Page 1 :
UNIT - I, , Introduction to MS Excel, , Introduction:, MS Office Excel – 2007 do provide powerful tools and features that can be used to analyse,, share, and manage data with ease. It do provide graphical user interface that makes it easy to, work, commands and features are available on task-oriented tabs that contains logical groups, combines, Drop down galleries display available options along with tooltip as well as previews., , MS Excel, It is a Microsoft office package with powerful spreadsheet or worksheet application that can be, used for managing, analyzing and presenting data in a graphical way., Examples: LOTUS 123, Quatro-Pro, Multiplan, Soft Calc, VP Planner, MS Excel., , Spreadsheet:, Spreadsheet or worksheet can be defined as any grid or arrays of text and numbers in rows and, columns used to calculate., , Features of MS Excel, 1. Trust Center: We can protect ourselves from malicious macros by disabling the macros except, those in workbooks that are stored in trusted locations on our personal computer., 2. PDF Add-in: Allow us to create an industry standard Adobe PDF file directly using Add in, available from Microsoft., 3. Table Header rows: Table header rows can be turned on or off when we move around in, worksheet., 4. Improved zooming: Zoom control or slider is available on right side of status bar used to, quickly zoom in or out on worksheet contents., 5. Color schemes: Appearance of Excel can be changed by applying one of three color schemes, (BLUE, SILVER, BLACK)., 6. Resizable formula bar: When editing lengthy formulas, we can increase or decrease height of, the formula bar by just clicking on bottom border of formula bar., 7. Lots of new templates: Templates are the new patterns available with Microsoft package to be, used regularly by the most need work., 8. Modern look with office art: We can design almost anything with charts.
Page 2 :
Advantages of Electronic Worksheet i.e. Spreadsheet, 1. Spreadsheet facilitates to draw graphs that show data using pictorial form called graphics., 2. Quick evaluation and analysis is possible with earlier and present reports generated by the, spreadsheets., 3. Computations or mathematical calculation is done very easily with formulas., 4. Annual reports can be generated based on monthly salary, which is easily prepared using, spreadsheets., 5. Sales analysis can be made very easily using spreadsheets., , Parts of a Spreadsheet, Rows: Rows are numbered from top to bottom at left edge of the worksheet such as 1, 2, 3, …,, upto 10,48,576., Columns: Columns are labeled from left to right with letters such as A, B, C, …., XFD (16,384), Cells: It is an intersection of row and column Example: A1: the upper most cell., Active Cells: The Cell with a border around, pointed for entering the data., Range of Cells: Two or more adjacent cell are referred as range of cells, these are identified with, first and last cell addresses., Worksheet: It is a collection of cells; it may contain all the data pertaining to a certain, application. Worksheet can be named as per the data contained in it., Cell Pointer: The cursor that takes us from one cell to another is called cell pointer. At any point, of time it is always pointing to a cell., Data: Raw facts and figure is commonly referred to as data included in spreadsheets., Workbook: Commonly referred as file that can store number of worksheets as well as charts, together. By default it can have only 3 worksheets or spreadsheets., Cell Address: An intersection of column name and row number identifies location of each cell., Example: A1, B10, …, Size of Worksheet: In a complete worksheet of excel has 16,384 columns and 10,48,576 rows., Thus in a complete worksheet there are 17,179,869,184 cells, i.e. cross multiplication of no. of, rows and no. of columns. 16384 X 10,48,576 = 17,179,869,184.
Page 3 :
How to get started with MS-EXCEL:, 1. Click on start button., 2. Choose program option and then choose Microsoft office and then lastly click on Microsoft, Excel 2007., , Parts of MS-EXCEL Window:, Parts of MS Excel window are illustrated in the following figure:, Minimize window button, Active Cell Indicator, , Maximize/Restore button, Window Close button, , Name box, , Formula bar, , Quick Access toolbar, Office button, , Application Close button, Column letters, Ribbon, , Sheet tab, Sheet tab scroll buttons, Row numbers, , Title bar, , Maximize/Restore button, , Minimize Application butoon, , Status bar, , Zoom control Slider, , Page View Buttons, Horizontal scroll bar, , Vertical Scroll bar
Page 4 :
Office button: This button is leads to lots of commands for working with document/Excel in, general., Quick Access Toolbar: It is a toolbar that we customize to hold commonly used commands., Title bar: All windows programs have a title bar, which displays the name of the program and, the name of the current workbook and also holds some control buttons that you can use to, modify the window., Application Close button: Clicking this button close the MS Excel., Maximize/Restore button: Clicking this button increases the application size to fill entire screen, space. If the application window is already maximized, clicking this button will restores excel, window down to its previous window size so that it no longer fills the entire screen., Minimize application button: Clicking this button minimize the application to get settled on to, status bar only., Ribbon: It is the main location to find Microsoft Excel’s Commands. Clicking any of the tab, changes the Ribbon buttons that appear on the bar., Window Close button: Clicking this button closes the active workbook window., Maximize/Restore Window button: Clicking this button increases the workbook windows size, to fill entire workspace. If the window is already maximized, clicking this button will restores, workbook window down to its previous window size so that it no longer fills the entire screen., Minimize Window button: Clicking this button will minimize the workbook window down to, the application., Active Cell Indicator: The dark outline surrounding the cell is called as Active cell, Indicator/Selector, that indicates the currently active cell i.e. one of 17,179,869,184 cells on each, worksheet., Column letters: Letters ranging from A to XFD one for each of the 16,384 columns worksheet., When we click on column heading selects an entire column of cells., Formula bar: When we enter information or formulas in to excel worksheet, they appear in the, formula bar., Sheet tabs: Each of the tabs represents a different sheet in the workbook. A Workbook can have, any number of sheets and each sheet has its name displayed in a sheet tab, by default each new, workbook that you create contains three sheets. We can add some more sheets by clicking the, Insert Worksheet button (Which is displayed after the last sheet tab)., Sheet tab Scroll buttons: These buttons allow us to scroll the sheet tabs to display tabs that are, not visible.
Page 5 :
Row Numbers: Numbers range from 1 to 10,48,576 one for each row in the worksheet. We can, click a row number to select an entire row of cells., Horizontal scrollbar: Allow us to scroll the sheet horizontally., Vertical scrollbar: Allow us to scroll the sheet vertically., Page view buttons: These buttons allow us to change the way worksheet is displayed., Status bar: It displays various messages as well as the status of the Num Lock, Caps and Scroll, Lock keys on the keyboard. It also shows summary information about the range of cells that is, selected and viewed by right clicking on status bar and allows us to change the information that, is displayed., Zoom control: It is a Slider control that allows to zoom worksheet content in and out., , Difference between MS Excel 2003 vs MS Excel 2007, Characteristic / Features, Number of Rows, Number of Columns, , MS Excel, 2003, 65,536, 256, , Amount of Memory used, , 1 GB, , Number of Colors, Number of Conditional formats per cell, Number of levels of Sorting, Number of levels of Undo, Number of items shown in the Auto Filter dropdown, The total number of characters that can display in a cell, Number of unique styles in a workbook, Maximum number of characters in a formula, Number of levels of nesting in a formula, Maximum number of function arguments, , 56, 3, 3, 16, 1,000, 1,000, 4,000, 1,000, 7, 30, , Regular activities that can be performed in MS Excel – 2007 are:, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., , Insertion to worksheet, Deleting worksheet, Renaming worksheet, Moving worksheet, Copying worksheet, Entering and editing data in a worksheet and Adding or deleting values., , MS Excel, 2007, 10,48,576, 16,384, Maximum allowed, by windows, 4.3 billion, Unlimited, 64, 100, 10,000, 32,000, 64,000, 8,000, 64, 255
Page 6 :
Performing activities in MS EXCEL -2007, Add/Delete Sheets within a workbook, Insertion or Adding worksheet into workbook:, By default workbook opens with three worksheets (Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3). Additional, worksheets can be inserted as and when we need. The new worksheet is always inserted to the, left of the selected worksheet but can be moved to any place afterwards., Procedure:, , Deletion of worksheet from workbook:, Worksheets that are no longer required can be deleted from the workbook. If there is existing, data on that worksheet, process will confirm the deletion of specific worksheet but will not allow, the user to undo the process., Procedure:, ➢ Click on an existing worksheet, ➢ Click Home tab: Delete button, ➢ Select or click on Delete sheet command., , Renaming worksheet: By default workbook opens with three worksheets (Sheet1, Sheet2, and, Sheet3). However, worksheets can be renamed to give more recognizable names that can, correspond to the data stored on them. Worksheet name is restricted to 31 characters and cannot, include special character (*. ?. [, ], etc.)., Procedure:, ➢ Double Click on preferred worksheet, ➢ Type the new worksheet name and press enter button to apply
Page 7 :
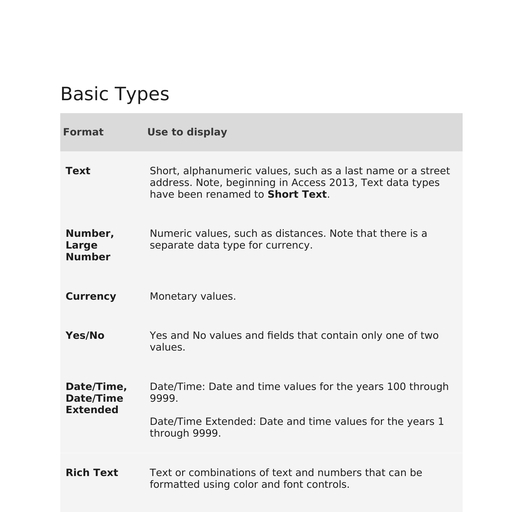
Moving worksheets: MS Excel do provide the facility to re-arrange worksheets into a preferred, order regardless of where they were created in that workbook., Procedure:, ➢ Select the preferred worksheet, ➢ Drag the worksheet tab to its new location in that workbook., , Copying worksheets: A very efficient method of duplicating the data layout on a worksheet is, to make a copy of that worksheet. Excel provides a process in which the user can create exact, duplicates of existing worksheets., Procedure:, ➢ Select the preferred worksheet, ➢ Hold down control key and drag the worksheet tab to its new location in that workbook creates a, copy of selected worksheet., , Entering / Editing data in Worksheet, Data can be defined as raw fact and figures; it describe the information entered into worksheet, cell such as: labels, values dates and formulas., Labels: Labels/text are any alphanumeric entry. It can be upto 32767 characters long including, spaces although only the first 1024 characters will display in the cell. Labels are left aligned by, default. Most importantly labels can overlap into adjacent cells as long as there is no other data, in those cells., Example: Ashok, 123 Main Street, 555-12-3456, (415) 555-1212, Values: Values or numbers are any numeric entry. Values cannot contain spaces, dashes, slashes,, etc. Values should be entered without any formatting (Eg: currency). Values donot show decimal, places unless they are required and can be formatted later. By default values are right aligned., Example: 10000, 125.75, 55.05, 7025.5, Dates: Dates are numeric values that are automatically formatted as a readable date entry. Dates, follow the same rules as entering values. As date and time are values, they can be added,, subtracted, and included in other calculations. Excel stores dates as sequential numbers, such as, 1 January 2008 can be stored as 39448 sum of days since January 1, 1900.
Page 8 :
Note: MS Excel interprets the year as follows:, 1. 00 through 29: Excel interprets the two-digit year values from 00-to-29 as years 2000 to, 2029. Example: 5/28/19(M/DD/YY) as May 28, 2019., 2. 30 through 99: Excel interprets the two-digit year values from 30-to-99 as years 1930 to, 1999. Example: 2/20/82(M/DD/YY) as February 20, 1982., Formulas: Formulas allow users to perform simple and complex calculations in an Excel, worksheet. All formulas start with an equal (=) sign or Symbol, it is important to note that, formulas use cell addresses rather than direct values so that we can link values contained in those, cells. Remember that formulas must not include their own cell in their formula result into an, error called “Circular Reference”., Example: =C1+C2+C3, =D5*E2, =E7-E8, F2/D2, etc., , Making changes the entered data editing the text and mumber:, To edit text or number in the cell which already contains some data, first place the cell pointer, where you want to edit the text / number, then press function key F2 and at the same time the, cursor will appear there. Thus we can edit the text / number / date / formula as we wishes., , How to exceed values in Column width:, Unlike labels, values must fit into the cell they are entered, otherwise a series of numeric symbols (#####), will appear in the cell until that column is made wider. In order to fix this situation, the column width (the, separator between columns) needs to be adjusted wider to accommodate that value., , Solutions:, Single Column: To change the width of one column, drag the boundary on the right side of the, column heading until the column is the width that we want., Multiple columns: Select the columns we want to change, then drag the boundary to the right of, a selected column heading., To fit the contents: Select the column or columns we want to change, then double click the, boundary to the right of a selected column heading., All columns in Worksheet: Click the Select All button, then drag the boundary of any column.
Page 9 :
Saving a Workbook (Ctrl + S): When we finish working in Excel worksheet it must be saved to, get back the worked data again and again, it can be performed either in following ways:, Method I., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Click the Microsoft Office button to display menu options., Click the Save option button that displays the Save dialogue box on screen., Select the folder where we want to save the file., Type Descriptive name for the file in the File name box., Click on Save button to save the file in the selected folder., , Method II., 1. Press Control + S shortcut key in keyboard that displays the Save dialogue box on screen., 2. Select the folder where we want to save the file., 3. Type Descriptive name for the file in the File name box., 4. Click on Save button to save the file in the selected folder., , Opening a Workbook (Ctrl + O): Whenever we want to open already saved Excel worksheet it, can be done in the following ways:, Method I., 1., 2., 3., 4., , Click the Microsoft Office button to display menu options., Click the Open option button that displays the Open dialogue box on screen., Select the folder from where we want to open the file from Look in dropdown list button., Double Click on the file we wanted to open or Select it and Click on Open button., , Method II., 1. Press Control + O shortcut key in keyboard that displays the Open dialogue box on, screen., 2. Select the folder from where we want to open the file from Look in dropdown list button., 3. Double Click on the file we wanted to open or Select it and Click on Open button., Printing the Workbook (Ctrl + P): Whenever we want to take a hard copy of drafted, worksheet it can be done in the following ways:, Method I., 1. Click the Microsoft Office button to display menu options., 2. Click the Print option button that displays the popup menu with following options: Print,, Quick print, Print preview
Page 10 :
3. Click on Print option that displays Print dialogue box on the screen that enable us to, provide several options that can control which printer to select, what part of the, workbook to print, which pages to print and how many copies to print, e.t.c.,, 4. Enter details by clicking on the options that we want to such as number of pages, number, of copies e.t.c.,, 5. Click on Ok button to start printing., Method II., 1. Press Control + O shortcut key in keyboard that displays the popup menu with following, options: Print, Quick print, Print preview, 2. Click on Print option that displays Print dialogue box on the screen that enable us to, provide several options that can control which printer to select, what part of the, workbook to print, which pages to print and how many copies to print, e.t.c.,, 3. Enter details by clicking on the options that we want to such as number of pages, number, of copies e.t.c.,, 4. Click on Ok button to start printing., Method III., 1. Click the Microsoft Office button to display menu options., 2. Click the Print option button that displays the popup menu with following options: Print,, Quick print, Print preview, 3. To print without using Print dialogue box, Click on the Quick Print option., Cancel Printing: Whenever we want to stop printing for which we have already given command, to print as above:, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , In Microsoft Windows XP, Click Start -> Setting -> Printer and faxes., Click on Printers and Faxes button to display dialogue box., Double click on the printer icon., Click on print job that we want to cancel printing., On the document menu, click Cancel option., , Closing workbook: Whenever user finishes his work in workbook need to quit from current, workbook by following procedure., Procedure:, 1. Click on Microsoft Office button to display menu options., 2. Click on the Close option.
Page 11 :
How to copy cell(s):, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Select the cell you want to copy., Click on the Home Tab of the Ribbon, Click on the Copy button from clipboard group., Select the destination cell by clicking the mouse., Click Paste button from Home Tab of the Ribbon., OR, Select the cell you want to copy., Click on Right click button on Mouse to display pop up menu., Click on the copy option., Select the destination cell by clicking the mouse., Click on the Paste button from Home Tab of the Ribbon belonging to clipboard group., , How to move cell(s):, 1., 2., 3., 4., , Select the cell you want to move., Click on the cut button from the Home Tab of the Ribbon., Select the destination cell by clicking the mouse., Click on the Paste button from Home Tab of the Ribbon belongs to clipboard group., , Drag and Drop data (to Move):, 1. Select the required cell range., 2. Drag the edge of the border around the cell range to the new location on that worksheet, , To paste particular parts of a cell selection, click the drop-down button that appears at the bottom, of the Paste command button on the Ribbon’s Home tab. Then, click Paste Special on its dropdown menu to open the Paste Special dialog box.
Page 12 :
You can specify which parts of the current cell selection to use by selecting the appropriate Paste, Special options:, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, , All to paste all the stuff in the cell selection (formulas, formatting, you name it). this is, what happens when you paste normally., Formulas to paste all the text, numbers, and formulas in the current cell selection without, their formatting., Values to convert formulas in the current cell selection to their calculated values., Formats to paste only the formatting from the current cell selection, without the cell, entries., Comments to paste only the notes that you attach to their cells (kinda like electronic selfstick notes)., Validation to paste only the data validation rules into the cell range that you set up with, the Data Validation command., All Using Source Theme to paste all the information plus the cell styles applied to the, cells., All Except Borders to paste all the stuff in the cell selection without copying any, borders you use there., Column Widths to apply the column widths of the cells copied to the Clipboard to the, columns where the cells are pasted., Formulas and Number Formats to include the number formats assigned to the pasted, values and formulas.
Page 13 :
•, , Values and Number Formats to convert formulas to their calculated values and include, the number formats you assigned to all the copied or cut values., , You can also perform some math when you paste based on the value(s) in the copied or cut, cell(s) and the value in the target cell(s):, •, , •, •, •, •, , None: Excel performs no operation between the data entries you cut or copy to the, Clipboard and the data entries in the cell range where you paste. This is the default, setting., Add: Excel adds the values you cut or copy to the Clipboard to the values in the cell, range where you paste., Subtract: Excel subtracts the values you cut or copy to the Clipboard from the values in, the cell range where you paste., Multiply: Excel multiplies the data you cut or copy to the Clipboard by the data entries, in the cell range where you paste., Divide: Excel divides the data you cut or copy to the Clipboard by the data entries in the, cell range where you paste., , Finally, at the bottom of the Page Special dialog box, you have a few other options:, •, •, , •, , Selecting the Skip Blanks check box tells Excel only to paste from those cells that, aren’t empty., Selecting the Transpose check box changes the orientation of the pasted entries. For, example, if the original cells’ entries run down the rows of a single column of the, worksheet, the transposed pasted entries will run across the columns of a single row., Clicking the Paste Link button establishes a link between the copies you’re pasting and, the original entries. That way, changes to the original cells automatically update in the, pasted copies, ., , Excel allows you to adjust your worksheets to achieve the desired look. Rows and columns can be resized, either automatically or manually to fit your information, and you can add or delete rows and columns if, necessary., , Adding and Removing Rows and Columns, When working with worksheets, you will often need to make changes to the original worksheets,, such as deleting old information or adding new information. To make this task easier, you can, add new rows and columns or delete existing rows and columns., , Adding Rows, 1. Select a cell below where you want to add a new row., 2. From the Ribbon, select the Home command tab.
Page 14 :
3. In the Cells group, click the arrow on the Insert button » select Insert Sheet Rows., A new row is added above the selected cell., , Adding Columns, 1. Select a cell to the right of where you want to add a new column., 2. From the Ribbon, select the Home command tab., 3. In the Cells group, click the arrow on the Insert button » select Insert Sheet Columns., A new column is added left of the selected cell., , Deleting Rows, WARNING: When you delete a row, everything in the row is deleted. If you do not want to delete, the whole row, delete information from specific cells instead., 1. To delete a single row, select any cell from the row to be deleted., To delete multiple non-contiguous rows, press [Ctrl] + select the cells from each row to, be deleted., 2. From the Ribbon, select the Home command tab., 3. In the Cells group, click the arrow on the Delete button » select Delete Sheet Rows., The row(s) are deleted., , Deleting Columns, WARNING: When you delete a column, everything in the column is deleted. If you do not want to, delete the whole column, delete information from specific cells instead., 1. To delete a single column, select any cell from the column to be deleted., To delete multiple non-contiguous columns, press [Ctrl] + select the cells from each, column to be deleted., 2. From the Ribbon, select the Home command tab., 3. In the Cells group, click the arrow on the Delete button » select Delete Sheet Columns., The column(s) are deleted., , Adjusting Row Height and Column Width, When you start working on a worksheet, all columns are 8.43 characters wide (in default font), and row heights are set to fit the content of the cell with a maximum of 15 points. Excel may, widen the column or increase the row height to fit the cell content. Adjusting the width or height, is easy to do and can be done using the Ribbon option or the Mouse option.
Page 15 :
Since columns and rows extend throughout the worksheet, the setting applies to the entire, column or row. If you need to have two settings, you will have to move some of your, information to another row or column with the correct settings., , Adjusting Row Height: Ribbon Option, 1. To adjust a single row, select any cell from the row to be adjusted., To adjust multiple non-contiguous rows, press [Ctrl] + select cells from each row to be, adjusted., 2. From the Ribbon, select the Home command tab., 3. In the Cells group, click Format., 4. In the Cell Size section, select Height..., The Row Height dialog box appears., , 5. In the Row height text box, type the desired height., 6. Click OK., The row height is adjusted., , Adjusting Row Height: Mouse Option, If you choose to adjust multiple rows at once, all selected rows will be adjusted the same amount, no matter which row border you move., 1. To adjust multiple non-contiguous rows, press and hold [Ctrl] while clicking the Row ID, for each desired row., To adjust multiple contiguous rows, press and hold [Shift] while clicking the first and last, Row ID for the desired range., 2. Along the row ID (e.g., 1, 2, 3, ...), point to the border below the row to be adjusted., 3. When the pointer turns into a double-arrow, click and drag., HINT: For a shorter row, drag up; for a taller row, drag down., A box appears next to the pointer, indicating the current row height as you drag it., , 4. When the row reaches the desired height, release the mouse button., The row height is adjusted., , Adjusting Column Width: Ribbon Option
Page 16 :
1. To adjust a single column, select any cell from the column to be adjusted., To adjust multiple non-contiguous columns, press [Ctrl] + select cells from each column, to be adjusted., 2. From the Ribbon, select the Home command tab., 3. In the Cells group, click Format., 4. In the Cell Size section, select Width..., The Column Width dialog box appears., , 5. In the Column width text box, type the desired width., 6. Click OK., The column width is adjusted., , Adjusting Column Width: Mouse Option, If you choose to adjust multiple columns at once, all selected columns will be adjusted the same, amount no matter which column border you move., 1. To adjust multiple non-contiguous columns, press and hold [Ctrl] while clicking the, Column ID for each desired row., To adjust multiple contiguous columns, press and hold [Shift] while clicking the first and, last Column ID for the desired range., 2. Along the column ID (e.g., A, B, C, ...), point to the border right of the column to be, adjusted., 3. When the pointer turns into a double-arrow, click and drag., HINT: For a narrower column, drag left; for a wider column, drag right., A box appears next to the pointer, indicating the current column width as you drag it., , 4. When the column reaches the desired width, release the mouse button., The column width is adjusted.
Page 17 :
Accessing the Page Setup Dialog Box, 1. Windows: From the Page Layout command tab, in the Page Setup group, click Page, Setup., Macintosh: From the File menu, select the Page Setup., The Page Setup dialog box appears., , Page Setup Dialog Box Tabs, The Page Setup dialog box consists of four tabs: Page, Margins, Header/Footer, and Sheet. Each, tab lets you customize elements of your Excel worksheet. For additional information, refer to, Customizing Page Layout (Win | Mac)., NOTES:, The following buttons are found on all tabs: Print... (opens the Print dialog box), Print Preview, (opens Print Preview), Options... (opens the (printer name) on print Properties dialog box), OK,, and Cancel., If you accessed the Page Setup dialog box differently than as described in Accessing the Page, Setup Dialog Box above, the Print... and Print Preview buttons may not appear., The options available in Page Setup dialog box will vary by operating system and printer model., , Page Setup Dialog Box Tabs: Page, The Page tab offers several options to help you specify how your worksheet(s) will print.
Page 18 :
Option, Orientation, Scaling, Paper size, Print quality, First page, number, , Description, Determines if your document prints as a portrait (i.e., lengthwise) or as a, landscape (i.e., widthwise)., Adjust to lets you to customize page scale by percentage. Fit to lets you, specify how many pages it takes to print your worksheet., HINT: Print Preview lets you see the effects of scaling before you print., Determines what size paper you will print on., Determines resolution., Indicates what number appears on the first printed page. If you want the, first page number to be 1, leave the selection as Auto., , Page Setup Dialog Box Tabs: Margins, The Margins tab lets you set your margins and center your data vertically, horizontally, or both., NOTE: All margin values are measured in inches.
Page 19 :
Page Setup Dialog Box Tabs: Header/Footer, Headers and footers are the text printed at the top and bottom of pages, such as the date, page, number, the filename, or other text. The Header/Footer tab provides options to customize page, headers or footers. For more information about headers and footers, refer to Modifying Headers, and Footers (Win | Mac).
Page 20 :
Option, Header, Footer, , Description, Provides several pre-written headers., Provides several pre-written footers., Lets you create your own header using the Header dialog box. For, Custom Header..., more information, refer to Adding Headers and Footers (Win | Mac)., Lets you create your own footer using the Footer dialog box. For, Custom Footer..., more information, refer to Adding Headers and Footers (Win | Mac)., Different odd and, Lets you create different headers or footers for odd and even pages., even pages, Different first, Lets you create a different header or footer for only the first page., page, Scale with, Adjusts the header and footer font and scaling to match the rest of the, document, document., Align with page, Sets headers and footers within the page margins., margins, , Page Setup Dialog Box Tabs: Sheet
Page 21 :
The Sheet tab gives you several options for determining which elements of your workbook are, printed. For more information, refer to Other Printing Options (Win | Mac)., , Option, Description, Print, Specifies a range of cells to print., area, Specifies the rows or columns to print on each page. These rows or columns are, Print, likely to be the headings that define what the rest of the row or column's, titles, information is used for., Allows you to print only certain elements of your worksheet. For more, Print, information, refer to Using Printing Options: Applying Additional Printing, Options (Win | Mac)., Page, Sets the order in which worksheet pages are numbered and printed., order
Page 22 :
UNDERSTANDING CELLS AND RANGES, , Cell: A Cell is a single element in a worksheet that can hold a value, some text, or a formula. A, Cell is identified by its address or reference, which consists of its column and row number., Ex: Cell : C12 is the cell in the Third column and the twelfth row, Range: A group of cells is called a range. We designate a range address by specifying its upper, left cell address and its lower right cell address, separately by a colon., Here are some examples of range addresses;, C2, , A range that consist of a single cell., , A6:B6, , Two cells that occupy one row and two columns., , A1:A150, , 150 Cells in Column A., , B1:E4, , 16 Cells, Four rows by four columns., , F1:F1048576 An entire column of cells, this range also can be expressed as F:F, A5:XFD5, , An entire row of cells, this range also can be expressed as 5:5, , A1:XFD1048576, , All cells in a worksheet., , Select Cells, Ranges, Rows or Column, A Single Cell, , Click the cell OR, , Press the arrow keys to move to the cell, , A Range of Cells:, Click the first cell in the range, and drag to the last cell, or Hold down, SHIFT while you press the arrow keys to extend the selection., OR, We can also select the first cell in the range and then press F8 to extend the selection by using, the arrow keys to stop extending the selection, press F8 again.
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic

























































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









