Uttrakhand) may opt for this scheme., REGISTRATION, Registration under GST law is compulsory for opting for the Composition scheme.
Page 22 :
SECTION 10 - COMPOSITION SCHEME, CONDITIONS AND RESTRICTIONS : Persons opting for composition levy has to comply, with following conditions:, The person opting for composition scheme is neither a casual taxable person nor a non-resident taxable person., The goods held in stock by person opting composition scheme have not been purchased from an unregistered supplier and, where goods are purchased from an unregistered supplier, the tax under reverse charge under section 9(4) has been paid., The person availing composition scheme shall pay tax under section 9(3)/9(4) (reverse charge) on the inward supply of, goods or services or both, The words “composition taxable person, not eligible to collect tax on supplies” has to be mentioned on the bill of supply, issued by composition taxable person; and, Such person shall mention the words “composition taxable person” on each notice or signboard at a prominent place at the, place of business., Such a person was not engaged in the manufacture of goods as notified under section 10(2)(e), during the preceding FY.
Page 23 :
SECTION 10 - COMPOSITION SCHEME, ELIGIBILITY: Persons not eligible to opt composition scheme are:, Service providers (other than the person engaged in the supply of food and drinks i.e. restaurant, services), , Producer of pan masala, or tobacco, ice cream, A non-resident taxable person, Casual taxable person, The person supplying goods through an e-commerce operator, , Supplier supplying exempt supplies
Page 24 :
INPUT TAX CREDIT, Input credit means at the time of paying tax on output, you can reduce the tax you have, already paid on inputs and pay the balance amount. This mechanism is called utilization of, input tax credit, The availability of Input Tax Credit (ITC) is to remove the cascading effect of taxes on, transactions, , , ELIGIBILITY FOR GETTING ITC (SECTION 16(1), Every registered person shall be entitled to ITC of GST charged on inward supply of, goods and / or services, ITC of GST will be available on goods and/or services which are bused in the course or, furtherance of the business
Page 26 :
INPUT TAX CREDIT, CONDITION FOR TAKING ITC (Section 16(2): A registered person will be entitled to, ITC on supply only if he fulfilled all four conditions:, 1. Possession of tax paying documents (section 16(2) with rule 36 of CGST RULE 2017), 2. Receipts of goods/and services (SECTION 16(2)(b), 3. Tax leviable on supply actually paid to government(section16(2)(c), 4. Filing of return(section 16(2)(d), TIME LIMIT FOR AVAILING ITC (SECTION 16(4):, The due date of filing GST Return for September of succeeding Financial year, OR, Date of filing the Annual Returns relevant for that Financial year
Page 27 :
APPORTIONMENT OF CREDIT(Section 17), APPORTIONMENT OF CREDIT (section 17): A registered person shall, be eligible for apportionment of credits of goods & services in the, following manner:, Input shall be restricted to the use by business partly for business and, partly for others., Input shall be restricted for the taxable & zero rated supplies partly for, taxable supplies including zero rated supply and partly for exempt supplies.
Page 28 :
blocked credit- Sec 17(5), The various goods and services on which credit is blocked are:, 1.Motor vehicle and other conveyance and related services(insurance, servicing and repair and, maintenance), 2. Supply of goods and services such as:, Food and beverages ,Outdoor catering,Beauty treatment, Health services,Cosmetic and, plastic surgery, Membership of club, health and fitness center, Travel benefits extended to its, employees on vacation:, 3. Work contract service for construction of immovable property, 4. Self construction of immovable property, 5. Inward supplies charged to tax under composition levy, 6. Inward supplies received by non-resident taxable person, 7. Inward supplies used for personal consumption, 8. Goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed of by way of gift / free sample, 9. No ITC in fraud cases: No benefit is given by law relating to any fraudulent transaction done, by the tax payer, thereby implying that ITC cannot be availed which has resulted into non or, short tax payment, excessive refund or ITC unutilized.
Page 29 :
E WAY BILL ( SECTION 68), Electronic way bill (E WAY BILL) is an electronic document issued by a carrier giving, details and instructions relating to the shipment of a consignment of goods., Section68 empowers the Government to prescribe rules to mandate the “person in charge of, conveyance carrying any consignment of goods exceeding such amount as specified” to carry, prescribed documents/ devices., Rules 138 of CGST RULE 2017 prescribe e way bill as a document to be carried for the, consignment of goods ., WHEN IS REQUIRED TO BE GENERATED(RULE 138(1):, Every Registered Person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding, Rs. 50000/. Movement should be, 1. in relation to supply; or, 2. for reasons other than supply; or, 3. due to inward supply from an unregistered person,
Page 30 :
E WAY BILL ( SECTION 68), WHO CAN GENERATE E WAY BILL: E way bill can be generated by, 1. The consignor; or, If the transportation is being done in own/hired conveyance, or by railway or by air or by vessel, 2. The consignee; or, 3. The transporter if goods are handed over to the transporter, INFORMATION TO BE FURNISHED:, , PART A, , • To be furnished by the registered person who is causing, movement of goods., , PART B, , • To be furnished by the person who is transporting the, goods.
Page 31 :
E WAY BILL ( SECTION 68), VALIDITY OF E WAY BILL:, DISTANCE, , VALIDITY PERIOD, , Up to 100 km, , 1 day in case other than over dimensional cargo**, , For every 100 km or part thereof after 1 additional day in case other than over dimensional cargo, For every 20 km, , 1 Day in case of Over Dimensional Cargo, , For every 20 km or part thereof after, , 1 additional dayay in case of Over Dimensional Cargo, , **over dimensional cargo means a cargo carried as a single indivisible unit which exceeds the dimensional limits prescribed in rule 93 of Central, MotorVehicle Rules 1989, , CANCELLATION OF EWAY BILL:, If goods are either not transported or not transported as per the details furnished in the, EWAY bill., Can be cancelled within 24 hours from the time of generation.
Page 32 :
ASSESSMENT UNDER GST, , , Assessment means determination of tax liability under GST law, , TYPES OF ASSESSMENT UNDER GST, Assessment, , By tax payer, Self assessment, , By tax authority, Provisional, assessment, , Summary, Assessment, , Scrutiny of, returns, , Best judgement, assessment, , Non filers, , Unregistered, persons
Page 33 :
ASSESSMENT UNDER GST, SECTION 59 – SELF ASSESSMENT The taxable person is required to pay tax on the basis of self-assessment, done by him. Hence, all GST return filings are based on self-assessment by the taxpayer .In other words;, Every registered taxable person shall himself assess the taxes payable and furnish a return for each tax period., This means GST continues to promote self-assessment just like the Excise, VAT and Service Tax under current, tax regime., SECTION 60 – PROVISIONAL ASSESSMENT Provisional assessment can be conducted for a taxable person, when the taxpayer is unable to determine the value of goods or service or both or determine the rate of tax, applicable thereto, PROCEDURE FOR PROVISIONAL ASSESSMENT, Step 1: The taxable person has to give, the concerned GST officer, a request for provisional assessment in, writing., Step 2: The GST officer on reviewing the application, will pass an order, within a period not later, than ninety days from the date of receipt of the request, allowing payment of tax on provisional basis or at, a GST rate or on such value as specified by him, Step 3: The taxable person, who is making payment on provisional basis, has to issue a bond with a security, promising to pay the difference between provisionally assessed tax and final assessed tax., Step 4: The GST officer will pass final assessment, with a period not exceeding six months from the date of, communication of order of provisional payment.
Page 34 :
ASSESSMENT UNDER GST, SECTION 61- SCRUTINY ASSESSMENT A GST officer can scrutinize the return to verify its, correctness. The officer will ask for explanations on any discrepancies noticed in the returns., BEST JUDGEMENT ASSESSMENT, Section 62- Assessment of non-filers of returns If a registered taxable person does not, file his return even after getting a notice, the proper officer will assess the tax liability to, the best of his judgment using the available relevant material., Section 63- Assessment of unregistered persons This assessment is done when a, taxable person fails to obtain registration even though he is liable to do so., The officer will assess the tax liability of such persons to the best of his judgement. The, taxable person will receive a show cause notice and an opportunity of being heard., SECTION 64 – SUMMARY ASSESSMENT Summary Assessment is done when the assessing, officer comes across sufficient grounds to believe any delay in showing a tax liability can harm, the interest of the revenue. To protect the interest of the revenue, he can pass the summary, assessment with the prior permission of the additional/joint commissioner.
Page 35 :
GST COUNCIL- article 279A, Goods & Services Tax Council is a constitutional body for making, , recommendations to the Union and State Government on issues related to Goods, and Service Tax., GST Council came into force on 12 th September, 2016, President constituted the GST Council on 15 th September, 2016, STRUCTURE OF GST COUNCIL, Chairperson – Union Finance Minister, Vice Chairperson - to be chosen amongst the Ministers of State Government, Members:, ❑ the Union Minister of State in charge of Revenue or Finance, ❑ the Minister in charge of Finance or Taxation or any other Minister nominated, by each State Government
Page 36 :
ROLE AND FUNCTIONS OF GST COUNCIL, ❖ The Goods and Services Tax Council shall make recommendations to the Union and the States on—, the taxes, cesses and surcharges levied by the Union, the States and the local bodies which may be, , , , , , , , , , subsumed in the goods and services tax;, the goods and services that may be subjected to, or exempted from the goods and services tax;, model Goods and Services Tax Laws, principles of levy, apportionment of Goods and Services Tax, levied on supplies in the course of inter-State trade or commerce under article 269A and the, principles that govern the place of supply;, the threshold limit of turnover below which goods and services may be exempted from goods and, services tax;, the rates including floor rates with bands of goods and services tax;, any special rate or rates for a specified period, to raise additional resources during any natural, calamity or disaster;, special provision with respect to the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir,, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand; and, any other matter relating to the goods and services tax, as the Council may decide.
Page 37 :
ROLE AND Functions of gst council, ❖ The Goods and Services Tax Council shall recommend the date on which the goods and, , services tax be levied on petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly, known as petrol), natural gas and aviation turbine fuel., ❖ The Goods and Services Tax Council shall be guided by the need for a harmonized, structure of goods and services tax and for the development of a harmonized national, market for goods and services.., ❖ The Goods and Services Tax Council shall establish a mechanism to adjudicate any dispute, between the Government of India and one or more States; or, between the Government of India and any State or States on one side and one or more other, , States on the other side; or, between two or more States, arising out of the recommendations of the Council or, implementation thereof.