Page 1 :
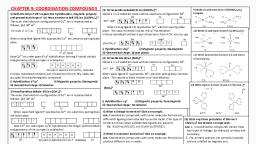
CHAPTER 8: d and f- Block elements, 1. Explain the manufacture of potassium dichromate, from chromite ore., Ans: Step; 1; Conversion of chromite ore into sodium, chromate, 4 FeCr2O4 + 8Na2CO3+7O2 ⎯⎯, → 8Na2CrO4 +2Fe2O3 + 8CO2, Step; 2; Conversion of sodium chromate to sodium, dichromate, 2Na2CrO4 + 2H+ ⎯⎯, → Na2Cr2O7 + 2Na+ + H2O, Step; 3: Conversion of sodium dichromate to, potassium dichromate., Na2Cr2O7 + 2KCl, , ⎯⎯, → K2Cr2O7 + 2NaCl, , 2. Explain the preparation of potassium permanganate, from MnO2., Ans: Finely powdered MnO2 is fused (melted) with KOH in, the presence of an oxidising agent like KNO3 produces dark, green coloured K2MnO4 (potassium manganate) which, disproportionate in a neutral or acidic solution to give, permanganate., , ⎯⎯, → 2 K2MnO4 + 2 H2O, + 4H ⎯⎯, → 2 MnO -4 + MnO2 + 2H2O, , 2 MnO2 + 4 KOH + O2, , 3 MnO, , 24, , +, , 3. What is lanthanide contraction? What is the reason for, it? Mention its consequences., Ans: The overall decrease in atomic and ionic radii from La, to Lu with increase in atomic number is called as, Lanthanoid contraction., Reason: Poor shielding of 4f orbital electrons, Consequence: (a) 4d and 5d series (or second and third, transition series) elements have same radii or Hf, and Zr have identical radii., (b) 4d and 5d elements exist together in the nature and, difficult to separate or chemistry of lanthanides are same, (c) Basic nature of hydroxides decreases from La to Lu, 4. Transition elements form complex compounds. Give, reasons, Ans: Reasons: a) Availability of vacant d-orbitals, b) Variable oxidation sates., c) High charge and small size of metal ions, d) High charge density as result of it they, can easily accept lone pair of electrons donated, by ligands., , 5. Give reason (i) Actinoid show variable oxidation state., (ii) Zr and Hf have almost identical radii., (iii) Cerium shows +4 oxidation states., (iv) Lanthanides are less reactive than actinides., Ans: (i) due to lesser energy difference between 5f, 6d and, 7s orbitals, (ii) Lanthanide contraction, (iii) Because in +4 cerium has noble gas configuration or it, attains Xe configuration which is more stable, (iv) Because lanthanides are non radioactive with less, variation in the oxidation state, 6. Give reason: Transition metals are good catalysts, Ans: 1) variable oxidation states, 2) Availability of vacant d-orbitals, 3) In finely provided form they provide large surface area, 4) They form intermediate compounds and provide a new, path for reaction of lower activation energy, , 11) With reference to first transition series name, (a) The metal with maximum number of unpaired electrons, in the ground state, Ans: Chromium, (b) Zero Spin only magnetic momentum in (i) +2 oxidation, state (ii) +3 oxidation state, Ans: (i) Zinc (ii) Scandium, (c) Exhibits maximum number of oxidation states, Ans: Manganese, (d) Does not exhibit variable oxidation state, Ans: Zinc or Scandium, (e) Shows maximum oxidation state, Ans: +7 by Mn in KMnO4, f) Among Zn2+ and Cu2+ which is colourless?, Ans: Zn2+, g) Between Ti2+ and V2+ which ion contains more number of, unpaired electrons?, Ans: V2+, , 7. Cu2+ ions are coloured and Zn2+ ions are colourless. Give, 12. Write differences between lanthanides and actinides., reasons., Lanthanides, Actinides, 2+, 2+, Ans: i) Cu ion has one unpaired eletron but Zn ion has, 1) Shows oxidation states, 1) Shows variable oxidation, no unpaired electrons, 2+,, 3+, and, 4+, only, states of 2+, 3+, 4+ , 5+, 6+, 7+, ii) d-d transition is present in Cu2+ but not in Zn2+, 8. Calculate the spin only magnetic moment of Fe2+ ., 2) Except promethium all, 2) All elements are radio, elements are nonactive, (Practice similar problems), radioactive in nature, Ans: Formula: = n(n + 2), 3) Form less number of, 3) Form more number of, complexes, complexes, In Fe2+, no. Of unpaired electrons = 4, 4) Form less basic, 4) Form more basic, = 4(4 + 2) = 24 = 4.90BM, hydroxides, hydroxides, 5) Contraction is less, 5) Contraction is more, 9) What are Interstitial compounds? Write its, characteristics, 13. Study of actinides is difficult. Give two reasons., Ans: Interstitial compounds are formed by the trapping, Ans: i) Actinoids are radioactive elements with less half lives, small atoms like C, N or H in crystal lattices of transition, ii) They are prepared in very less quantities, metals., 14) What is Mischmetal?, Characteristic properties: i) They have high melting point, Ans: Mischmetal is alloy of lanthanide. It contains, than metal (ii) They are hard in nature (iii) They are, good conductor of electricity (iv) They are chemically inert. lanthanide(94-95%) iron(5%) and traces of S,C,Si,Ca and Al, 10) Between Cu2+ and Cu+ which is more stable in, aqueous solution? Why?, Ans: Cu 2+ is more stable in aqueous solution due to high, negative hydration enthalpy, , 15) What is the common oxidation state shown by, (a) 3d series elements (b) Lanthanides or actinides, Ans: 3d series elements show common oxidation state of +2 and, Lanthanides or actinides show common oxidation state of +3