Page 1 :
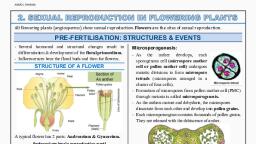
Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants, Q. 1 Multiple choice questions., 1. Insect pollinated flowers usually posses ……………, a)Sticky pollens with rough surface. b) Large quantities of pollens, c) Dry pollens with smooth surface d) Light coloured pollens, 2. In ovule, Meiosis occurs in……a) Integument b) Nucellus c) Megaspore d) Megaspore mother cell, 3. The ploidy level is not the same in …, a)Intefuments and nucellus b) Root tip and shoot tip c)Secondary nucleus and endosperm, d) Autipodals and synergids, 4. Which of the followi ng types require pollinator but result is genetically similar to autogamy?, a) Geitonogamy b) Xenogamy c) Apogamy b) Cleistogamy, 5. If diploid chromosome number in a flowering plant is 12, then which one of the following will have 6 chromosomes ?, a) Free nuclear divisions of megaspore b) polar nuclei, c) polar nuclei and male gamete, 7. point out the odd one………………, a) Nucellus b) Embryo sac c) Micropyle d)Pollen grain, 8. In wall fo mature anther,…………… shows fibrous thickenings., a) epidermis b) Endothecium c) middle layer d) tapetum, 9. heterostyly; perimula flowers :: Herkogamy : ?, a) Gloriosa b) calotripis c)thea d) salvia, 10)Which flower exhibits turn pipe mechanism of pollination?, a)salvia b) Zostera c)Cestrum d) callistemon, 11) when diplod sporophytic cell froms diploid gametophyte without meiosis it is phenomenon of ……, a) Malic acid b) Sucrose c) Boric acid d) Indole acetic acid, 12)Citrus seeds : Polembryony :: Papaya fruits: ?, a) Diplospory b) Apogamy c) parthenocarpy d) Apospory, select the plant having both chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers, a) Viola b) Primula c)Thea d)Fritillaria, 14)Identify the mismatched pair, a) Cellular endosperm –Balsam b)Nuclear endosperm—Wheat, c)Helobial endosperm – Asphodelus d)Mosaic endosperm--- Coconut, 15) How many meiotic divisions are required for the formation of the 100 seeds?, a) 25 b)50 c) 100 d) 125, 16) If the number of chromosome number in an endosperm cell is 27 what will be the chromosome number in the definitive nucleus, a)9 b) 18 c)27 d)36, Q.2 Very short answer type questions :, 1. Name the part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen grain., 2. How many haploid cells are present in a mature embryo sac?, 3. Even though each pollen ghas 2 male gametes, why atleast 20 pollen grains are required to fertilize 20 ovules in a particular carple?, 4. Define megasporogenesis., 5. What is hydrophily ?, 6. Name the layer which supplies nourishment to the developing pollen grains., 7. Define parthenocarpy., 8. Are pollination and fertilization necessary in apomixes?, 9.Name the parts of pistil which develop into fruits and seeds., 10. What is the function of filiform apparatus?, 11)What is the function of flower?, 12)Enlist the wall layers of mature anther., 13) what is hay fever?, 14) what is the main role of pistil in pollen pistil interaction, 15) what type is the endosperm of coconut ?, 16)what is the origin of embryos in adventives polyemryony, 17)what is the triple fusion?, 18)what is an anatropous ovule, 19)what is dichogamy?, 20)How is dipoled condition restored in angiosperms?, Q .3 Short Answer Questions:, Howpolyembryony can be commercially exploited ?, Pollination and seeds formation are very crucial for the fruit formation. Justify the statement., Incompatibility is a natural barrier in the fusion of gametes. How will you explain this statement?, Describe three devices by which cross pollination is encouraged in Angiosprems by avoiding self pollination., Distinguish between Autgamy (self pollination )and Xenogamy(cross pollination), Distinguish between Hypohydrophily and Epilydrophily, Give significance/Importance of the following, 1)sexual reproduction 2)Pollen visbility 3) Synergid /Fillformapparatus 4)Herterostyly/Heteroanthy (Hetermorphy) 5) Double fertilization, 6)Endosperm 7) Apomixis 8) Parthenocarpy, 8. Name of the following, 1) Condition in the flower when androecium matures before that of gynoecium, 2 )A diplod nucleus in central cell of embryo sac in plants, 3)Components necessary to induce germination of pollen in the synthetic medium, 4) A condition of flowers where its sex organs are eposed, 5) The part of pistil which develops into fruits and seed, 6)A state of metabolic arrest that helps in survival of organism in adverse conditions, 9) Sktch and label 1) the T.S.of anther 2) Development of female gametophyte 3) Development of male gametophyte, 10. Give Reasons, 1)The development of embryo sac is described as monosporic, 2) Pollination is prerequisite fertilization in plants, 3) castor seed is endospermic or albuminous, 4) Parthenocarpic fruits are without seed, 5)Nucellar polyembryony is significant in horticulture, 11. Write short note, 1)Seed Dormancy 2)Parthenocarpy 3)Anemophily 4) Ornithophily 5)Embryosac 6) Entmophily 7) Endosperm, 12)Why do some plants have both chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers, 13) pollination and seeds formation are verycrucial for the fruits formation, 14) what are the different types of the cross pollination based on the abiotic pollinating agents, 15)Give the floral adaptatios for chiropterphily, 16) How polyembryony canbe commercially exploited, 17) Describe the T.S. of anther, 18) Describe the structure of a mature anatropous ovule or a typical angiospermic ovule, 19) What are different types of cross pollination based on the biotic pollinating agents, 20)Describe three device by which cross pollination is encouraged in Anigiosperms by avoiding self pollination, Q.4 Long Answer Questions, 1. Describe the process of double fertilization., 2. Explain the stages involved in the maturation of microspore into male gametophyte., 3. Explain the development of dicot embryo., 4. Draw a labeled diagram of the L.S. of anatropous ovule and list the components of embryo sac and mention their fate after fertilization., 5) What are the three types of endosperm? Describe them brifly, 6) What is apomixes ? Explain the categories of apomixes