Page 2 :
Database Security, ●, , Database security is the protection of the database against intentional and, unintentional threats that may be computer based or non-computer based.It, involves protection a database from unauthorised access and malicious, destruction and even any accidental loss and misuse
Page 3 :
Need of data security, 1., 2., 3., 4., , It must protect the database and servers on which they reside., It must administer and protect the rights of internal database users., It must Guarantee the confidentiality of customers as they access database., With increase in internet continually growing the threat to data travelling over, network increases
Page 4 :
Levels of security measures, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Physical, Human, OS, Network, Database System
Page 5 :
Data Security Requirement, 1. Confidentiality, 2. Integrity, 3. Availability
Page 6 :
Types Of DB Users, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , Sophisticated user, Database Designer user, Naive user, Application Programmers, Database Administrator, Specialized user
Page 7 :
Function OF Database Administrator, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , Storage Structure, Integrity Constraints Specification, Schema definition, Backup and recovery, Physical Organisation Modification, Granting authorization
Page 8 :
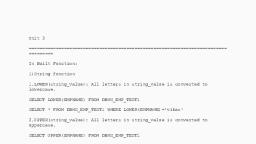
Creating User, ●, , Creating User:Database having many users.Each user must have user account.DBA have a, authority to specify new users,Specify user roles and grant general privileges for users., Create User Username identified by password, Create user dbtest identified by dbtest
Page 9 :
Altering and deleting User, ●, , We can change the database user password by altering the user, Alter User username identified by password, Alter user dbtest identified by dbmstest1, , ●, , We can delete the database user using drop command, Drop user username, Drop user dbtest
Page 10 :
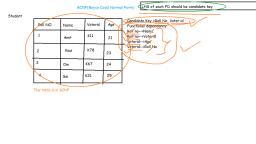
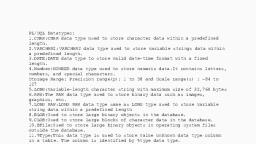
Database Privileges, ●, ●, , The set of action that use can perform on database object are called the privileges., Privileges is right to execute particular SQL statement on database., Types of database:, , 1., 2., , System privileges, Object privileges
Page 11 :
System privileges, ●, ●, , A system privileges is right to perform a particular action on any object of particular type.Object, such as table,view,synonyms,indexes,sequences,PL-SQL function,procedure etc, CREATE object : Allows the user to create the specified object in their own schema., , Create table,Create sequence,Create index,Create view, ●, , CREATE ANY object: Allows users to create the specified object in any schema, Create any table,Create any sequence,Create any index,Create any view
Page 12 :
Object Privileges, ●, ●, ●, , Object privileges are rights and restrictions to change content of database objects., User requires object to manipulate the content of object within database., Once we have created object in database after some time there may be few changes, needs to be introduced in object., Privilege, , Description, , SELECT, , Privilege to perform SELECT statements on the table., , INSERT, , Privilege to perform INSERT statements on the table.
Page 13 :
Object Privileges, Privilege, , Description, , UPDATE, , Privilege to perform UPDATE statements on the table., , DELETE, , Privilege to perform DELETE statements on the table., , REFERENCES, , Privilege to create a constraint that refers to the table., , ALTER, , Privilege to perform ALTER TABLE statements to change the table definition., , INDEX, , Privilege to create an index on the table with the create index statement., , ALL, , All privileges on table.
Page 14 :
Grant privileges, Grant: use to grant privileges on tables ,views and procedures to other users or roles, Grant select,update,insert on emp to dbmstest;, , Grant all on emp to dbmstest1;, Grant Update(name),Insert (ID,name) on emp to dbmstest;
Page 15 :
Revoke Privileges, Revoke:Use to take back privileges granted to other users and role, Revoke select,update,insert on emp to dbmstest;, , Revoke Update on emp to dbmstest1;
Page 16 :
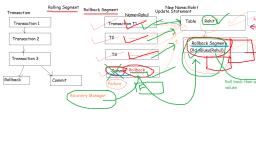
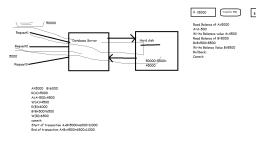
Transaction, It is a set of operations used to perform a logical unit of work., It represents changes in database e.g ATM ,Money transfer, Operations:, Read, Write, 3. Commit:permanently save the changes done in the transaction in tables/databases., 4. Rollback:undo the transactions that have not been saved in database., , ●, ●, ●, 1., 2.
Page 17 :
ACID Properties, 1. Atomicity: Either all or none, 2. Consistency: Before transaction start and after transaction completed sum of, total money should be same, , 3. Isolation: Converting parallel schedule to serial schedule, 4. Durability: Changes should be permanent
Page 18 :
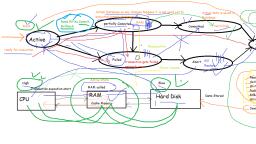
States of Transaction, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Active, Partially Committed, Failed, Aborted, Terminated
Page 19 :
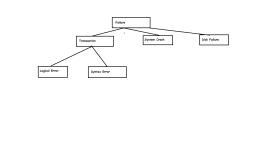
Types of Failures, To find that where the problem has occurred, we generalize a failure into the following categories:, ●, , Transaction failure:The transaction failure occurs when it fails to execute or when it reaches a point, from where it can't go any further. If a few transaction or process is unable to execute, then this is, called as transaction failure. Such as Logical error:If a transaction cannot complete due to some code, error or an internal error condition, then the logical error occurs. and Syntax Error: It occurs where the, DBMS itself terminates an active transaction because the database system is not able to execute it., For example, The system aborts an active transaction, in case of deadlock or resource unavailability.
Page 20 :
Types of Failures, , ●, , System crash:System failure can occur due to power failure or other hardware or, , software failure. e.g Operating system error., ●, , Disk failure:Disk failure occurs due to the formation of bad sectors, disk head crash, and, , unreachability to the disk or any other failure, which destroy all or part of disk storage.
Page 21 :
Causes of failure, 1., 2., 3., , 4., 5., , System Crashes:In this case system gets hang and need to restart.These failures occur due to, hardware malfunction or OS itself., User Error:unintentional deletion of row or table., Carelessness:Carelessness with destruction of data i.e The process of destroying data stored on, tapes, hard disks and other forms of electronic media so that it is completely unreadable and, cannot be accessed or used for unauthorized purposes., Intentional data corruption:Intentionally corrupt data ,hardware or software., Statement Failure:Running user program the transaction may have multiple statements and one, of that gets failed due to various reason.
Page 22 :
Causes of failure, ●, ●, ●, ●, , Application software error:Logical error in program., Network Failure:Network gets disturb due to this communication between client and server gets, failed., Media Failure:Hard disk gets failed., Natural Physical disasters:Data loss due to fire,floods,earthquakes,power failures.
Page 23 :
Types of backups, 1. Physical backup, 2. Logical backup
Page 24 :
Database Recovery, ● If any database failure effects the operation of database system then, database must be received and return to normal operation., ● Recovery is protecting the database and associated users from, unnecessary problems and avoid or reduce the possibility of having to, duplicate work manually.
Page 25 :
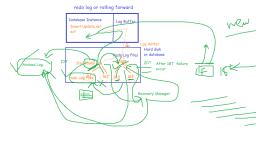
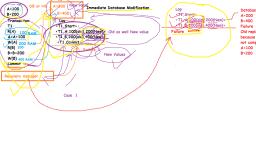
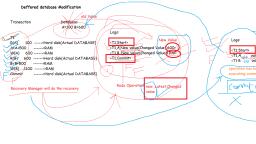
Recovery Techniques, ●, , ●, ●, , Recovery techniques are heavily dependent upon the existence of special file, known as system log.It contains information about the start and end of each, transaction and any updates which occurs in transactions., The logs keeps track of all transaction operations that affects the database, items.this information is needed to recover from transaction failure., To undo the a transaction the log must contain a copy of every database record, before it was changed such record are called as before-images.
Page 26 :
Recovery Techniques, ●, , To redoing the transaction the log must contain a copy of every database record after it, was changed these records are called after images., , Log entry information:, ●, ●, ●, ●, ●, ●, , Start transaction(T), read_item(T,X), Write_Item(T,X,Old_value,new_value), Commit, Abort, checkpoint
Page 27 :
Log based recovery mechanism, ● Deferred database modification, ● Immediate database modification
Page 28 :
Types of Recovery Techniques, ●, ●, , Rollback segment or Rolling back, Redo Log or Rolling Forward