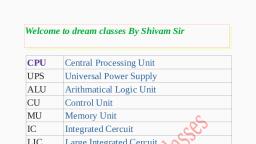
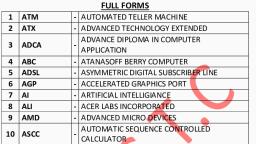
Page 1 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), Memory and Storage Related Questions, , 1. Cache memory is used as a ___________memory., a) primary, b) secondary, c) territory, Ans. d, , d) Scratch, , 2. MSB stands for_____., a) mobile source bit, c) module significant bit, Ans. b, , b) most significant bit, d) more social bit, , 3. LSB stands for______., a) localHeetson bit, c) least significant bit, Ans. c, , b) local significant bit, d) large significant Heetson, , 4. _____ can be treated as the waiting room for the computers processor., Ans. RAM, 5. _______ store data or information temporarily and pass it on as directed by the control unit., Ans. Register, 6. Common type of storage devices are_____, Ans. Optical, 7. _____ files contains permanent data and gets updated during the processing of Transactions., Ans. Master, 8. ______ helps to protect Floppy disks from data getting accidentally erased., Ans. Write Protect notch, 9. _____ memory is having more memory addresses than are physically available., Ans. Virtual
Page 2 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 10. A ______ is a location for storing files on your computer., Ans. Directory, 11. RAM memory space is divided into _____., Ans. Backs, 12. Decoder decodes the _______ address., Ans. Memory, 13.Main memory ______ data after power off., (a) retains, (b) remembers, (c) does not keep, (d) keeps all, Ans. c, 14.Since main memory looses data after power off, it is called ______., (a) data storage, (b) volatile storage, (c) power storage, (d) secondary storage, Ans. b, 15.SRAM stands for ____., (a) Static Random Access Memory, (b) Stable Random Access Memory, (c) Static Read Access Memory, (d) Static Random Arithmetic Memory, Ans. a, 16.DRAM stands for _____., (a) Draft Random Access Memory, (b) Direct Random Access Memory, (c) Disk Random Access Memory, (d) Dynamic Random Access Memory, Ans. d, 17.FPM DRAM stands for _____., (a) First Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory, (b) Fast Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory, (c) Fill Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory, (d) Fast Package Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory, Ans. b, 18. EDO DRAM stands for _____., (a) Extended Disk Out Dynamic Random Access Memory, (b) Expanded Data Out Dynamic Random Access Memory, (c) Extended Data Out Dynamic Random Access Memory, (d) Extended Data Onboard Dynamic Random Access Memory, Ans. c
Page 3 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 19.SDRAM stands for _____., (a) Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory, (b) Simple Dynamic Random Access Memory, (c) Synchronous Double Random Access Memory, (d) Syntax Dynamic Random Access Memory, Ans. A, 20. DDR SDRAM stands for _____., (a) Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory, (b) Double Data Rate Simple Dynamic Random Access Memory, (c) Double Data Rate Synchronous Double Random Access Memory, (d) Double Data Rate Syntax Dynamic Random Access Memory, Ans. a, 21.RDRAM stands for ______., (a) Resultant Random Access Memory, (b) Reactive Random Access Memory, (c) Rational Random Access Memory, (d) Rambus Random Access Memory, Ans. d, 22.VRAM stands for _____., (a) Visual Random Access Memory, (b) Video Random Access Memory, (c) Virtual Random Access Memory, (d) Vintage Random Access Memory, Ans. b, 23.MPDRAM stands for ____., (a) Major Port Dynamic Random Access Memory, (b) Multi-Point Dynamic Random Access Memory, (c) Multi-Port Dynamic Random Access Memory, (d) Multi-Port Data Random Access Memory, Ans. c, 24.SGRAM stands for _____., (a) Synchronous Graphics Random Access Memory, (b) Syntax Graphics Random Access Memory, (c) Simple Graphics Random Access Memory, (d) Synchronous Gross Random Access Memory, Ans. a, 25.CD/DVD drive uses _______ for data storage and retrieval., (a) LASER beam acting on light sensitive layer, (b) magnetic disk mounted in spindle, (c) flash memory, (d) plastic magnetic plate, Ans. a, 26.SD card, mini SD card and micro SD card use _____ for data storage and retrieval., (a) LASER beam acting on light sensitive layer, (b) magnetic disk mounted in spindle, (c) flash memory, (d) plastic magnetic plate, Ans. c
Page 4 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 27.Floppy disk used_______ for data storage and retrieval., (a) LASER beam acting on light sensitive layer, (b) magnetic disk mounted in spindle, (c) ash memory, (d) plastic magnetic plate, Ans. d, 28.Mini SD card is expanded as ______., (a) Secure Digital Card, (b) Mini Secure Digital Card, (c) Micro Secure Digital Card, (d) Major Secure Digital Card, Ans. b, 29.Micro SD card is expanded as _____., (a) Secure Digital Card, (b) Mini Secure Digital Card, (c) Micro Secure Digital Card, (d) Major Secure Digital Card, Ans. c, 30.PCMCIA stands for ______., (a) Protected Computer Memory Card International Association, (b) Personal Computer Memory Card International Association, (c) Personal Complementary Memory Card International Association, (d) Pen drive Computer Memory Card International Association, Ans. b, 31.The smallest storage unit permitting storage of 0 and 1 is called ______., (a) bit, (b) nibble, (c) byte, (d) kilo byte, Ans. a, 32.One bit can store ______ range of values., (a) 0 or 1, (b) 0 to 255, (c) 0 to 512, (d) 0 to 1024, Ans. a, 33.4 bits of memory is called _____., (a) bit, (b) nibble, (c) byte, (d) kilo byte, Ans. b, 34.Nibble is a storage unit consisting of ____ bits., (a) 8, (b) 16, (c) 4, (d) 64, Ans. c, 35.8 bits of memory is called ______., (a) bit, (b) nibble, (c) byte, (d) kilo byte, Ans. c
Page 5 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 36.Byte is a storage unit consisting of ____ bits., (a) 8, (b) 16, (c) 4, (d) 64, Ans. a, 37.1024 KB of storage is called ______., (a) byte, (b) Kilo Byte (KB), (c) Mega Byte (MB), (d) Tera Byte (TB), Ans. c, 38.1 MB = ______ KB., (a) 1024, (b) 1048576, (c) 1073741824, (d) 1099511627776, Ans. a, 39.1 MB = _____ bits., (a) 1024, (c) 1073741824, Ans. b, , (b) 1048576, (d) 1099511627776, , 40.1024 MB of storage is called _______., (a) byte, (b) Kilo Byte (KB), (c) Mega Byte (MB), (d) Tera Byte (TB), Ans. d, 41.1 TB = ______ MB., (a) 256, (b) 512, (c) 1024, (d) 2048, Ans. c, 42.1024 TB = 1______., (a) Mega Byte (MB), (b) Tera Byte (TB), (c) Peta Byte (PB), (d) Exa Byte (EB), Ans. c, 43.1 PB = 1024 _____., (a) Mega Byte (MB), (b) Tera Byte (TB), (c) Peta Byte (PB), (d) Exa Byte (EB), Ans. b, 44.1024 PB = 1 ______., (a) Mega Byte (MB), (b) Tera Byte (TB), (c) Peta Byte (PB), (d) Exa Byte (EB), Ans. d
Page 6 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 45.1 EB (Exa Byte) = 1024 _____., (a) Mega Byte (MB), (b) Tera Byte (TB), (c) Peta Byte (PB), (d) Exa Byte (EB), Ans. c, 46.The storage capacity of a Secure Digital (SD) card/ Mini SD card/ Micro SD card or pen drive, can be in the range of ______., (a) 1 bit to 8 bits, (b) 4 bits to 8 bits, (c) 2GB to 128GB (d) 1 MB to 1024MB, Ans. c, 47.Permitting storage of files on a web based server is called _____., (a) cloud storage, (b) local storage, (c) email storage, (d) had disk storage, Ans. a, 48.Cloud storage can be accessed from any host having a ______., (a) RS232 port, (b) Internet connection, (c) USB port, (d) VGA port, Ans. b, 49.Documents in Microsoft One Drive can be edited using _____., (a) online version of Microsoft office tools using browser, (b) installed version of Microsoft office tools, (c) both a & b, (d) none of them, Ans. c, 50. A permanent memory, which hold data and instructions for start-up the computer and does not, erase data after power off., a) Network interface card, b) CPU, c) RAM, d) ROM, Ans. d, 51. Which of the following memories must be refreshed many times per second?, a) EPROM, b) ROM, c) Static RAM, d) Dynamic RAM, Ans. d, 52. USB-type storage device is –, a) Secondary, b) Axilary, c) Tertiary, d) Primary, Ans. a
Page 7 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 53. Which of the following places the common data elements in order from smallest to largest?, a) Character, File, Record, Field, Database, File, b) Character, Record, Field, Database, File, c) Character, Field, Record, File, Database, d) Bit, Byte, Character, Record, Field, File, Database, Ans. c, 54. Which device is used to back-up the data?, a) Floppy Disk, b) Tape, c) Network Drive, d) All of these, Ans. d, 55. Main memory of computer is –, a) Internal, b) External, c) Both A and B, d) Auxiliary, Ans. a, 56. What is the permanent memory built into your computer called?, a) RAM, b) ROM, c) CPU, d) CD-ROM, Ans. b, 57. With a CD you can _____, a) Read, b) write, c) Read and write, d) either read or write, Ans. a, 58. Magnetic tape is not practical for applications where data must be quickly recalled because, tape is ______, a) A random access medium, b) A sequential Access medium, c) A read only medium, d) An Expensive storage medium, Ans. b, 59. What is the main advantage of magnetic core memory over semiconductor RAM memory?, a) More compact and smaller, b) More economical, c) A bit does not have to write after reading, d) Non-volatile, Ans. d, 60. Hard disk drives are considered _____ storage, a) Flash, b) Non-Volatile, c) Temporary, d) Non-permanent, Ans. b
Page 8 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 61. Permanent instructions that the computers uses when it is turned on and that cannot be, changed by other instructors are contained in –, a) ROM, b) RAM, c) ALU, d) CPU, Ans. a, 62. A Winchester disk is a ______., a) disk stack, b) removable disk, c) flexible disk, d) all of these, Ans. A, 63. Typical acronym of reusable optical storage will be …., a) CD, b) CD – RW, c) DVD, d) RPM, Ans. b, 64. Data gathering in computer means, they allow to use ____ data., a) Present b) Input, c) Output, d) Store, Ans. d, 65. When we work on any document on PC, it is stored temporarily on –, a) RAM, b) ROM, c) CPU, d) Flash memory, Ans. a, 66. The faster, costlier and relatively small from of storage managed by computer system, hardware is:, a) Main memory, b) Flash memory, c) Cache, d) Disk, Ans. c, 67. The analytical engine used ____ as a memory unit., a) RAM, b) Floppies, c) Cards, d) Counter wheels, Ans. d, 68. Breaking logical memory into blocks of the same size is called as:, a) Frames, b) Segments, c) Packets, d) Pages
Page 9 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), Ans. d, 69. Where data will remain intact even when the computer is turned of, a) RAM, b) Mother board, c) Secondary storage device, d) Primary storage device, Ans. c, 70. For permanent memory in computer objects used are –, a) Floppy disk, b) Magnetic tape, c) Hard disk, d) Optical disk, e) All of these, Ans. E, 71. Main memory works in conjunction with _____, a) RAM, b) CPU, c) Graphics card, Ans. b, , d) LAN, , 72. A nonvolatile type of memory that can be programmed and erased in sectors, rather than one, byte at a time is:, a) Flash memory b) MPROM, c) EPROM, d) EEPROM, Ans. a, 73. Memory that loses its contents when power is lost is:, a) random, b) volatile, c) nonvolatile, d) static, Ans. b, 74. When power is supplied to the system then to maintain data with the life of battery, computer, BIOS contains the following., a) CMOS, b) RAM, c) DRAM, d) CPU, Ans. a, 75. The two kind of main memory are, a) ROM, b) direct and sequential, c) primary and secondary, d) Floppy disk and hard disk, Ans. c, 76. Which one is the secondary memory device?, a) CPU, b) ALU
Page 10 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), c) Floppy disk, d) Mouse, Ans. c, 77. Which of the following is an example of non-volatile memory?, a) ROM, b) VLSI, c) LSI, d) RAM, Ans. a, 78. The term “memory” applies to which one of the following?, a) Logic, b) Storage, c) Control, d) Input device, Ans. b, 79. The work „computer‟ usually refers to the central processor unit plus, a) external memory, b) internal memory, c) input device, d) output device, Ans. B, 80. What are the two basic types of memory that your computer uses?, a) RAM/ROM, b) RW/RAM, c) ROM, d) ERAM, Ans. a, 81. Which of the following memories below is often used in typical computer operation?, a) DRAM, b) ROM, c) FDD, d) HDD, Ans. a, 82. The storage that supplements the primary internal storage of a computer is known as, a) secondary storage, b) primary storage, c) back-end storage, d) background storage, Ans. c, 83. ______ is a form of permanent memory that holds all the instructions the computer needs to, start up and does not get erased when the power is turned off., a) The network interface card, b) The CPU, c) RAM, d) ROM, Ans. d, 84. What is the name given to the memory which works on time sharing principle in order to create, an illusion of infinite memory space?, a) Cache memory b) Register, c) Virtual memory d) Primary memory, Ans. c
Page 11 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 85. Which contents are lost when the computer turns off?, a) Storage, b) Input, c) Output, d) Memory, Ans. d, 86. The following computer‟s memory is characterised by low cost per bit stored _______, a) Primary, b) Secondary, c) Hard disk d) All of these, Ans. b, 87. A memo data type of access can hold _____ characters., a) 31000, b) 32000, c) 33000, d) 34000, Ans. b, 88. The main advantage of semiconductor RAM is its ability to:, a) retain stored data when power is interrupted or turned off, b) be written to and read from rapidly, c) be randomly accessed, d) be sequentially accessed, Ans. B, 89. Which of the following is one of the basic characteristics of DRAM‟s?, a) DRAMs must have a constantly changing input., b) DRAMs must be periodically refreshed in order to be able to retain data., c) DRAMs have a broader “dynamic” storage range than other, d) DRAMs are simpler devices than other types of memories., Ans. b, 90. Which of the following memories not needs refresh?, a) SRAM, b) DRAM, c) ROM, d) All of these, Ans. a, 91. Which statement is valid?, a) 1 KB = 1024 bytes, b) 1 MB = 2048 bytes, c) 1 MB = 10000 kilobytes, d) 1 KB = 100 bytes, Ans. a, 92. A name or number used to identify a storage location devices?, a) A byte, b) A record, c) An address, d) All of these, Ans. c
Page 12 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 93. High density double sided floppy disks could store ____ of data, a) 1.40 MB, b) 1.44 GB, c) 1.44 MB, d) 1.40 GB, Ans. c, 94. CD – ROM stands for, a) Compactable Read only memory, b) Compact Data Read only memory, c) Compact Disk Read only memory, d) Compact Disk Read only memory, Ans. d, 95. Select the smallest memory size., a) Terabyte b) Gigabyte, c) Kilobyte d) Megabyte, Ans. c, 96. Before a disk drive can access any sector record, a computer program has to provide the, record‟s disk address. What information does this address specify?, a) Track number, b) Sector number, c) Surface number, d) All of these, Ans. d, 97. A storage area used to store data to a compensate for the difference in speed at which the, different units can handle data is, a) Memory, b) Buffer, c) Accumulator, d) Address, Ans. b, 98.Instructions and memory address are represented by, a) Character code, b) Binary codes, c) Binary word, d) Parity bit, Ans. b, 99. Fragmentation is –, a) dividing the secondary memory into equal sized fragments, b) dividing the main memory into equal size fragments, c) fragments of memory words used in a page, d) fragments of memory words unused in a page, Ans. a, 100. Bootstrap loader is always stored in –, a) Cache, b) ROM, c) RAM, d) Disk, Ans. b
Page 13 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 101. Which memory unit has lowest access time?, a) Cache, b) Register, c) Magnetic Disk, d) Main memory, Ans. b, 102. Copying computer program/ software without permission of its author is called –, a) High way robbery, b) Larcencyheetson, c) Software piracy, d) Embezzlement, Ans. c, 103. Cache memory –, a) has greater capacity than RAM, b) is faster to access than CPU register, c) is permanent storage, d) faster to access than RAM, Ans. d, 104. The memory implemented using the semiconductor chips is ____, a) Cache, b) Main, c) Secondary, d) Registers, Ans. b, 105. Size of the _____ Memory mainly depends on the size of the address bus., a) Main, b) Virtual, c) Secondary, d) Cache, Ans. a, 106. Which of the following is independent of the address bus?, a) Secondary memory, b) Main memory, c) Onboard memory, d) Cache memory, Ans. a, 107. _______ storage is a system where a robotic arm will connect or disconnect off-line mass, storage media according to the computer operating system demands., a) Secondary, b) Virtual, c) Tertiary, d) Magnetic, Ans. c, 108. What is the location of the internal registers of CPU?, a) Internal, b) On – chip, c) External, d) Motherboard, Ans. b
Page 14 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 109. All of the following are non volatile memory except, a) ROM, b) PROM, c) flash memory, d) RAM, Ans. d, 110. Computer memory is measured in terms of, a) bits, b) bytes, c) cells, d) units, Ans. b, 111. A nibble is composed of, a) 8 bits, b) 4 bits, c) 2 bits, d) 6 bits, Ans. b, 112. Data is written to and read from the disk via a magnetic _____ head mechanism in the floppy, drive., a) cylinder b) read/write, c) cluster, d) recordable, Ans. b, 113. What is the difference between static RAM and dynamic RAM?, a) Static RAM must be refreshed, dynamic RAM does not., b) Dynamic RAM must be refreshed, static RAM does not., c) There is no difference, d) Both A and B, Ans. b, 114. Advantage of an EEPROM over an EPROM is/are:, a) The EEPROM has the ability to erase and reprogram individual words, b) The EEPROM can be erased with ultraviolet light in much less time than an EEPROM, c) The EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed without removal from the circuit, d) The EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed without removal from the circuit, and can be, erase and reprogram individual words, Ans. d, 115. The mask ROM is _____, a) MOS technology, b) diode technology, c) resister diode technology, d) DROM technology, Ans. a, 116. The storage element for a static RAM is the _____, a) diode, b) resistor, c) capacitor, d) flip-flop, Ans. d
Page 15 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 117. 1024 bits of storage is called _____ ., (a) bit, (b) nibble, (c) byte, (d) kilo byte, Ans. d, 118. Which of the following medium is used between CPU & RAM to speed up the processing, power of a CPU?, a) Virtual memory, b) D RAM, c) Flash Memory, d) Cache Memory, Ans. d, 1. MAR stands for _____, a) Memory address register, b) Main address register, c) Main accessible register, d) Memory accessible register, 2. Which type of ROM can be erased by an electrical signal?, a) ROM, b) EPROM, c) mask ROM, d) EEPROM, 3. The program which are as permanent as hardware and stored in ROM is known as., a) Hardware, b) Software, c) Firmware, d) All of these, 4. One nibble is equal to how many bits?, a) 4 bits, b) 8 bits, c) 12 bits, d) 16 bits, 5. Data and program stored in ______ memory when the Processor uses them., a) Main, b) Secondary, c) Tertiary, d) etsony, 6. Bit is a short form of ______., a) Binary digit, b) Nibble, c) Byte, d) Register
Page 16 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 7.The storage which handles data required for the processor (by fetching data from or saving data, to secondary storage) is called ______., (a) main memory, (b) primary storage/ volatile storage, (c) Random Access Memory (RAM), (d) all of them, 8.RAM is expanded as _____., (a) Right Access Memory, (b) Random Active Memory, (c) Random Access Memory, (d) Random Access Meter, 9. Secondary storage is otherwise called _____., (a) auxiliary storage, (b) permanent storage, (c) both a & b, (d) main memory, 10. Data store in secondary storage is ____., (a) volatile, (b) lost after power off, (c) is deleted after every reboot, (d) permanent (available till deletion), 11. Hard disk uses ______ for data storage and retrieval., (a) LASER beam acting on light sensitive layer, (b) magnetic disk mounted in spindle, (c) flash memory, (d) plastic magnetic plate, 12. SD card is expanded as ______., (a) Secure Digital Card, (b) Mini Secure Digital Card, (c) Micro Secure Digital Card, (d) Major Secure Digital Card, 13. The storage capacity of a Compact Disk (CD) is ______ ., (a) 700MB (b) 4.7GB, (c) 512MB (d) 1TB, 14. The storage capacity of a Digital Versatile Disk (DVD) is ______., (a) 800MB (b) 4.7GB, (c) 512MB (d) 1TB, 15. Storage Capacity of a Blue Ray Disk is _____, (a) 25GB, (b) 4.7GB, (c) 512MB (d) 1TB, 16. The storage capacity of a common hard disk is _____., (a) 256MB, (b) 512GB, (c) 1TB, (d) any one of a, b or c
Page 17 :
These Questions Prepared By: Sonu (HEETSON), 17. Popular cloud storages are ______., (a) Microsoft One Drive, (b) Google Drive, (c) Dropbox/ Apple iCloud, (d) all of them, 18.Cloud storage can be accessed from _____., (a) computers, (b) mobile devices, (c) both a & b, (d) none of them, 19. Storage which stores or retains data after power off is called –, a) Volatile Storage, b) Non – Volatile storage, c) Sequential storage, d) Direct storage, 20. A half byte is known as ______., a) data, b) bit, c) half bit, d) nibble, 21. What is the full form of ROM?, a) Read only memory, b) Read on Memory, c) Read only Menu, d) Recall only memory, 22. Virtual memory is _____., a) Memory on the hard disk that the CPU uses an extended RAM, b) in RAM, c) only necessary if you do not have any RAM in your computer, d) a backup device for floppy disk, 23. USB stands for –, a) Uniform service Bus, c) Universe Service Bus, , b) Universal Serial Bus, d) Universel Service Bus, , 24. What is meant by the term RAM?, a) Memory which only be read, b) Memory which both read and written, c) Memory which is used for permanent storage, d) Memory which can only be written, , Click here for Answers, , Computer MCQ for All Competitive Exams