Page 1 :
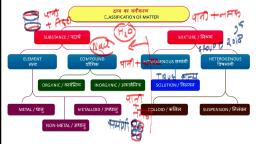
Is Matter Around Us Pure, By Alok Aditya, 1.) More than one kind of pure form of matter combines forming……….., a) Texture, b) Solution, c) Mixture, d) Component, 2.) Dissolved sodium chloride can be separated from water by…………………, a) Chemical process, b) Physical process, c) Chemical process of extraction, d) Physical process of evaporation, 3.) Non uniform compositions of solutions called………….. solutions., a) Mixture, b) Texture, c) Homogenous, d) Heterogeneous, 4.) Uniform compositions of solutions called………… solutions., a) Mixture, b) Texture, c) Homogenous, d) Heterogeneous, 5.) Homogenous solution may separated by………………., a) Chemical process, b) Physical process, c) filtration, d) Physical process of evaporation, 6.) Mixture of two or more metals , or metals and non-metals called as…………, a) Alloy, b) Solution, c) Mixture, d) Metallic mixture, 7.) Alloy cannot be separated by……………..method, a) Chemical, b) Evaporation, c) Extraction
Page 2 :
d) Physical, 8.) Brass is mixture of………….. and……….. ., a) Zinc, carbon, b) Zinc, Mg, c) Zinc, Co, d) Zinc, Copper, 9.) Zinc and Copper get mixed by forming………., a) Steel, b) Brass, c) Gold, d) Zinc carbon mixture, 10.) Component present in large amount in solution called…………., a) Solute, b) Sugar, c) Solvent, d) Mixture, 11.) The component of solution that dissolved in solvent called……………, a) Solute, b) Sugar, c) Solvent, d) Mixture, 12.) A component present in lesser quantity in solution called……….., a) Solute, b) Sugar, c) Solvent, d) Mixture, 13.) A component present in more quantity in solution called……………, a) Solute, b) Sugar, c) Solvent, d) Mixture, 14.) Sugar in water..in that case sugar is ………….., a) Solute, b) Small particles, c) Solvent, d) Mixture, 15.) Air is ………………….. mixture.
Page 3 :
a) Heterogeneous, b) Gas, c) Solid, d) Homogenous, 16.) if the solute particle size is smaller than …… then it cannot seen by naked eyes., a) 1m, b) 1cm, c) 1mm, d) 1nm, 17.) When no more solute can be dissolved in solution at given temperature is called………., Solution., a) Homogenous, b) Heterogeneous, c) Saturated, d) Unsaturated, 18.) The amount of the solute present in the saturated solution at this temperature is called, its…………………., a) Unsaturation, b) Diffusion, c) Collusion, d) Solubility, 19.) If the amount of solute contained in the solution is less than the saturation level…it called, as……………, a) Saturated solution, b) Unsaturated solution, c) Homogenous solution, d) Heterogeneous, 20.) The concentration of solution is the depend on amount of …………………. Present in given, solution., a) Solvent, b) Solution, c) Pericles, d) Solute, 21.) Mass of solute divided by mass of solution multiply by 100 then we get?, a) Solution, b) Mass, c) Mass percentage of solution
Page 4 :
c) Mass percentage of solution, d) Volume, 22.) Mass of solute divided by volume of solution multiply by 100 then we get?, a) Solution, b) Mass, c) Mass percentage of solution, d) Mass by Volume percentage of solution, 23.) If the solution is 400 ml and solvent is 300ml so what is percentage of solute?, a) 30, b) 40, c) 45, d) 25, 24.) Solids are disperse in liquids called……, a) Diffusion, b) Dissolution, c) Collusion, d) Suspension, 25.) Suspension is ……………… mixture., a) Saturated, b) Unsaturated, c) Homogenous, d) Heterogeneous, 26.) Mixture of water and milk shows……………….. effect., a) Solubility, b) Diffusion, c) Tyndall, d) Brightening, 27.) Colloid is ………… mixture., a) Saturated, b) Unsaturated, c) Homogenous, d) Heterogeneous, 28.) …………….. particles are scattered a beam of light passing through it and make its path, visible., a) Solute, b) Solvent, c) Colloidal, d) None of the above, 29.) Foam is the example of…………
Page 5 :
29.) Foam is the example of…………, a) Scattering light, b) Colloids, c) Saturated solution, d) Unsaturated solutions, 30.) We can separate the volatile component from its non volatile solute by the method of…………., a) Extraction, b) Separation, c) Filtration, d) Evaporation, 31.) Solid particle are not soluble in solution. That can be separated by the………, a) Extraction, b) Separation, c) Filtration, d) Evaporation, 32.) Solid particles are very small in solution which cannot separated by filtration that solution, separated by …………………., a) Dissolution, b) Collusion, c) Suspension, a) Centrifugation, 33.) Centrifugation do not used in……….., a) Diagnostic laboratories, b) Separate butter and cream, c) To separate water and sugar, d) Used in washing, 34.) Two immiscible layers can separate out in layer depending on their …………………, a) Volume, b) Surface tension, c) Density, d) Viscosity, 35.) ……………………….solutions can separated depending upon their densities., a) Miscible solution, b) Water, c) Immiscible, d) Colloidal, 36) Separation of camphor and salt done by…………… method, a) Dissolution
Page 6 :
a) Dissolution, b) Collusion, c) Sublimation, d) Suspension, 37.) Separation of dyes and black ink using ……………………. Method., a) Dissolution, b) Chromatographic, c) Sublimation, d) Suspension, 38.) ………………. Is a mixture of 2 or more colors., a) Alloy, b) Dyes, c) Ink, d) Paints, 39.) Kroma means?, a) Dyes, b) Colors, c) Paints, d) Natural colors, 40.) ……………………….. is method to separate two miscible liquids., a) Collusion, b) Sublimation, c) Suspension, d) Distillation, 41.) Chromatographic method used to separate, a) Colors in dye, b) Drug from blood, c) Tea powder from factory, d) Drugs from blood, 42.) Two miscible liquids having boiling point less than 25K can separated by …………….., a) Distillation, b) Sublimation, c) Suspension, d) Fractional distillation, 43.) ………………………… method used for separation of petroleum products., a) Distillation, b) Sublimation
Page 7 :
c) Suspension, d) Fractional distillation, 44.) Boiling point of oxygen., a) -280, b) -183, c) -130, d) -220, 45.) Boiling point of nitrogen, a) -196, b) -183, c) -130, d) -220, 46.) Crystallization method is used to purify……….., a) Liquid, b) Gas, c) Solid, d) Miscible liquids, 47.) ………………….. method is used to purify solid., a) Distillation, b) Sublimation, c) Fractional distillation, a) Crystallization, 48.) Crystal alum separated from impure samples by……………………. Method., a) Distillation, b) Sublimation, c) Fractional distillation, d) Crystallization, 49.) Chemical change shown in reaction called……………, a) Physical reaction, b) Chemical reaction, c) Saturated, d) Substitution reaction, 50.) Two or more atoms combined together forming…., a) Element, b) Molecule, c) Atoms, d) None of the above