Page 1 :
=» ALL, , pach CAREER INSTITUTE, , , , , , eS, , , , , , Chemistry:, , , , Periodic Table, , , , , , ontents, , 1, , Introduction, , , , 02., , Development of periodic table, , , , 03., , Group, petiod & block identification, , , , 04., , Periodicity, , , , 05., , Screening efféct & Z effective, , , , 06., , Atomic radius, , , , 07., , Ionization energy, , , , 08., , Electron affinity, , , , 09., , Electronegativity, , , , oo ——— NEET SYLLABUS, , , , |_______», , , , , , PERIODIC TABLE : Modern periodic law and long form of periodic table, periodic trends in properties of elements, atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, valence.
Page 2 :
OBJECTIVES, , After studying this unit, you will be able to :, , Understand the Periodic Law., , Understand the significance of atomic number and electronic configuration as the basis, for periodic classification;, , Name the elements with Z >100 according toJUPAC nomenclature;, , Classify elements into s, p, dj fblocks and learn their main characteristics;, , Recognise the periodic trends in physical.and chemical properties of elements;, , use scientific vocabulary appropriately to communicate ideas related to certain important, properties of atoms e.g., atomic/ ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy,, , electronegativity, valence of elements., , She Setadic Jatle ts aguallly the most important concept in chemistry, bath in principle and ia, , practice. Un awareness of the Periedit Galle is essential ta anyane whe wishes te disentangle the wald, and sec how it is Cult up fem the fundamental building llacks of the chemistup, the chemical cements., , Glenn T. Seaborg
Page 4 :
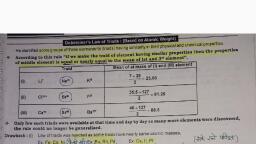
BE Medical : Chemistry ALLEN",, , PERIODIC TABLE, , , , 1.0, , INTRODUCTION :, , The arrangement of all the known elements according to their properties in such a way that the elements with, similar properties are grouped together in a tabular form is called periodic table., , DEVELOPMENT OF PERIODIC TABLE, , (A), , (B), , (C), , LAVOISIER CLASSIFICATION :, (i) Lavoisier classified the elements simply in metals and non metals., Metals are the one which have the tendency of losing the electrons., Na > Na* + & and K>Kt+e, Non-metals are the one which have the tendency of gaining the electrons., F+eeoF and Cl+e 3dr, , (ii) Drawback or Limitation :, (a) As the number of elements increases, this classification became insufficient for the study of elements., , (b) | There are few elements which have the properties of both metals as well as non-metals and they are, called metalloids. Lavoisier could not decide where to. place the metalloids., , PROUT'S HYPOTHESIS :, He simply assumed that all the elements are made up of hydrogen, so we can say that, , Atomic weight of element,= n x (Atomic weight of one hydrogen atom), , Atomic weight of H, , where n = number of hydrogen atom= 1, 2, 3,...., Drawback or Limitation:, (i) Every element can not be formed, by‘Hydrogen., (ii) Atomic weight of all elements were not found as the whole numbers., Ex. Chlorine (atomic weight 35.5) and Strontium (atomic weight 87.6), , DOBEREINER TRIAD RULE [1817] :, (i) He made groups of three elements having similar chemical properties called TRIAD., , (ii) In Dobereiner triad, atomic weight of middle element is nearly equal to the average atomic weight of first, and third element., , , , Ex. C Br I Ca Sr Ba Li Na K, 35.5 80.0 127 40 87.6 137 7 23 39, | Bat soy E SOEs [ «732-2, , Where x=average atomic weight, (iii) | Other examples - (K, Rb, Cs), (P, As, Sb), (S, Se, Te), , Drawback or Limitation : All the known elements could not be arranged as triads. It is not applicable for, dand f-block elements., , , , IM z \ncotca\ 2080 5a\ TARGET CHEM ENG MODUL, , g, §, Z, 5
Page 5 :
PIN] 2800£02\ 9080-84 TARGET CHEM ENG\MODULE2\1-PERIODIC TABLE\OT-THEORY.P65, , ; ALLEX®, , @), , (E), , NEWLAND OCTAVE RULE [1865], , (i) He arranged the elements in the increasing order of their atomic mass and observed that the properties, of every 8" element was similar to the 1* element. (like in the case of musical vowels notation), , (ii) At that time inert gases were not known., , Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni, 2 3 4 5 6 7, , , , H, Li Be B C N O F, , Na| Mg /Al/Si]/P |S | Cc, K | Ca, , (ii) | The properties of Li are similar to 8" element i.e. Na and Be are similar to Mg and so on., , , , , , , , , , Drawback or Limitation :, , (a) This rule is valid only upto Ca because after Ca due to presence of d-block element there is a difference, of 18 elements instead of 8 elements., , (b) After the discovery of Inert gas and including them in the periodic table, it has become the 8" element, from Alkali metal so this law had to be dropped’out., , LOTHAR MEYER'S CURVE [1869] :, , (i) He plotted a curve between atomic weight and atomicvolume of different elements., , (ii) The following observation can be made from the curve —, , (a) Most electropositive elements i.e. alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) occupy the peak positions, on the curve., , (b) Less electropositive i.e. alkaline earth metal (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba) occupy the descending position, on the curve., , (c) Metalloids (Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te}, Po, At) and transition metals occupy bottom part of the curve., (d) Most electronegative i.e. halogens (F, Cl, Br, I) occupy the ascending position on the curve., Note : Elements having similar properties‘occupy similar position on the curve., Conclusion : On the basis of this;curve Lother Meyer proposed that the physical properties of the elements, are periodic function of their atomic weight and this has become the base of Mendeleev's periodic table., Periodic function : When the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic weight, elements, having similar properties gets repeated after a regular interval., , Atomic Volume, , , , Metalloid and transition metals, , , , Atomic Weight, , , , Pre-Medical : Chemistry