Page 6 :
Practice Time, OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS, , Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs), 1., , Ketones, , can be obtained in one, , step by (where R and R′ are alkyl groups), (a) hydrolysis of esters, (b) oxidation of primary alcohols, (c) oxidation of secondary alcohols, (d) reaction of alkyl halides with alcohols., 2. Aldehydes other than formaldehyde react, with Grignard’s reagent to give addition products, which on hydrolysis give, (a) tertiary alcohols, (b) secondary alcohols, (c) primary alcohols, (d) carboxylic acids., 3. Which of the following compounds will, undergo Cannizzaro reaction?, (b) CH3COCH3, (a) CH3CHO, (c) C6H5CHO, (d) C6H5CH2CHO, 4. Propanal on treatment with dilute sodium, hydroxide gives, (a) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO, (b) CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CH2CHO, (c) CH3CH2CH(OH)CH(CH3)CHO, (d) CH3CH2COOH, 5. Various products formed on oxidation of, 2,5-dimethylhexan-3-one are, (i), , (ii), , (iii) CH3COOH, (iv) HCOOH, (a) (i) and (iii), (b) (i), (ii) and (iii), (c) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) (d) (iii) and (iv), 6. Alkene (X) (C 5H 10) on ozonolysis gives a, mixture of two compounds (Y) and (Z). Compound, (Y) gives positive Fehling’s test and iodoform, , test. Compound (Z) does not give Fehling’s test, but give iodoform test. Compounds (X), (Y) and, (Z) are, X Y, Z, (a) C6H5COCH3, CH3CHO, CH3COCH3, (b), , CH3CHO, , CH3COCH3, , (c) CH3CH2CH == CH2, CH3CH2CHO HCHO, CH3CHO, (d) CH3 —CH == CH — CH3 CH3CHO, 7. A compound (X) with a molecular formula, C 5 H 10 O gives a positive 2,4-DNP test but a, negative Tollen’s test. On oxidation it gives a, carboxylic acid (Y) with a molecular formula, C3H6O2. Potassium salt of (Y) undergoes Kolbe’s, reaction and gives a hydrocarbon (Z). (X), (Y), and (Z) respectively are, (a) pentan-3-one, propanoic acid, butane, (b) pentanal, pentanoic acid, octane, (c) 2-methylbutanone, butanoic acid, hexane, (d) 2, 2-dimethylpropanone, propanoic acid,, hexane, 8. Which of the following statements is, incorrect?, (a) FeCl3 is used in the detection of phenols., (b) Fehling solution is used in the detection of, glucose., (c) Tollens’ reagent is used in the detection of, unsaturation., (d) NaHSO3 is used in the detection of carbonyl, compounds., 9. Which of the following compounds will, give a coloured crystalline compound with, ?, (a) CH3COCl, (c) CH3COCH3, , (b) CH3COOC2H5, (d) CH3CONH2
Page 7 :
10. Which of the following reagents are not, correctly matched with the reaction?, (a) CH3CH CHCHO, CH3CH CHCOOH, �, : Ammonical AgNO3, (b) CH3CH CHCHO, CH3CH CHCH2OH, �, : H2/Pt, (c) R — COOH, R—CH2OH : NaBH4, (d) CH3CH2COCl, CH3CH2CHO, �, : H2, Pd/BaSO4, 11. In the following reaction, product (P) is, O, R—C—Cl, , H2, , P, , Pd/BaSO4, , (a) RCHO, (c) RCOOH, , (b) RCH3, (d) RCH2OH, , 12. Which of the following will not give aldol, condensation?, (a) Phenyl acetaldehyde, (b) 2-Methylpentanal, (c) Benzaldehyde, (d) 1-Phenylpropanone, 13. Which of the following statements is correct, regarding formic acid?, (a) It is a reducing agent., (b) It is a weaker acid than acetic acid., (c) It is an oxidising agent., (d) When its calcium salt is heated, it forms, acetone., 14. The condensation product of benzaldehyde, and acetone is, (a), O, , (b) C6H5CH2 C CH CH2, (c), (d), 15. Which among the following is most reactive, to give nucleophilic addition?, (a) FCH2CHO, (b) ClCH2CHO, (c) BrCH2CHO, (d) ICH2CHO, 16. Which of the following IUPAC names is not, correctly matched?, (a), (b), , (c) PhCH2CH2COOH : 3-Phenylpropanoic acid, (d), , 17. Which of the following is the most reactive, isomer?, (a), (b), (c), (d), 18. The correct order of increasing acidic, strength is, (a) Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid <, Acetic acid, (b) Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid <, Acetic acid, (c) Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic, acid, (d) Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol <, Ethanol, 19. To differentiate between pentan-2-one and, pentan-3-one a test is carried out. Which of the, following is the correct answer?, (a) Pentan-2-one will give silver mirror test, (b) Pentan-2-one will give iodoform test., (c) Pentan-3-one will give iodoform test, (d) None of these., 20. What happens when a carboxylic acid is, treated with lithium aluminium hydride?, (a) Aldehyde is formed., (b) Primary alcohol is formed., (c) Ketone is formed., (d) Grignard reagent is formed., 21. Which of the following will not undergo HVZ, reaction?, (a) Propanoic acid, (b) Ethanoic acid, (c) 2-Methylpropanic acid, (d) 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid
Page 11 :
(c) CH3CH2CHO + CH3CHO, (d) 2CH3CH2CHO, , (B) + (C), , (A) + C2H5OH, , 55. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic, medium and in the presence of Hg2+ ions as a, catalyst. Which of the following products will be, formed on addition of water to but-1-yne under, these conditions?, , (C) + HOH, (D), , [O], , H+, , (B) + (D), , (B), , (B) + Ca(OH)2, , Calcium salt + H2O, dry distillation, , �, , , , (A), , (a), , (a), (b), (c), (d), , (b), (c), (d), 56. An organic compound (X) with molecular, formula C 9 H 10 O gives positive 2,4-DNP and, Tollen’s tests. It undergoes Cannizzaro, reaction and on vigorous oxidation it gives, 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Compound (X) is, (a) benzaldehyde, (b) o-methylbenzaldehyde, (c) p-ethylbenzaldehyde, (d) 2, 2-dimethylhexanal, O, , 57. R CH CH CHO + NH2 C NHNH2, (X) in the above reaction is, , H+, , X, , (a), (b), (c), (d), 58. Which of the following will not yield acetic, acid on strong oxidation?, (a) Butanone, (b) Propanone, (c) Ethyl ethanoate, (d) Ethanol, 59. Which of the following compounds does not, react with NaHSO3?, (a) HCHO, (b) C6H5COCH3, (c) CH3COCH3, (d) CH3CHO, 60. Study the following reactions and mark the, appropriate choice., , (B), , CH3COCH3, (Acetone), , (C), , (D), , (CH3CO)2O CH3COOH CH3COOC2H5, , C2H5OH, , CH3COCl, , HCOOH, , CH3COOCH3, , CH3OH, , CH3COOH, , CH3OH, , CH3COOCH3, , CH3OH, , CH3NH2, , CH3COOH CH3COOCH3, , C2H5OH, , 61. Compound (X) with molecular formula, C 3 H 8 O is treated with acidified potassium, dichromate to form a product (Y) with molecular, formula C3H6O. (Y) does not form a shining silver, mirror on warming with ammoniacal AgNO3., (Y) when treated with an aqueous solution of, NH2CONHNH2. HCl and sodium acetate to give, a product (Z). The structure of (Z) is, (a), (b), (c), (d), 62. Aldehydes and ketones are isomers as, they have same general formula but different, functional groups. Both these functional groups, can be distinguished by various tests., A compound with molecular formula C9H10 has, two isomers P and Q which undergo ozonolysis, to give two functional isomers (R and S) with, formula, C8H8O., (i) O3/CH2Cl2, , P (ii) Zn/H O, 2, , (i) O /CH Cl, , R + HCHO,, , 3, 2 2, Q (ii) Zn/H O S + HCHO, 2, Which of the given options can not be correct for, P, Q, R and S?, I. If P is 4-vinyl toluene then R gives Cannizzaro, reaction but not haloform reaction., II. If Q is 4-vinyl toluene then S gives haloform, reaction but not Cannizzaro., III. If Q is 2-phenylpropene then S gives haloform, reaction but not Cannizzaro., IV. If P is 2-phenylpropene then R gives both, Cannizzaro and haloform reaction., (a) I and II only, (b) I and III only, (c) II and III only, (d) II and IV only
Page 12 :
63. Study the given reactions chart carefully :, Compound [A], (C5H12O), , COOH, , Oxidation, X2/NaOH, , No, , haloform, reaction, , [B], , 2,4-DNP, , (C5H10O), , 2,4- Dinitrophenylhydrazone, , Ag+/OH–, , No silver mirror is formed, Which is correct for compounds A and B?, (a) B is an aldehyde., (b) B is a ketone but not methyl ketone., (c) A is a primary alcohol., (d) B convert to A using Zn–Hg/HCl., 64. Acidic nature of carboxylic groups depends, on various factors like presence of electron, withdrawing groups (–I, –R effect), presence of, electron donating groups (+I, +R effect), distance, of attached groups. Stability of carboxylate ion, plays an important role in the acidic nature of, carboxylic acid., Vinita, a class 12 student has written the following, orders of acidity for various carboxylic acids :, COOH, COOH, COOH, COOH, >, , I:, , >, , NO2, , >, CH3, , OCH3, , II : CH3CH2CH COOH >, , �, , CH3, , CH, , CH3, , F, CH, , F, , CH2COOH >, , CH2COOH > CH2 CH2CH2COOH, , Cl, , Cl, , >, , III :, , COOH, , COOH, >, , OH >, , COOH, CH3, , NO2, Which of the following orders is not correct and, what is the reason behind it?, (a) Order I, +R effect of –OCH 3 group is not, interpreted correctly., (b) Order II, position of electronegative group, is not interpreted correctly., (c) Order III, ortho effect is not considered., (d) All the orders I, II and III are correct., 65. Carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel Craft’s, reaction because, (a) —COOH group is meta directing, (b) —COOH group is resonance stabilised, (c) carboxyl group is deactivating and gets, bonded to Friedel Craft’s catalyst, (d) all of above., 66. A ketone ‘A’ (C 4H 8O), which undergoes a, haloform reaction, gives a compound ‘B’ on, reduction. ‘B’ on heating with sulphuric acid, gives a compound ‘C’ which forms mono-ozonide, ‘D’. ‘D’ on hydrolysis with zinc dust gives only,, ‘E’., Identify the correct statement., (a) A is butan-2-one; B is butan-2-ol., (b) B is but-2-ene; C is acetaldehyde., (c) D is acetaldehyde; E is butan-2-ol., (d) B is butan-1-one; D is but-2-ene., , Case Based MCQs, Case I : Read the passage given below and, answer the following questions :, Carboxylic acids having an a-hydrogen atom, when treated with chlorine or bromine in the, presence of small amount of red phosphorus gives, a-halocarboxylic acids. The reaction is known as, Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction., R — CH2 — COOH + X2, , red P, , When sodium salt of carboxylic acid is heated, with soda lime it loses carbon dioxide and gives, hydrocarbon with less number of C-atoms., R — COOH, Carboxylic, acid, , R—CH—COOH, X, , (X = Cl, Br), , �, , NaOH, , R— COONa, Sod., carboxylate, , NaOH + CaO, D, , R— H + Na2CO3, Alkane
Page 13 :
In the following questions (Q. No. 67-71), a, statement of assertion followed by a statement, of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out, of the following choices on the basis of the above, passage., (a) Assertion and reason both are correct, statements and reason is correct explanation, for assertion., (b) Assertion and reason both are correct, statements but reason is not correct, explanation for assertion., (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is, wrong statement., (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is, correct statement., 67. Assertion : (CH 3) 3CCOOH does not give, H.V.Z reaction., Reason : (CH3)3CCOOH does not have, a-hydrogen atom., 68. Assertion : H.V.Z. reaction involves the, treatment of carboxylic acids having a-hydrogens, with Cl2 or Br2 in presence of small amount of, red phosphorus., Reason : Phosphorus reacts with halogens to, form phosphorus trihalides., 69. Assertion : Propionic acid with Br2/P yields, CH2Br —CHBr —COOH., Reason : Propionic acid has two a-hydrogen, atoms., 70. Assertion : C6H5COCH2COOH undergoes, decarboxylation easily than C6H5COCOOH., Reason : C6H5COCH2COOH is a b-keto acid., 71. Assertion : On heating 3-methylbutanoic, acid with soda lime, isobutane is obtained., Reason : Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH + CaO, in the ratio 3 : 1., Case II : Read the passage given below and, answer the following questions from 72 to 76., Aldehydes and ketones having acetyl group, O, , CH3—C— are oxidised by sodium hypohalate, (NaOX) or halogen and alkali (X2 + OH–) to, corresponding sodium salt having one carbon, atoms less than the carbonyl compound and give, a haloform., , O, NaOX, , R — C — CH3 or X + NaOH, 2, , O, R— C—ONa + CHX3 (X = Cl, Br, I), , �, , Sodium hypoiodite (NaOI) when treated with, compounds containing CH3CO — group gives, yellow precipitate of iodoform. Haloform reaction, does not affect a carbon-carbon double bond, present in the compound., 72. Which of the following compounds will give, positive iodoform test?, (a) Isopropyl alcohol, (b) Propionaldehyde, (c) Ethylphenyl ketone (d) Benzyl alcohol, 73. Which of the following compounds is not, formed in iodoform reaction of acetone?, (a) CH3COCH2I, (b) ICH2COCH2I, (c) CH3COCHI2, (d) CH3COCI3, 74. For the given set of reactions,, , starting compound A corresponds to, O, O, (b), (a), CH2COOH, CH2COOH, O, O, (c), (d), COCH3, COCH3, 75. In the following reaction sequence, the, correct structures of E, F and G are, *, , (* implies 13C labelled carbon), (a), (b), (c), (d), 76. An organic compound ‘A’ has the molecular, formula C 3 H 6 O. It undergoes iodoform test.
Page 14 :
When saturated with HCl it gives ‘B’ of molecular, formula C9H14O. ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively are, (a) propanal and mesityl oxide, (b) propanone and mesityl oxide, (c) propanone and 2,6-dimethyl-2,5-heptadien‑4‑one, (d) propanone and propionaldehyde., , 78. Which of the following compounds would, be the main product of an aldol condensation of, acetaldehyde and acetone?, (a) CH3CH CHCHO, (b) CH3CH CHCOCH3, (c) (CH3)2C CHCHO, (d) (CH3)2C CHCOCH3, , Case III : Read the passage given below and, answer the following questions from 77 to 81., The addition reaction of enol or enolate to the, carbonyl functional group of aldehyde or ketone is, known as aldol addition. The b-hydroxyaldehyde or, b-hydroxyketone so obtained undergo dehydration, in second step to produce a conjugated enone. The, first part of reaction is an addition reaction and the, second part is an elimination reaction. Carbonyl, compound having a-hydrogen undergoes aldol, condensation reaction., O, O, , 79. Which combination of carbonyl compounds, gives phenyl vinyl ketone by an aldol, condensation?, O, , 2CH3CH2, , C, , –, , OH, , H D, , CH3CH2CH, , C, , O, , O, CH, , H, , CH3, , Mechanism :, , HO + H, , C, , C, , H –H O H3C, 2, , CH, , C, , H, , CH3, CH3CH2, , O, , O, , C +CH, , C, , H, , H CH3, , O, CH3CH2, , �, , OH, H2O, , CH3CH2 CH, , O, , CH, , C, , H, , �, , H, , –H2O, D, , CH3, CH3CH2, , C, , CH3, , O, CH, , CH, , O, CH, , C, , C, , H, , CH3, , 77. Condensation reaction is the reverse of, which of the following reaction?, (a) Lock and key hypothesis, (b) Oxidation, (c) Hydrolysis, (d) Glycogen formation, , (a), (b), (c), (d), , Ph, Acetophenone and, Acetophenone and, Benzaldehyde and, Benzaldehyde and, , Formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acetone, , 80. Which of the following will undergo aldol, condensation?, (a) HCHO, (b) CH3CH2OH, (c) C6H5CHO, (d) CH3CH2CHO, 81. Which of the following does not undergo, aldol condensation ?, (a) CH3CHO, (b) CH3CH2CHO, (c) CH3COCH3, (d) C6H5CHO, Case IV : Read the passage given below and, answer the following questions :, Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic, addition reactions., Nu, Nu, R1 +d –d Nu, E+, C O, C, C, R2, R1 R O, R1 R OE, 2, 2, Carbonyl carbon is electron deficient hence acts, as an electrophile. Nucleophile attacks on the, electrophilic carbon atom of the carbonyl group, from a direction perpendicular to the plane of the, molecule., R1 +d, C, R2, , Nu, d, , O, , Nu, Slow, , C, R1 R O, 2, , Nu, Fast, H+, , C, R1 R OH, 2, , In this process, hybridisation of carbon atom, changes from sp2 to sp3 and a tetrahedral, alkoxide ion is formed as intermediate. This, intermediate captures proton from the reaction, medium to give the neutral product. Aldehydes, are generally more reactive than ketones in, nucleophilic addition reactions.
Page 15 :
In the following questions (Q. No. 82-86), a, statement of assertion followed by a statement, of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out, of the following choices on the basis of the above, passage., (a) Assertion and reason both are correct, statements and reason is correct explanation, for assertion., (b) Assertion and reason both are correct, statements but reason is not correct, explanation for assertion., (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is, wrong statement., (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is, correct statement., 82. Assertion : Benzaldehyde is more reactive, than ethanal towards nucleophilic attack., Reason : The overall effect of –I and +R effect of, phenyl group decreases the electron density on, the carbon atom of C O group in benzaldehyde., 83. Assertion : (CH3)3CCOC(CH3)3 and acetone, can be distinguished by the reaction with, NaHSO3., Reason : HSO3– is the nucleophile in bisulphite, addition., , Reason : Reactivity of carbonyl group is due to, electrophilic nature of carbonyl carbon., Case V : Read the passage given below and, answer the following questions from 87 to 91., When an aldehyde with no a-hydrogen reacts with, concentrated aqueous NaOH, half the aldehyde, is converted to carboxylic acid salt and other half, is converted to an alcohol. In other words, half of, the reactant is oxidized and other half is reduced., This reaction is known as Cannizzaro reaction., O, , 2, , 85. Assertion : The formation of cyanohydrin, from an aldehyde or ketone occurs very slowly, with pure HCN. This reaction is catalysed by a, base., Reason : Base generates CN– ion which is a, stronger nucleophile., CHO, 86. Assertion :, , is more reactive towards, NO2, , CHO, ., , nucleophilic addition reaction than, CH3, , Conc. NaOH, , C, , �, Mechanism :, , O, Ph, , H, , C, , OH, , Ph, , ONa +, O, , C, , H+ C, , C, , O, , H, , +, , H, , C, , H, , Ph, , H, Ph, , �, , Ph, , O, , O, Ph, , CH2OH, , O, , OH, , (I), CH3CHO(II) and, , CH3COCH3(III) is I > II > III., Reason : Aldehydes and ketones undergo, nucleophilic addition reactions., , H, , O, , 84. Assertion : Ease of nucleophilic addition, COCH3, of the compounds, , C, , OH, , O, C, , O, , + H, , C, , Ph, , H, , 87. A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde, on heating with aqueous NaOH solution gives, (a) benzyl alcohol and sodium formate, (b) sodium benzoate and methyl alcohol, (c) sodium benzoate and sodium formate, (d) benzyl alcohol and methyl alcohol., 88. Which of the following compounds will, undergo Cannizzaro reaction?, (b) CH3COCH3, (a) CH3CHO, (c) C6H5CHO, (d) C6H5CH2CHO, 89. Trichloroacetaldehyde is subjected to, Cannizzaro’s reaction by using NaOH. The, mixture of the products contains sodium, trichloroacetate ion and another compound. The, other compounds is, (a) 2, 2, 2-trichloroethanol, (b) trichloromethanol
Page 16 :
(c) 2, 2, 2-trichloropropanol, (d) chloroform., 90. In Cannizzaro reaction given below :, 2PhCHO, step is, , OH, , –, , PhCH2OH +, , PhCO2–, , the slowest, , –, , (a) the attack OH at the carboxyl group, (b) the transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group, , (c) the abstraction of proton from the carboxylic, group, (d) the deprotonation of PhCH2OH., 91. Which of the following reaction will not, result in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?, (a) Cannizzaro reaction, (b) Wurtz reaction, (c) Reimer-Tiemann reaction, (d) Friedel-Crafts’ acylation, , For question numbers 92-105, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose, the correct answer out of the following choices., (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion., (b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion., (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement., (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement., 92. Assertion : Aromatic aldehydes and, formaldehyde undergo Cannizzaro reaction., Reason : Aromatic aldehydes are almost as, reactive as formaldehyde., 93. Assertion : a-Hydrogen atoms in aldehydes, and ketones are acidic., Reason : The anion left after the removal of, a-hydrogen is stabilised by inductive effect., 94. Assertion : Hydrogen bonding in carboxylic, acids is stronger than alcohols., Reason : Highly branched carboxylic acids are, more acidic than unbranched acids., , Reason : Carboxyl group increases the electron, density at the meta-position., 99. Assertion : Boiling point of aldehydes lie, in between parent alkanes and corresponding, alcohols., Reason : Aldehydes cannot form intermolecular, hydrogen bonds like alcohols., 100. Assertion : Carboxylic acids are stabilised, by resonance., Reason : Chloroacetic acid is weaker than acetic, acid., 101. Assertion : Benzaldehyde undergoes aldol, condensation., Reason : Aldehydes having a-hydrogen atom, undergo aldol condensation., , 95. Assertion : m-Chlorobenzoic acid is a, stronger acid than p-chlorobenzoic acid., Reason : In m-chlorobenzoic acid both – I-effect, and +R-effect of Cl operate but in p-chlorobenzoic, acid only +R-effect of Cl operates., , 102. Assertion : Formic acid is a stronger acid, than benzoic acid., Reason : pKa of formic acid is lower than that of, benzoic acid., , 96. Assertion : Ketones can be converted into, acids by haloform reaction., Reason : Addition of Grignard reagents to dry, ice followed by hydrolysis gives ketones., , 103. Assertion : NaHSO 3 is used for the, purification of carbonyl compounds., Reason : They are used in the blending of, perfumes and flavouring agents., , 97. Assertion : Acetic acid in vapour state, shows a molecular mass of 120., Reason : It undergoes intermolecular hydrogen, bonding., , 104. Assertion : Carboxylic acids have higher, boiling points than alkanes., Reason : Carboxylic acids are resonance hybrids., , 98. Assertion : Nitration of benzoic acid gives, m-nitrobenzoic acid., , 105. Assertion : o-Substituted benzoic acids are, generally stronger acids than benzoic acids., Reason : Increased strength is due to ortho-effect.
Page 17 :
SUBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS, , Very Short Answer Type Questions (VSA), 1. Arrange the following in the increasing order, of their boiling points., CH3CHO, CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH, 2. Write chemical equations for the following, reactions :, Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in presence of, Pd/BaSO4., 3. Write structures of compounds A and B in, each of the following reactions., , 4. Write structures of compounds A and B in, each of the following reactions :, , 5., , Give reasons :, Chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid., , 6. Write the IUPAC name of the following, compound :, , 7. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling, points than corresponding alcohols. Why?, 8., , Complete the following reactions :, , 9., , Write the IUPAC name of the following :, , 10. Write the equation involved in Etard, reaction., , Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I), 11. A compound ‘A’ of molecular formula, C 2 H 3 OCl undergoes a series of reactions as, shown below. Write the structure of A, B, C, and D in the following reactions :, (C2H3OCl)A, , B, , C, , D, , 12. Write chemical equations for the following, reactions :, (i) Propanone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)2., (ii) Acetophenone is treated with Zn(Hg)/Conc., HCl, 13. Give reasons :, (i) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid, takes place at meta-position., (ii) Carboxylic acids do not give the characteristic, reactions of carbonyl group., 14. Describe how the following conversions can, be brought about :, , (i) Ethylbenzene to benzoic acid, (ii) Bromobenzene to benzoic acid, 15. Which acid of each pair shown here would, you expect to be stronger?, (i) F—CH2—COOH or Cl—CH2—COOH, (ii), , or CH3COOH, , 16. The reaction of carbonyl compound with, pure HCN is very slow and becomes fast in, presence of a base., 17. A compound having the molecular formula, C 3 H 6 O forms a crystalline white ppt. with, sodium bisulphite and reduces Fehling’s, solution. Suggest the structural formula and, IUPAC name of this compound. Name an isomer, for it from a group other than its own.
Page 18 :
18. Account for the following :, (a) Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo, Friedel–Crafts reaction., (b) pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than, that of benzoic acid., 19. (i) What is the advantage of using DIBAL-H, as reducing agent?, (ii) Which of the following can be nitrated more, , easily and why? Benzoic acid or phenol., 20. Account for the following :, (i) CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3, towards reaction with HCN., (ii) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide, (H2NNHCONH2)., However, only one is involved in the formation of, semicarbazone., , Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II), 21. Write the equation of the reactions of ethanal, with, (i) Fehling’s solution (ii) Phenylhydrazine, (iii) Hydroxylamine., 22. Illustrate the following name reactions, giving a chemical equations in each case :, (i) Clemmensen reaction, (ii) Cannizzaro reaction, 23. (i) Write the structures of compounds A, B, and C in each of the following reactions :, , (b) Etard reaction, (ii) Distinguish between CH3COOH and HCOOH., 26. Two moles of organic compound ‘A’ on, treatment with a strong base gives two compound, ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ on dehydrogenation, with Cu gives ‘A’ while acidification of ‘C’ yields, carboxylic acid ‘D’ with molecular formula of, CH2O2. Identify the compounds A, B, C and D, and write all chemical reactions involved., , (b), , 27. (a) Write the chemical reaction involved in, Wolff-Kishner reduction., (b) Arrange the following in the increasing order, of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition, reaction., C6H5COCH3, CH3 CHO, CH3COCH3, , (ii) Do the following conversion in not more than, two steps :, Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde, , (c) A and B are two functional isomers of, compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and, I2, isomer B forms yellow precipitate of iodoform, whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate., Write the formulae of A and B., , (a), , 24. During practical exams, lab assistant, provided two test tubes containing 5 mL benzoic, acid and 5 mL acetaldehyde to every student. A, student, Rahul found that test tubes given to, him were unlabelled. He informed the teacher, before performing any experiment with the, given chemicals., How can the chemicals be distinguished for, correct labelling?, 25. (i) Write the equations involved in the, following reactions :, (a) Stephen reaction, , 28. (a) Write the main product in the following, equations :, (i) CH3 C CH3 LiAlH4 ?, O, , (ii), (b) Write the product in the following reaction :, CH3, , CH, , CH, , CH2CN, , (i) DIBAL-H, (ii) H2O, , 29. Write the products formed when ethanal, reacts with the following reagents :
Page 19 :
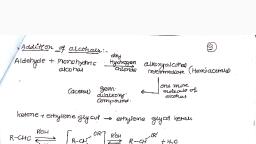
(i) CH3MgBr and then H3O+, (ii) Zn-Hg/conc. HCl, (iii) C6H5CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH, 30. (a) Draw the structures of the following :, (i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde, (ii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one, (b) Describe how the following conversions can, be brought about :, Cyclohexanol to cyclohexan 1-one, 31. (A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional, isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular, formula C 4 H 8 O. Isomers (A) and (C) give, positive Tollens’ test whereas isomer (B) does, not give Tollens’ test but gives positive iodoform, test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with, Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D)., (a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D)., (b) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is, least reactive towards addition of HCN?, 32. In an industry aldehydes are being prepared, by controlled oxidation of primary alcohol using, acidified K2Cr2O7 or aqueous or alkaline KMnO4, as oxidant. Mohan suggested the owner of, factory to use Collin’s reagent instead of acidic, potassium dichromate. The yield of factory, increased sharply., Now answer the following questions :, (i) What is Collin’s reagent?, , (ii) What are the advantages of using Collin’s, reagent over conventional oxidising agent?, 33. Identify A and E in the following series of, reactions :, , NaOOC, , 34. (i)How will you bring about the following, conversions?, (a) Ethanal to but-2-enal, (b) Propanone to propene, (ii) Write the IUPAC name of the compound :, , 35. Write the structures of the main products of, the following reactions :, anhydrous AlCl3, , + C6H5COCl, , (i), (ii) H3C, , C, , C, , H, , CS2, , 2+, , Hg , H2SO4, , CH3, 1. CrO2Cl2, , (iii), , 2. H2O, , NO2, , Long Answer Type Questions (LA), 36. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in, the following reactions :, C6H6, , CH3COCl, , Anhyd. AlCl3, , A, , Zn–Hg/conc.HCl, , NaOI, , D+E, , B, , (i) KMnO4 – (ii) H3O+, KOH, �, , C, , 37. Identify A to E in the following reactions :, , 38. (a) �Give a plausible explanation for each, one of the following :, (i) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide., , However, only one such group is involved in the, formation of semicarbazones., (ii) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good, yield but 2,4,6-trimethylcyclo-hexanone does not., (b) An organic compound with molecular, formula C9H10O forms 2,4-DNP derivative,, reduces Tollens’ reagent and undergoes, Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation it, gives 1,2-benzene-dicarboxylic acid. Identify the, compound., 39. (a) Identify A, B and C in the following, sequence of reactions :, CH3CHO, , (i) C2H5MgCl, (ii) H2O, , A, , B, , C
Page 21 :
13. (a) : Formic acid acts as a reducing agent it reduces, Fehling’s and Tollen’s reagent, etc., 14. (d) :, C6H5, , CH, , CH2, , C, , CH3, , CH, , C, , CO, + HCl, , O, C, , + (C6H5)2Cd, , CH3, , 15. (a) : FCH2CHO is most reactive towards nucleophilic, addition since presence of most electronegative F withdraws, electrons from carbon of carbonyl group making it more polar., 16. (a) :, , (iii), , AlCl3, , 27. (b) :, , O, CH, , +, , COCl, , � –H2O, , C6H5, , 26. (c) : (i), , O, , OH, C6H5CHO + CH3COCH3, , COCl, , is 2-methylcyclopentanecarboxylic, , acid., 17. (a) : Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones., 18. (c) : Due to –I effect of Cl, chloroacetic acid is a stronger, acid than acetic acid. Due to stabilization of phenoxide ion by, resonance, phenol is a stronger acid than ethanol., , 28. (b) :, , is called Clemmensen, , reduction., 29. (a) :, Nucleophile attacks at the positive C centre of carbonyl group, hence the addition is nucleophilic addition., 30. (a) :, , 19. (b) : Pentan-2-one will give positive iodoform test while, pentan-3-one will not give this test., , 20. (b) :, 21. (d) : 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid will not undergo HVZ, reaction due to absence of an a-H atom., , 22. (b) :, , 23. (a) : 2CH CH + 3H2O, , 420°C, Mg or, Zinc vanadate, , CH3COCH3 + CO2 + 2H2, 24. (a), 25. (a) : Ketones are less reactive than aldehydes., , 31. (c) : The electron withdrawing strength of halogen, groups is in the order of F > Cl > Br. Hence, the strength of, acids is, FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH., 32. (b) : Aldehydes give silver mirror test with Tollen’s, reagent while ketones form oximes with hydroxylamine., Hence the compound is a ketone. Alcohol and ethers do not, give this test., 33. (a) : Pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one can be, differentiated by iodoform test., , 34. (d) : HCHO will be most polar due to lowest electron, density on carbon of carbonyl group., 35. (a) : Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards, nucleophilic addition reactions. Aromatic aldehydes and, ketones are less reactive than corresponding aliphatic, aldehydes and ketones., 36. (d) : Both butanal and propanal does not give iodoform, test, hence cannot be distinguished from each other.
Page 23 :
56. (c) :, , 63. (b) :, , O, , 57. (b) : R, , CH, , CH, , CHO + H2N, , C, , NHNH2, H+, , R CH, , CH, , CH, , N, , NH, , O, C, , NH2, , 58. (c) : CH3COOC2H5 will not give acetic acid on oxidation., 59. (b) : Aromatic ketones are less reactive than aliphatic, ketones which in turn are less reactive than aldehyde. Hence,, acetophenone does not react with NaHSO3., 60. (a) :, , Since (B) on reaction with 2,4-DNP forms a derivative, it, implies that (B) has, group., (B) gives –ve Tollens’ test, hence it is not an aldehyde, but it, is a ketone., (B) gives –ve haloform test, thus it is not a methyl ketone., (B) is formed from the oxidation of (A), thus (A) is a 2°alcohol,, and among the given options,, (A) is, and (B) is, C == O, aldehyde/, ketones, , Zn-Hg/, HCl, , — CH2 —, alkanes, , 64. (c) : Ortho-effect says that all the o-substituted benzoic, acids are stronger acids than benzoic acid, so the correct order, is, 61. (b) :, , COOH, , COOH, >, , COOH, CH3 >, , OH >, , (ortho-effect, pronounced due, (-R effect of to H-bonding in, —NO2 group) carboxylate ion), , NO2, , COOH, , (ortho-effect), , Thus, Order III given is incorrect as in this ortho-effect is not, considered., /C, , 62. (d) : H3C, , /H, , (P), , 4-Vinyltoluene, , Order I and II are correct., 65. (c) : Carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel Craft’s, reaction because carboxyl group is deactivating and gets, bonded to the catalyst in Friedel Craft’s reaction., 66. (a) : A undergoes Iodoform reaction hence contains a, methyl ketone. So the structure of A is, , �, , /C, (Q), , CH3, , /H, , �, , (Butan-2-one), , A (butan-2-one) on reduction gives butan-2-ol (B).
Page 25 :
78. (b) : CH3CHO + CH3COCH3, , Cl, , CH3CH(OH)CH2COCH3, , 2Cl, , CH3CH, , C, , NaOH, , C, , C, Cl, , , , CHCOCH3, , Cl, , H, , Cl, , � –H2O, , Cl, , O, , O, C, , O–, , trichloroacetate ion, , 79. (a), + Cl, , 80. (d), 81. (d) : Benzaldehyde(C 6H 5CHO) with no a-hydrogen, cannot undergo aldol condensation., 82. (a), 83. (b) : HSO3– is a bulky nucleophile, hence, cannot attack, on sterically hindered ketones., 84. (d) : Aromatic aldehydes and ketones are less reactive, than the corresponding aliphatic analogues towards, nucleophilic addition reactions due to the +R effect of, benzene ring. Further, aldehydes are more reactive than, ketones due to +I effect and steric effect of alkyl group., Therefore, the ease of nucleophilic addition will follow the, order :, , �, , Cl, , OH, , C, , CH2, , Cl, , �, , 2, 2, 2-trichloroethanol, , 90. (b) : Hydride transfer is the slowest step., O, Ph, , C, , –, , O, OH + Ph, , C, , slow, , H step, , H, �, 91. (a) : C, , O, Ph, , C, , OH + Ph, , CH2O–, , C bond is not formed in Cannizzaro reaction, , while other reactions result in the formation of C, , C bond., , 92. (c) : Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde do not, contain a-hydrogen and thus undergo Cannizzaro reaction., Formaldehyde is more reactive than aromatic aldehydes., 85. (a) : Formation of cyanohydrin from an aldehyde or, ketone occurs very slowly with pure HCN because it is feebly, ionised. This reaction is catalysed by a base. Base generates, CN– ion which is a stronger nuclephile and readily adds to, carbonyl compound., OH + HCN, CN + H2O, d+, , O–, , d, , O + •• CN, , C, , C, , CN, , H+, , OH, C, , CN, , 86. (b) : Electron withdrawing group (–NO2) increases the, reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions, whereas, electron donating group (–CH3) decreases the reactivity, towards nucleophilic addition reactions., 87. (a) : It is an example of cross Cannizzaro reaction where, aromatic aldehyde gets reduced to alcohol and aliphatic, aldehyde gets oxidised to its sodium salt (both aldehydes, must not contain any a-hydrogen)., CH2OH, CHO, + NaOH + HCHO, , ∆, , 93. (c) : The anion left after the removal of a-hydrogen is, stabilized by resonance effect., 94. (c) : Highly branched carboxylic acids are less acidic, than unbranched acids. The +I effect of alkyl groups in, branched acid increases the magnitude of negative charge., Thus, –COOH group is shielded from solvent molecules, and cannot be stabilized by solvation as effectively as in, unbranched carboxylic acids., 95. (c) : In p-chlorobenzoic acid, both +R and –I effect, operate together but in m-chlorobenzoic acid only –I effect, operates. Therefore, m-chlorobenzoic acid is a stronger acid, than p-chlorobenzoic acid., 96. (c) : Addition of Grignard reagents to dry ice followed, by hydrolysis gives carboxylic acid not ketone., , 97. (a), + HCOONa, , 88. (c), 89. (a) : The Cannizzaro product of given reaction yields 2,, 2, 2-trichloroethanol., , 98. (c) : Carboxyl group only marginally decreases the, electron density at m-position relative to o- and p-positions., 99. (b) : Aldehydes have higher molecular weight than, parent alkanes as well as polarity in aldehydes shows higher, boiling point than parent alkanes. Aldehydes do not have
Page 26 :
any hydrogen atom attached directly to the oxygen so they, cannot form hydrogen bond with each other., 100. (c) : Chlorine atom has –I effect which increases, the ionisation of chloroacetic acid and stabilizes the, chloroacetate ion by dispersal of negative charge. In, acetic acid, methyl group due to +I effect destabilizes the, acetate ion by intensification of negative charge. Hence,, chloroacetic acid dissociates to a greater extent than acetic, acid., 101. (d) : Aldehydes having a methyl or methylene group, in the a-position or more correctly having atleast one, hydrogen atom in the a-position undergo dimerisation in, presence of a base at low temperature to form b-hydroxy, aldehydes called aldols. As benzaldehyde does not have any, a-hydrogen hence it does not undergoes aldol condensation., 102. (b) : Due to overall electron-donating effect of, the phenyl group, benzoate ion is less stable than formate, ion., 103. (b) : Carbonyl compounds form solid additive products, with NaHSO3 which are separated out. The solid bisulphites of, carbonyl compounds on hydrolysis with dilute acid regenerate, original carbonyl compounds and thus, this property is used, for the purification of carbonyl compounds as well as for, their separation., 104. (b) : Boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher due, to their tendency to associate and form dimers to a greater, extent by hydrogen bonding., 105. (a) : o-Substituted benzoic acids are generally, stronger acids than benzoic acid. This is regardless of the, nature (+I or –I) of the substituent. This is called orthoeffect and is probably due to a combination of steric and, electronic factors., , SUBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS, 1., , Increasing order of boiling point :, , �, 5. Chloroacetic acid has lower pKa value than acetic acid;, ‘Cl’ in chloroacetic acid shows –I effect, it creates less electron, density on oxygen of carboxylic acid. Thus, release of proton, becomes easier. In case of acetic acid, the state of affair is, just opposite. Hence, chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic, acid., OH, 6., CHO, 2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, , 7. The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower, than that of corresponding alcohols and acids due to absence, of intermolecular H–bonding in aldehydes and ketones., 8., , 9. Hex-2-en-4-yn-oic acid, 10. Etard reaction :, CH3, CS2, + CrO2Cl2 →, , CH(OCrOHCl2)2, , Chromium, complex, , Toluene, , →, , CH3 CHO < C2H5OH < CH3 COOH, , 4., , H 3O +, , 2., , CHO, , Benzaldehyde, , 3., , 11., OH, , �, , O, , �, , CH3 CH CH2 C H, , CH3 CH CH C H, (D), , O, , (C)