Page 1 :
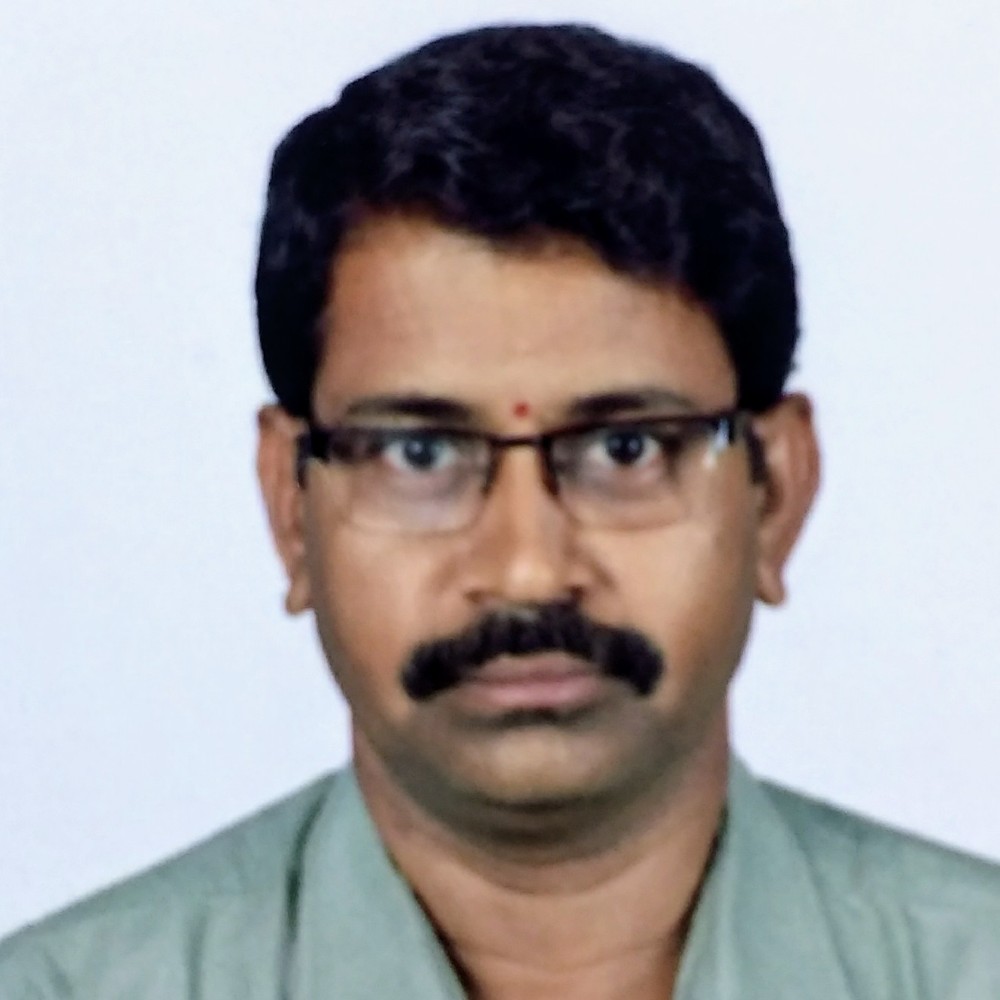
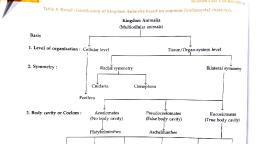
Concise Zoology, , Animal Kingdom, , page 1, , Cellular grade: Body is made up of many, cells, which are independent and do not form, tissue., Eg: sponges, , ANIMAL KINGDOM, 4.1. Basis of Classification., 4.2. Classification of Animals, , Animal Taxonomy - Basic Terminology, Habitat, Def: It is the place of living / dwelling., Terrestrial: That lives on land., Aquatic: lives in marine / fresh water., Burrowing: That lives in burrows., Arborial: living on trees., Aerial: That lives in sky / air., Amphibious: That lives both in water for, feeding (with aquatic respiration) and on, land, for, reproduction, (with, aerial, respiration)., Habit, It refers to body plan, organization,, symmetry (shape), behaviors like locomotion,, feeding etc., Solitary: Lives in single or alone., , Tissue grade: Body is made up of tissues to, perform different functions., Eg: Hydra to Man., Organ grade of organization: in multicellular, organisms, cells coordinate to form tissues,, organs and organ systems., Eg: Flatworms to mammals., Organ systems are absent in plants, Coelom / Body cavity:, It is the space b/w body wall & alimentary canal, (digestive tract)., a) Acoelomate: The animal without body cavity., Eg: Tape worm, liver fluke., b) Pseudocoelom: Body cavity is not lined, by epithelium. Eg: Roundworm., c) Eucoelom: (= true coelom): Body cavity is, lined by epithelium (ie, mesoderm)., Eg: Earthworms to higher animals including man., , Colonial: Live in groups or together., Sedentary: Attached to the substratum., Diploblastic: Body wall (of embryo) made, up of ectoderm and endoderm ie, body, tissues are derived from these two germ, layers., Eg: Coelenterates, Triploblastic: Body wall (of embryo), contains, ectoderm,, endoderm, and, mesoderm; ie, body tissues are derived, from these three germ layers., Eg: Flatworms to mammals., Nocturnal: The animals that are more, active during nights., Eg: Cockroach, Symmetry (Shape / Physic), Bilateral symmetry: When an animal is, cut into two equal parts only in one, longitudinal plane, passing through the, central axis., Eg: Frog, man, cockroach., Radial symmetry: When an animal is cut, into 2 equal parts in any longitudinal, plane, passing through the central axis., Eg: Hydra, jelly fish, Pleurobrachia, star, fish., Asymmetry: Without definite shape., Eg: Amoeba, sponges, snail., Organ grade of organization: in multicellular, organisms, cells coordinate to form tissues,, organs and organ systems., Eg: Flatworms to mammals., Organ systems are absent in plants, Levels of organization, Acellular / unicellular: Body is made up, of single cell., Eg: Protozoans, yeast fungi, bacteria, algae, (Chlamydomonas, diatom)., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , Digestive system, a) Extra cellular digestion: Digestion of food, outside the cell ie, within the lumen of, digestive tract., Eg: Hydra, higher animals like man., b) Intra cellular digestion: Digestion of food, within the cell., Eg: Phagocytes, Amoeba, Hydra etc., c) Complete digestive system: Anus present., d) Incomplete digestive system: Anus absent., e) Blastopore: Opening of the blastocoel, cavity in embryo stage. Blastopore may, develops into mouth (group Protostomia),, or it may develops into anus (group, Dueterostomia)., f) Parasite: The animals which depends on the, host body for food, shelter, reproduction etc., g) Endoparasite: It lives inside the host body, and depends completely on it., Eg: Tapeworm, round worm, malarian, parasite, virus, bacteria., h), , Ectoparasite: It depends on host without, entering into the host body., Eg: Mosquito, leech, head lice, bedbug, tics., , Circulatory system, a) Open type: Blood capillaries absent. Blood, moves through tissue spaces and coelomic, spaces called sinuses / sinusoids., Eg: Arthropods (cockroach),, Molluscans (snail), Liver of man., b) Closed type of: Blood passes through, definite capillaries., Eg: Annelids (earthworm) & all vertebrates., c) Haemocoel: The coelomic spaces filled, with blood in open type of circulatory, system., Eg. Cockroach (insects), molluscans.
Page 2 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, d) Single Circulation: Eg. Fishes., , page 2, Ranga Rao R H, Sira, 6. Tracheal respiration: Respiration through, trachea (wind pipes)., Gills, Gills, Eg. Cockroach, insects, Millipedes., Respiratory, Animals, organs, O2, CO2, O2, Skin / cuticle, Annelids, amphibians, Heart, Gills, fishes,, CO2, Ctenidia (= gills), Molluscans, Trachea, Insects (cockroach),, Tissues, Book lungs, Arachnids (scorpion), Lungs, Higher vertebrates, Heart receives only impure blood from, Dermal papillae, Echinoderms (star fish), tissues by one complete circulation. From, the heart, it is supplied to the gills for, purification. Then the purified blood is, Excretory system, directly supplied to the tissues., a) Excretory Organs, - Examples, e) Double Circulation: The Heart receives, * Body wall / cell surface - Sponges,, both pure and impure bloods by two, Hydra,, circulations say pulmonary circulation, *, Contractile, vacuoles, Protozoans, and systemic circulation., * Protonephridia (flame cells) -flat worms, Eg: Frog, Reptiles, Birds, Mammals, * Nephridia, - Annelids, including man., * Malpighian Tubules, - Cockroach, CO2, CO2, * Kidneys (nephrons), - Molluscans,, Lungs, Heart, Tissues, (= Metanephridia), man &, O2, O2, vertebrates, f) Myogenic Heart: Heart beat is originated, b) Nitrogenous wastes – organisms:, by a group of specialized muscular, 1) Ammonia - Ammonotelic, animals:, tissue called pace maker., (protozoans, invertebrates, bony fish., Eg. Human heart, heart of vertebrates, 2) Urea – Ureotelic animals (Amphibians molluscans., frog, cartilage fish–shark, mammals)., g) Neurogenic, Heart:, Heart, beat, is, 3), Uric acid – Uricotelic animals (Aerial &, originated by a group of nervous tissue, desert animals like reptiles, birds, insects,, called pace maker., Eg. Heart of, camel, kangaroo rat etc), invertebrates except molluscans., , , , , , , , 1., 2., 3., , 4., , 5., , In Annelids, RBCs are absent; blood is red, due to hemoglobin in plasma., In molluscans, blood is blue due to, Haemocyanin pigment in plasma., In vertebrates hemoglobin is in RBC., Lymph: Colourless blood without RBC., In insects blood is colourless (no pigment), and is called haemolymph., Eg. Cockroach (Arthropods), Mode of Respiration, Aerial / Lung / pulmonary respiration:, Exchange of gases between lungs & air., Aquatic/gill/brachial, respiration:, Exchange of gases b/w gills & water., Aerobic, respiration:, Complete, oxidation of glucose in the presence of, oxygen., Such, organisms, are, called, aerobes. Eg: Higher animals & plants., Anaerobic respiration:, Incomplete, oxidation of glucose in the absence of, oxygen., Such, organisms, are, called, anaerobes., Eg:, Endoparasites, like, tapeworm,, roundworm, microbes like yeast etc., Cutaneous / Skin respiration: Exchange, of gases through the skin., Eg. Earth worm, Frog., , Reproduction, , a) Hermaphrodite, , b), , c), , d), e), f), , (= Bisexual): Sexes, united, ie, both male & female sex organs, present in the same animal., Eg: Flatworm, earthworm, hydra., Heterophrodite (= Unisexual): Sexes, separated ie, male & female sex organs are, present in different individuals., Eg: Frog, man & higher animals., Sexual Dimorphism:, When animals of, same species differentiated into male &, female sexes sharply by external characters, is called sexual dimorphism., Eg: Cockroach, round worm,, silk moth, hen - cock., Copulation: Mating (physical contact), between male and female / bisexuals during, reproduction., Fertilization: Fusion of haploid male &, female gamete (sperm with the egg) to form, a diploid zygote., External fertilization: Fusion of gametes, takes place out side the female body ie, in, water medium., Eg: Aquatic animals like, frog, bony fishes, most of invertebrates.
Page 3 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, page 3, Ranga Rao R H, Sira, Eg. Insects like cockroach, moths,, f) Internal Fertilization: Fertilization takes, flatworms, frog etc., place inside the female body. (ie, in, c) Metamorphosis: The morphological and, fallopian tube = oviduct). Here male, physiological changes taking place in larva, contains copulatory organ to transfer the, to become an adult / young one., sperms into the female body., d) Complete Metamorphosis: The larva does, Eg: Man, vertebrates, cartilage fish., not resemble the adult in many respects., g) Cross fertilization: Fertilization between, Eg. Silk moth, Butterfly, Frog., the gametes produced by two different, e), Incomplete, metamorphosis: The larva, bisexual (or unisexual) animals. Eg., more or less resembles the adult except, Earthworm, flatworm., one, or, two, differences., Here, the, h) Self Fertilization: Fertilization between, developmental stage is called nymph., the gametes produced by same bisexual, Eg: Cockroach., animal., Eg. Tapeworm., f) Metagenesis, /, Alternation, of, i) Protandry: Testes mature earlier than, generations: Sexual generation alternates, ovaries., Eg. Leech, earthworm etc., with the asexual generation. Thus in life, j) Protogyny: Ovaries mature earlier than, cycle, the animal has two types of body, the testes. Eg. sponges, namely,, k) Regeneration / self amputation and, 1) Sexual zooid (gametophyte in plants), autotomy: Development of lost parts by, 2) Asexual zooid (sporophyte in plants), the body (by tissue growth)., Eg. Hydra, Obelia, jellyfish, Eg. Earthworm, flatworm, starfish, wall lizard., Body temperature, l) Oviparous animals: The animals which, lay eggs., Eg: Birds, amphibians,, 1. Homeotherms, (=, warm, blooded, reptiles (lizards, snakes except viper), egg, animals): Body temperature is always, laying mammals like Platypus (duck bill),, kept constant irrespective of environmental, Echidna (spiny ant eater), temperature., Eg: Birds & mammals., m) Viviparous animals: The animals, which, 2. Poikilotherms (= cold blooded animals):, give birth to young ones. (Embryo, They fluctuate their body temperature, develops inside female body ie, womb /, according to the environmental temperature., uterus)., Eg: Fishes, amphibians & reptiles., Eg: Viper snake, mammals etc., These animals show following behavior;, P) Ovo-viviparous animals: The animals, a) Hibernation (= winter sleep): Animals, which lay eggs, but after hatching, the, hide themselves during winter and become, young ones develop inside the womb /, inactive., pouch for some time, till they grow, Eg. Frog, lizards, silk moth egg., completely. Eg: Scorpion, shark, ray fish., b) Aestivation (= summer sleep): The, animals hide in shady areas during hot, Larval stage, Phylum, summer months and become inactive, stop, 1. Amphiblastula, Porifera (sponges), feeding. Eg. Some amphibians., 2. Planula, Coelenterata (hydra), 3. Miracidium, Platyhelminthes, Skeleton / Protective structures, 4. Trochophore, Annelida (earthworm), a), Endoskeleton:, Present inside the body,, 5. Catter piller, Arthropoda (silk, made, up, of, bone, or cartilage or both. In, / Nymph, moth, cockroach), echinoderms, it, is, made up of calcareous, 6. Glochidium, Mollusca, plates,, spicules, in, sponges., 7. Bipinnaria /, Echinodermata (star, b) Exoskeleton(integumentary, system):, Auricularia, fish / sea cucumber), Nonliving structures, outside the body,, 8. Fingerlings, Fish, derived by the epidermis / skin., 9. Tadpole larva, Frog (amphibian), • Sclerites (chitinous plates) in arthropods, Mode of development, • Corals in coelenterates, a) Direct development: Development of, • Calcareous shell in Molluscans, embryo inside the egg, without larval, • Spines & dermal plates in Echinoderms, stage, where it hatches out in the form of, • Epidermal scales / shields / plates in fishes, young one. It resembles the adult in, and reptiles, many respects., Eg: Reptiles & birds., • Shell in tortoise / turtle, b) Indirect development: Development of, • Epidermal feathers in birds, embryo inside the egg is incomplete,, • Epidermal hair, fur, wool, nails, claws, horns,, where it hatches out in the form of larva, antlers, hoofs, etc. in mammals., which then undergoes further development, •, through metamorphosis. Larva do not, resembles the adult.
Page 4 :
Concise Zoology, a), b), c), d), e), f), g), h), i), j), , Animal Kingdom, , page 4, , Locomotory structures, Pseudopodia / flagella / cilia – in, protozoans, Tentacles - hydra (coelenterates)., Suckers & hooks for attachment tapeworm (flatworms)., Setae / parapodia / suckers in, Annelids., Wings, jointed legs in arthropods., Foot / arms in molluscans., Tube feet in star fish (echinoderms)., Paired and unpaired fins in fishes., Pentadactyle – tetrapod limbs & tail, in vertebrates., Wings in birds., ADDITIONAL POINTS, , 1. Metamerism, /, Metamerical, segmentation:, Division of body into, segments, called, ‘metameres’, by, grooves called annuli; each segment has, its own organ systems. Thus segments, are, similar, both, externally, &, internally. (ie, repetition of internal and, external, body, parts, is, called, metamerism)., Eg: annelids, arthropods, [body cavity also divided by septa]., 3. Cephalization: Formation of head by, the fusion of few anterior segments, during larval stage (with well developed, eyes, mouth parts & sense organs)., Eg: Annelids and Arthropods., 4. Amniota: Group of animals where the, embryo is protected by extra embryonic, membranes viz. amnion, allantois,, chorion, yolk sac & placenta. Eg:, Reptiles, birds, mammals, 5. Anamniota: Group of animals the, embryo of which do not contain, amnion. Eg. Fishes & Amphibians., Connecting links, b/n the groups, Peripatus, (Onychophora), Neopilina, (Living fossil), Auricularia larva of, echinoderms, Lung fishes, (Dipnoii group), Archaeopteryx, (= fossil bird), Monotremes(Prototheria), (echidna & platypus), , Annelida &, Arthropoda, , Hemichordates, (Balanoglossus), , Non - chordata &, Chordates, , Annelida &, Mollusca, Echinodermata, Protochordata, , &, , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , Animal diversity, On the earth, the Animal kingdom includes, more than 1.7 million living species. They, vary from single celled protozoans to complex, multicellular animals with wide variety of, habitats and habits., Out line classification of, Animal Kingdom, Classification of animals was suggested by L., H. Hyman (1940). According to this, animals, have been grouped into two major kingdoms, namely;, 1) Kingdom Protista: It includes acellular, animals represented by a single phylum, called protozoa., 2) Kingdom, Metazoa:, It, includes, multicellular animals and further classified, into two groups namely,, A) Non – Chordata / Invertebrata:, without notochord (= backbone)., B) Chordata / Vertebrata: with notochord, (= backbone)., Non-chordata is further classified into 11, phyla. The phyla included in animal kingdom, are as follows:, 1. Phylum: Protozoa – acellular grade., 2. Phylum: Porifera – cellular grade., 3. Phylum: Coelenterata – primitive, tissue grade, radial symmetry., 4. Phylum: Ctenophora – tissue grade,, radial symmetry ith sexual reproduction, only., 5. Phylum: Platyhelminthes – bilateral, symmetry, acoelom., 6. Phylum: Aschelminthes = Nematoda, =, Nematyhelminthes, –, with, pseudocoelom., 7. Phylum:, Annelida, –, eucoelom,, segmented body., 8. Phylum: Arthropoda – eucoelom,, segmented body, jointed legs., 9. Phylum:, Mollusca – eucoelom, soft, bodied., 10. Phylum: Echinodermata – radial, symmetry in adult stage (but bilateral, symmetry in larval stage)., 11. Phylum:, Hemichordata, (minor, phylum) – connecting link with primitive, type of notochord., 12. Phylum: Chordata – advanced, with, well developed notochord / backbone., , Fishes & Amphibia, Reptiles &, , Birds, , Reptiles & Mammals, , *****
Page 8 :
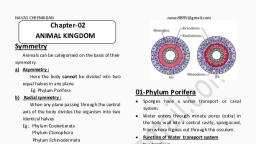
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 8, , Phylum: COELENTERATA / CNIDARIA, Eg: Hydra (fresh water), Obelia, Aurelia (jelly, fish), Physalia (Portuguese man of war),, Adamsia (sea anaemone/sea flower), coral, animals like brain coral, red coral etc., General characters/ salient features:, 1. Simple, primitive, metazoans, with, primitive tissue grade of organization,, diploblastic and radial symmetry., 2. Tentacles / arms are the locomotory, structures present around the mouth., 3. Polymorphic colony: Presence of two or, more zooids (= bodies) to perform, different functions. They are;, a) Polyp = nutritive, asexual zooid, hydra, like., b) Medusa = sexual zooid, umbrella like., Eg: Obelia, Physalia, Halistema etc., 4. Nematocysts (=cnidoblasts / stinging, cells) are present in ectoderm (more in, tentacles). They help in defence and inject, a poison into the prey., 5. The body cavity is known as GVC, (Gastro Vascular Cavity=coelenteron), 6. Digestion, is, both, intracellular, &, extracellular with mouth; anus absent., 7. Sexual reproduction (uni / bisexual),, show metagenesis (= alternation of, generations)., Classification of phylum Coelenterata:, Phylum coelenterata is classified based on, the type of zooids., Classes, Examples, Class – 1., Hydra,, Hydrozoa:, Obelia (sea fur),, Both, polyp, & Physalia, (Portuguese, medusa, zooids man of war), are present., Halistema, Class – 2., Aurelia (jelly fish), Scyphozoa:, Main zooid is free, swimming medusa, Class – 3., Adamsia (sea flower /, Anthozoa:, sea anaemone),, Polyp is the main Meandrina (brain coral), zooid., They Fungia, produce, corals (mushroom coral), (except, sea Gargonia (sea fan),, anaemone)., Pennatula (sea pen), Astraea(stony coral),, Corallium (red coral), Coelenterates, are, aquatic,, mostly, marine (except Hydra which is fresh, water)., Between ectoderm & endoderm is a jelly, like, non-cellular, layer, called, mesogloea., Asexual reproduction is by exogenous, budding., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , GVC is lined by gastroderm (=, endoderm) and opens outside through, the mouth., Planula is the common larva of, coelenterates., NOTE ON CORALS: The polyp / hydra, of anthozoans produce an exoskeleton, of calcium carbonate called corallite., The corallites of the entire colony, together form a coral. Inside the coral, the animals are well protected. Corals, are of different size, shape & colour., They are found in large deposits, inhabiting mountains in seas, which is, called coral reef., Eg: Great Barrier Reef at Australia., Significance of corals: They form, large source of petroleum deposits., They are also used as ornamentals., Eg: Brain coral, sea fan, stony coral,, mushroom coral, etc., Minor Phylum:, Ctenophora / Acnidaria, Eg:, Pleurobrahia, (sea, gooseberry),, Hormiphora (sea walnut) Ctenoplana,, General / salient features:, 1. They are marine, free swimming, radially, symmetrical, diploblastic animals with, primitive tissue grade, commonly called, ‘comb jellies’ or ‘sea walnuts’., 2. Body is globe like with 8 rows of ciliated, comb plates for locomotion., 3. A pair of long tentacles with colloblasts, help in feeding., 4. Stinging cells are absent, 5. Digestive system (GVC) is complete with, anus. Digestion is both extra cellular &, intracellular., 6. Body, is, transparent, and, exhibit, bioluminescence (emitting light)., 7. Sexes united (bisexual), only with, sexual reproduction., 8. Fertilization is external with indirect, development., Phylum: PLATYHELMINTHES, (Greek: platy = flat, helminthes= worms), Eg: Liver fluke, tapeworm, blood fluke,, Planaria, etc., General characters/ salient features:, 1. Acoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical, &, triploblastic with tissue / organ grade of, organization,, commonly, called, flat, worms., 2. Flame cells / solenocytes / protonephridia are the excretory organs., 3. Regeneration capacity is more., 4. In free living flat worms like Planaria,, ciliated epidermis help in locomotion.
Page 9 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 9, , Parasitic adaptations in flat worms:, 5. Body is dorso-ventrally compressed leaf, / tape like and so called flat worms., 6. Body of endoparasites is covered by, cuticle to protect from the action of host, enzymes., 7. Suckers & hooks are the organs for, attachment & absorption of food., 8. Digestive system is simple (without, glands) & incomplete (anus absent)., 9. Reproduction: Mostly bisexual, life cycle, is complex with two 2-5 larval stages, in two host bodies., Flame cells open into excretory canal., Flat worms show anaerobic respiration, (so called obligate parasites)., Nervous system in flat worms is simple,, ladder type with two pairs of ganglia, (= brain ring) and double ventral, nerve cord., Some flat worms like Palnaria, show the, high power of regeneration., Development in indirect. Self or, cross fertilization with the common, larva - Miracidium., Larval stages in flat worms are:, Miracidium, Redia, Cercaria etc., Liver fluke completes its life cycle in, two hosts – sheep and snail., Pig tapeworm completes its life cycle, in two hosts - man and pig, Classification of phylum, Platyhelminthes, Classes, Examples, Class-1:, Liver fluke, Trematoda:, (Fasciola hepatica),, Endoparasites,, Blood fluke, commonly, called, leaf worms., Class– 2: Cestoda: Pig tapeworm,, Endoparasites, body (Taenia solium),, is, segmented, Cattle tape worm, commonly, called (= beefworm)., tape worms., Class–3:, Planaria / Dugesia, Turbellaria:, Fresh water, free, living., Phylum: NEMATODA, (Aschelminthes / Nemathelminthes), Eg: Ascaris lumbricoides (Round worm),, Filarial worm (Wucheraria), Hook worm, (Ancylostoma), Pin worm (Enterobius), eye, worm (Loa loa) etc., General characters/ salient features:, 1. Mostly endoparasites, few are soil, nematodes, commonly called round, worms., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , 2. Body, is, cylindrical,, unsegmented,, triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical, with organ systems., 3. Body cavity is called pseudocoelom, because it is not lined by epithelium., 4. Body wall is dermomuscular., 5. Respiratory organs absent. They show, anaerobic mode of respiration., 6. Excretory system has excretory canals., Flame cells absent., 7. Sexual reproduction: Sexes separate, (heterophrodite / unisexual) with sexual, dimorphism. Generally female is longer, than male., 8. Fertilization internal; development is, complex with two/more larval stages., •, •, •, , •, , •, , Alimentary, canal, is, complete, with, muscular pharynx., Life cycle includes one/ two host bodies., Classification: Phylum Nemathelminthes, has only one class called Nematoda,, which includes all round worms., Filariasis (= Elephantasis): Disease, caused by filarial worm, transmitted, through Culex mosquito) enlargement of, lymphoid tissues of legs,, Ascariasis: Infection by round worm,, head ache, stomach pain, lack of appetite,, more eating of food., , Phylum: ANNELIDA, Eg:, Earthworm, Leech, Aphrodite (Sea, mouse), Nereis (rag worm / clam worm),, General characters/ salient features:, 1. Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblas-tic, with dermomuscular body wall and, eucoelomate animals., 2. Metamerism: Segmentation of body into, divisions called metameres / annuli., Each segment has its own organ systems., 3. Setae, parapodia (= side legs) and, longitudinal & circular muscles of the, skin help in locomotion., 4. Cephalization: Formation of head by the, fusion of anterior segments (in larval, stage) with mouthparts, eyes and sense, organs., 5. Digestive system is complete, with, digestive glands. Digestion, is extra, cellular., 6. Circulatory system is closed type with, lateral hearts; blood is red due to, haemoglobin in plasma., 7. Excretory, organs, are, segmentally, arranged nephridia., 8. Neural system is made up of nerve ring, and a double ventral nerve cord with, segmentally arranged paired ganglia., 9. Sexes separate (= unisexual =, heterophrodite) or united (= bisexual =, hermaphrodite = earth worm).
Page 10 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 10, , Annelids are mostly marine, few fresh, water, some in moist soil, few are, ectoparasites., Eucoelom: body cavity is lined with, epithelium, Respiration is through the skin or by, external gills., Development, is, indirect, with, the, common larva called Trochopore., Dermomuscular, body, wall:, Skin, epidermis with well developed muscles,, covered by cuticle & mucus., Leech sucks the blood from cattle & man., It produces an anticoagulant- hirudin,, which prevent the clotting of blood. It also, acts as painkiller., Annelids are the first animals to show, Metamerism, eucoelom, cephalization, & the presence of digestive glands., Earthworm, shows, the, power, of, regeneration., Body cavity in Annelids is filled with, coelomic fluid., Classification: Phylum Annelida is based on, number of setae., Classes, Examples, Class – 1., Nereis (rag worm, Polychaeta, = clam worm),, (Chetopoda):, Sabella, Parapodia with more, (peacock worm), setae. They are marine. Aphrodite, (sea mouse), Class –2. Hirudinea:, Indian cattle leech, suckers for, (Hirudinaria), attachment. They are, fresh water animals., Class–3., Earthworm sps., Oligochaeta:, (Megascolex,, Found in moist soil. Pheritima etc), Setae are in the skin., Phylum: ARTHROPODA, (Gr: arthro = jointed; poda = legs), Eg: Prawn, crab,, King crab (Limulus),, hermit crab (shelled), Lobsters, scorpion,, spider, centipede, millipede, cockroach, (Periplanata, americana),, insects, like, mosquitoes (Anopheles, Culex, Aedes),, butterfly, moths, housefly, honey bee, (Apis), silk moth (Bombyx), wasp, bug,, beetle, ant, fruit fly (Drosophila), Lac insect, (Laccifer), Locust (Locusta - grass hopper),, silver fish, Peripatus etc., , General characters/ salient features:, 1., , 2., , Body, is, bilaterally, symmetrical,, triploblastic,, eucoelomate, &, metamerically segmented. Body is, divisible into head, thorax & abdomen., Exoskeleton: Body is covered with thick, chitinous cuticle., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , 3., , Segments of body bear paired jointed, appendages and legs., 4. Circulatory system is open type with, many chambered heart., 5. Body cavity is filled with haemolymph, (colourless, blood), and, so, called, haemocoel., 6. Trachea, book gills, book lungs are the, respiratory organs., 7. Excretion is by malpighian tubules or, green glands., 8. Nervous system consists of nerve ring, with double ventral nerve cord; some, have compound eyes with mosaic, vision., 9. Sexes separate, (heterophrodite =, unisexual), fertilization is internal., 10. Development indirect, metamorphosis is, complete or incomplete with larval stage, called “caterpillar / nymph”., Classification of phylum Arthropoda:, Classes, Examples, Class–1., Prawn (Pelaemon /, Crustacea: Aquatic Penaeus),, gill respiration, Crab (Cancer), Lobsters, Class–2., scorpion, Arachnida: Mostly (Palamnaeus),, terrestrial, 4 pairs of spider, king crab, legs. respiration by, book lungs / book, gills / trachea, Class–3., centipede, Myriapoda:, (chilopoda),, Each segment bears millipede, one / two pairs of (diplopoda), legs., Class – 4 Insecta:, 3 pairs of legs, 2, pairs of wings; respiration by trachea,, excretion, by, malpighian tubules,, Class–5,, Onychophora:, Connecting link b/w, Annelida & Arthropoda, , Coackroach, insects, like, mosquitoes,, butterfly, house fly,, honey bee, wasp,, silkmoth, ants, bugs,, beetles, fruit fly,, Peripatus., , Arthropoda is the largest phylum., Cephalization: Some of the anterior, , , , , segments fuse to form distinct head (in, larval stage) with mouthparts, eyes and, sense organs., Chitinous exoskeleton is found in the, form of dorsal and ventral plates called, sclerites., Compound eye: made up of units, called ommotidia – each producing, image of minute part of visual field, thus, producing a mosaic image.
Page 11 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 11, , Ommotidia:, , , , , , , , , , , , The visual units of, compound eye., Cinderella of genetics = Drosophila, Social behavior is observed in honey, bees, ants, wasps etc., Haemolymph: Blood in Arthropods /, insects is colourless / white because, haemoglobin is absent; such blood is, called haemolymph., Spiracles:, External, opening, of, respiratory system / trachea., Entomology: Study of insects., Ecdysis or Moulting: It is the process, of removal of external skin periodically, during growth of larva., Instar: The stage b/n the two moults., King crab (Limulus) is known as “living, fossil.’, Locusts are known as gregarious pests., , Phylum: MOLLUSCA, Eg: Apple snail, Fresh water mussel, Pearl, oyster (Pinctada - marine mussel), Chiton,, Elephant tusk shell (Dentalium), Octopus, (devil fish) Sepia (cuttle fish), Loligo, (squids), Aplysia (sea hare) etc., , General characters/ salient features:, 1. Mostly marine and fresh water, body is, soft, unsegmented without jointed, appendages., 2. Body is divided into head, muscular foot, and visceral mass, which is covered by, a fold of skin called mantle membrane., 3. Generally a calcareous shell is present, around the body (produced by mantle)., 4. Digestive system is simple and mouth, cavity contains a grinding organ called, “Radula”., 5. Respiratory organs are a pair of gills, called “ctenidia” in mantle cavity., 6. Circulatory system is open type with, myogenic heart. Blood is colourless or, green or blue., 7. Excretion is by metanephridia or, “organs of Bojanas” - the primitive type, of kidneys., 8. Nervous system consists of paired, ganglia with connecting nerves. Sense, organs like eyes, tentacles are present., 9. Unisexual (heterophrodite), fertiliza-tion, is internal or external with a common, larva called “Glochidium”., 10. The shell may be spiral, cone shaped,, , internal or external., Mollusca is second biggest phylum., The shell may be spiral, cone shaped,, internal or external., Ganglion = group of nerve cell bodies., Ganglion = group of nerve cell bodies., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , Classification of phylum Mollusca:, Classes, Examples, Class–1., Polyplacophora:, Chiton, Ventral foot, dorsal, shell with 8 plates., Class–2., Gastropoda, Apple snail (Pila),, (Univalviata):, Slugs, Univalved, shell,, spiral/cone shaped., Class–3., Fresh water, Pelecypoda, mussel (Unio),, (Bivalviata):, Pearl oyster, Bivalved shell, head (marine mussel)., absent., Class–4., Scaphopoda:, Elephant tusk shell, wormlike body, shell (Dentalium)., long tube like., Class–5., Cephalopoda:, Octopus (devil fish), Shell is internal / Sepia (cuttle fish)., absent,, Foot, is Loligo (squids), modified into arms., Oyster mussels are used and cultured to, get natural pearls (made up of a white, substance called nacre., Shell of molluscans is rich in CaCO3 and, so used in calcium tablets, syrup, in, lime industry, sugar industry and for, ornamental purpose., Archituithis is an octopus species which, is the biggest invertebrate., Ink gland is found in some cephalopods, like Sepia. It releases out the ink into the, water when the animal is attacked /, disturbed., Phylum: ECHINODERMATA, (Echino = spines, derma = skin), Eg: Asterias (starfish), Ophiura (brittle, star), Echinus (sea urchin),, heart urchin,, cake urchin, Cucumaria (sea cucumber),, Antedon (sea lilly = feather star) etc., General characters/ salient features:, 1. Exclusively marine animals, free living,, no parasites., 2. Body is triploblastic; eucoelomate,, radial symmetrical but larva is, bilaterally symmetrical., 3. Body with pentaradiate condition (5 arms), and oral & aboral surfaces. Head is, absent., 4. Body is covered by calcareous spines and, plates which form exoskeleton., 5. Pedicellaria (forceps like / scissors like), help in feeding., 6. Tube, feet, are, the, locomotory, structures.
Page 12 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 12, , 7. Water vascular system is a unique, feature that helps in locomotion, excretion, & transportation of food and gases., 8. Finger like dermal papillae (= dermal, gills) – are the respiratory structures., 9. Sexes separate, no sexual dimorphism., Fertilization is external., 10. Development, is, indirect, with, free, swimming, larva, commonly, called, ‘Bipinnaria’, or, ‘Auricularia’, (with, bilateral symmetry)., Classification of phylum, Echinodermata:, Class with characters, Examples, Class–1, Asteroidea:, Asterias,, Commonly called star Astropecten, fishes & sea stars., Class–2, Ophiuroidea:, Brittle stars., Arms are very long., Class–3, Echinoidea:, Sea urchin,, Globe like without arms., Heart urchin., Class–4,, Holothuroidea:, Sea cucumber, Elongated body, leathery, skin, spines absent., Class–5, Crinoidea:, Sedentary, arms long & Sea Lilly, branched., (feather stars), Water vascular system is made up of, stone canal, madreporite (= opening, of stone canal) ring canal, radial, canals and lateral canals filled with, water., Nervous system – Made up of nerve, ring and radial nerves., Auricularia, larva, of, echinoderms, resembles, the, larva, of primitive, chordates (ie, Tornaria larva of, Balanoglosses), and, so, form, the, connecting link b/n the two groups., Echinoderms like star fish has the power, of regeneration and autotomy., Autotomy is self-amputation of body, parts to escape from the enemy., Eg: starfish, wall lizard., Minor Phylum: HEMICHORDATA, Eg: Balanoglossus (tongue worm),, Saccoglossus, 1. Hemichordata was earlier considered as a, sub-phylum under phylum chordata. But, now it is separated as a phylum under, non-chordata., 2. Marine burrowing, notochord., , animals, , 3. Body, is, worm, like,, bilaterally symmetrical,, and eucoelomate., , with, , out, , unsegmented, triploblastic, , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , 4. Body is cylindrical with proboscis, a collar, and a long trunk., 5. Circulatory system is of open type., 6. Respiration is by gills slits similar to that, of chordates., 7. Excretion is by proboscis gland., 8. Sexes separate, fertilization is external;, development is indirect with larval stage, called ‘Tornaria’., , Phylum: CHORDATA, General characters / salient features:, Phylum Chordata shows the following three, general / fundamental characters., 1. Presence of notochord or vertebral, column or back bone in embryonic, stage or through out the life., 2. Dorsal tubular nerve cord: Rod like,, present on the dorsal side of the, notochord., 3. Pharyngeal gill clefts / gill slits - these, are openings present in pharynx to out, side; help in aquatic respiration., Pharyngeal gills are present through out the, life in fishes, only during larval stages in, frog & only in embryonic stage in man and, higher vertebrates., In addition, chordates show the following, other characters., a) Bilateral symmetry & triploblastic body, wall., b) Cephalization with sense organs., c) Well developed eucoelom, d) Ventral, myogenic, heart,, closed, circulatory, system,, RBC, with, haemoglobin., e) Presence of tetrapod limbs., f) Presence of tail., Classification, of, phylum, Chordata:, Phylum Chordata is divided into 3 subphyla., Sub Phylum–1: Urochordata:, Notochord is present in the tail region only, in larval stage but absent in adult., Eg: Ascidia (sea squirts), Salpa, Doliolum., Sub Phylum–2: Cephalochordata:, Notochord is present in the head region, through out the life., Eg: Amphioxus / Lancelet (Branchiostoma), Sub phylum–3: Vertebrata (=Craniata), 1. The anterior end of nerve cord is, modified into brain & posterior part into, spinal cord., 2. Brain covered by cranium/ brain box., 3. Notochord of embryo is modified into, vertebral column or backbone in the, adult. [It encloses the spinal cord]., [Thus all vertebrates are chordates but all, chordates are not vertebrates].
Page 13 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 13, , 4. Endoskeleton made up of cartilage,, bone or both., 5. Ventral heart with 2, 3 or 4 chambers., 6. They, process, hormone, producing, endocrine glands., 7. Paired fins / limbs help in locomotion., , Subphyla Urochordata & Cephalochordata, , , , , are grouped under Proto-chordata, (Acraniata = primitive chordates without, brain box / cranium)., Tail = post anal part of the body., Retrogressive metamorphosis: It is, found in Urochordates like Ascidia. It is, the disappearance of some advanced, characters, from, larva, during, metamorphosis., Eg: Presence of notochord in larva &, absent in its adult., , Vertebrata is divided into two divisions., Division – 1: Agnatha., It has only one class – Cyclostomata., General, characters, of, Agnatha, /, Cyclostomata:, 1. Mouth is circular without jaws., 2. Body is fish like, with 6-15 gill slits., 3. Epidermal scales and paired fins are, absent., 4. Both cranium and vertebral column are, cartilaginous., 5. Marine and migrate to fresh water for, spawning., 6. They live as ectoparasites on some fishes., Eg: Petromyzon (Lamprey), Myxine (Hag fish), Division – 2: Gnathostomata, 1. Mouth with jaws., 2. Division Gnathostomata is again divided, into two series viz; Pisces & Tetrapoda., Series, , Series (1), Pisces, , Series (2), Tetrapoda, , Classes, 1. Placodermi (extinct fishes), 2. Dipnoii (= lung fishes), 3. Chondrichthyes, (Elasmobronchii), 4. Osteichthyes, (Teleostomi), 1. Amphibia, 2. Reptiles, 3. Aves (birds), 4. Mammalia, , Series: PISCES (Fishes), General characters/ salient features:, 1. They are poikilotherms (cold blooded), animals., 2. Body is streamlined (spindle or boat shaped), and divided into head, trunk and tail., , 3. Body is covered by scales which form, exoskeleton to prevent the loss of water, & maintain body temperature., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , 4. Head bears a pair of eyes, spiracles (=, nostrils), mouth with homodont teeth (all, teeth are similar type)., 5. Gills are the respiratory organs, four or, five pairs and covered by operculum in, bony fishes., 6. Fins help in swimming and steering the, body, they are of two types namely,, paired fins (pectoral fins & pelvic fins), and unpaired fins (dorsal, ventral, anal, and caudal fin)., 7. Heart is two chambered, one atrium, and one ventricle with single circulation., 8. Brain and spinal cord well developed., Lateral, line, sense, organs, with, pressure receptors help in balancing, body., 9. Sexes separate, oviparous, larval stage is, called ‘fingerling’., Examples for cartilage fishes:, Scoliodon (Shark / dog fish),, Pristis (saw fish),, Trygon (sting ray),, Torpedo (electric ray fish), Sphyrna (Hammer headed fish), Differences b/n:, Cartilage fishes, Bony fishes, 1 All are marine., 1 Some marine &, some fresh water., 2 Endoskeleton is 2 Endoskeleton, is, cartilagenous., made both bony &, cartilagenous., 3 Gills 5 pairs, 3 Gills 4 pairs, 4 Gills are naked, 4 Gills covered by, operculum., 5 Mouth ventral, 5 Mouth terminal, 6 Body covered by 6 Body covered by, placoid type of, cycloid / ctenoid, scales., scales., 7 Swim bladder 7 Swim, bladder, absent, (so, it, present in some,, swims, continuhelp in buoyancy., ously to avoid, sinking), 8 Cloaca present, 8 Cloaca absent, 9 Claspers present 9 Claspers absent in, in male., male, 10 Ureotelic (urea 10 Ammonotelic, is the metabolic, (ammonia is the, waste), metabolic waste), 11 Fertilization, is 11, internal., 12 Caudal, fin, is 12, heterocercal, (unequal lobes), , Fertilization, is, external., Caudal, fin, is, homocercal type, (with equal lobes), , Dipnoii is a group of lung fishes form, connecting link between fishes &, amphibians.
Page 14 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 14, , Examples for Bony fishes:, A) Carp fishes:, Labeo rohita (Rohu),, Fresh water, Catla catla (Katla),, fishes, Cirrhina mrigal (Mrigala), B) Cat fishes:, Clarias (Magur) –fresh water, Macrone, Saccobronchus,, Wallago attu,, C) Other fishes:, Anabas (climbing perch)- fresh water, Exocetus (flying fish) - marine, Hippocampus (sea horse) - marine, Anguilla (eel fish) - marine, Lamprey (sucker fish) - marine, Betta (fighting fish), Pterophyllum (angel fish), , , , , , Aquarium, fishes, , Note, Ichthyology – Study of fishes., Sauropsida – Study of Reptiles., Herpatology – Study of Snakes, Ornithology – Study of birds., , Fishes are first formed vertebrates on, the earth., Fishes are adapted to live only in water, and so called primary aquatic., Swim bladder = air bladder: Present, only in some bony fishes. It helps in, buoyancy (floating) and moving up &, down in water., Cloaca – It is a common chamber for, digestive, urinary and reproductive, systems., Claspers: Copulatory organs in male, to transfer the sperms into the female, body., In, fishes, extra, embryonic, membranes like amnion, allantois, are absent; and so they are grouped, under Anamniota., Series: TETRAPODA, Class: AMPHIBIA, Examples:, Frog (Rana sps), Tailless /, Toad (Bufo), lung, Tree frog (Hyla), amphibians, Flying frog (Rhacophorus), Salamandra (Salamander), Ambistoma (tiger salamander), Necturus (mudpuppy), Ichthyophis -- Limbless amphibians, (caecilians = blind amphibians), , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , General characters/ salient features:, 1. Amphibians are poikilothermic (cold, blooded) animals, adapted to live both in, water and on land., 2. Pentadactyle limbs are present, each, with 4 or 5 digits., 3. Skin is moist and without scales., 4. Endoskeleton is cartilagenous and, bony. Pectoral and pelvic girdles give, support to muscles & limbs., 5. Heart is myogenic, three chambered;, two auricles and one ventricle with, double circulation., 6. Respiration is done by 4 methods., a) Cutaneous respiration-through skin,, b) Buccal respiration – through mouth,, c) Pulmonary respiration– thro’ lungs., d) Gill respiration – by larva, some adults., 7. Nervous system is well developed with, brain and spinal cord. 10 pairs of cranial, nerves present., 8. Sense organs well developed. Eyes with, eye lids. Tympanum (= ear drum) helps, in receiving the air born sounds., 9. Sexes separate, fertilization is external,, oviparous, with, larval, stage, called, tadpole., , Amphibians, , , , , , are, the, first, land, vertebrates., RBCs in frog are biconvex and, nucleated., Neoteny, (Paedogenesis):, The, phenomenon where larva becomes, mature & reproduce without undergoing, ‘metamorphosis’. Eg. Ambystoma, Amphibians, are, grouped, under, Anamniotes., , , Class: REPTILIA, Examples given:, Chelone (turtle- aquatic),, Testudo (tortoise - terrestrial),, Crocodiles, (Crocodilus,Alligator,Gavialis),, Sphenodon., Lizards: Hemidactylus (wall lizard),, Chameleon (tree lizard),, Calotes (garden lizad),, Mabuya (, ), Varanus (Indian Monitor),, Draco (flying lizard)., Poisonous snakes:, Naja naja (cobra), king cobra,, Vipera (viper), Bungarus (Krait),, sea snake, etc., Non-poisonous snakes: Python, green, snake, rattle snake, water snake, etc.
Page 15 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 15, , Salient features of Reptilia:, 1. They are true land vertebrates and, poikilotherms (cold blooded)., 2. Exoskeleton is made up of hard, epidermal scales (scutes) / plates /, shields., 3. Two pairs of pentadactyle limbs with, digits and powerful claws. They are used, for creeping, / crawling mode of, locomotion., 4. Heart three chambered, 2 auricles and, one ventricle (except crocodile) with, double circulation., 5. Respiration by lungs (pulmonary)., 6. 12 pairs of cranial nerves present., Tympanum present except snakes., 7. Sexes separate (Heterophrodites =, unisexual), fertilization is internal., 8. They are oviparous (except viper); the, eggs are called cleiodoic type., 9. Fertilization internal. They are oviparous,, development is direct., , , , , , , , , , , Repiles are grouped under amniota., Mesozoic era: Age of reptiles., Jurassic period: Age of dinosaurs., Squamata: Group of lizards & snakes., Turtles and crocodiles are secondary, aquatic animals., Crocodile is biggest reptile, fresh, water inhabitant, heart with 4 chambers., Varanus – famous for its power grip., Sphenodon:, Found, only, in, New, Zealand, it has third eye., Cleiodoic egg: Egg contains sufficient, amount of yolk for the complete, development of embryo, hence young, one hatches out from the egg. The egg is, covered by shell., , Class: AVES (Birds), Eg: 1) Extinct birds, Archaeopteryx (fossil bird), Dudo, 2) Flightless birds:, Struthio (Ostrich - in desert),, Kiwi (New Zealand),, Emu (Austria),, Aptenodytes (penguin - sea bird) etc., 3) Flying birds:, Pavo cristatus (peacock),, Corvus (crow), Columba (pigeon), Psittacula (parrot), Neophron (vulture), Gallus gallus (red jungle fowl), Woodpecker, Humming bird etc., , , , , J. Huxley called the birds as “Glorified, reptiles”., Archaeopteryx forms the connecting, link between reptiles and birds., Some birds show active & passive flight., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , Birds are adapted for aerial mode of life., Their body shape, organ systems &, physiology are modified for flight., Volant adaptations (OR), Flight mechanisms in birds (OR), Salient features in birds:, 1. Birds are homeotherms (warm blooded, animals)., 2. Body boat shaped, Feathers form, exoskeleton and insulation to control, body temperature., 3. Fore limbs are modified into wings with, flight muscles., 4. Heart is four chambered with only right, aortic arch., 5. Lungs are spongy, elastic and contain 9, air sacs to accommodate more O2., Syrinx is present below trachea that, produces sound., 6. Metabolic wastes are released in the form, of solid uric acid to conserve water., Urinary bladder is absent., 7. Brain is with good memory power that, helps in migration. Specialized comb like, - ‘pecten’ in eye ball helps in powerful &, acute vision., 8. Sexes, separate, (Heterophrodites,, fertilization is internal., 9. Fertilization, is, internal., They, are, oviparous; development is direct. Egg is, cleiodoic type., 10. Endoskeleton: It shows the following, adaptive characters., a) Pneumatic bones (hallow, air filled) to, reduce body weight., b) Sternum is boat shaped to protect the, internal organs during flight., c) Posterior vertebrae fused to form, Synsacrum., d) Cervical, (neck), vertebrate, are, heterocoelous type, help to rotate, head in all directions., e) Absence of teeth in beak., , , , , , , , , , , , Birds are grouped under amniota., Boat shaped body enables to fly easily &, reduce the friction during flight., Sternum is the bone of pectoral girdle. It, gives attachment of flight muscles., Sweat glands are absent in birds to, conserve water., Oil glands are present in tail region, that help in cleaning and preening., Hind limbs are shifted forward to, maintain body balance; feet modified for, different mode of locomotion., Birds are famous for their migration,, nest building and parental care., Metabolic rate is more in birds to, produce more energy used for flight., Birds have single ovary with single, oviduct to reduce body weight.
Page 16 :
Concise Zoology Animal Kingdom, , Page 16, , Class: MAMMALIA, 1) Egg laying mammals - oviparous, (Monotremes = Prototherians):, Ornithorhynchus ( platypus = duck bill), Echidna (spiny ant eater - found in, Australia & Tasmania, 2) Marsupials, (pouched mammals - viviparous):, Macropus (kangaroo - Australia), Opossum (South America), 3) Placental mammals - (true mammals viviparous): Hedge hog, mole, shrew,, Pteropus (flying fox - bat), Balaenoptera, blue whale, dolphins, wolf, fox, Canis, (dog), Felis (cat), tiger, cheetah, leopard,, lion, bear, seal, walrus, mongoose, Equus, (horse),, ass,, pig,, camel,, zebra,, rhinoceros, hippopotamus, deer, antelope,, giraffe, goat,, cattle, buffalo, sheep,, Elephas (elephant), rabbit, squirrel, hare,, mice, rat, porcupine, guinea pig, Pangolin, (scaly ant eater), sloth, armadillo, dugong, etc., Primates like lemur, Loris, Macaca(monkey),, apes (tailless monkeys) like chimpanzee,, baboon, man, gorilla., General characters / salient features:, 1. They are homeothermic animals., 2. Exoskeleton made up of hair, fur, claws,, hoof, scales or spines., 3. Mammary glands, sweat, glands,, sebaceous (oil) glands present in skin., 4. Presence of external ear pinna., 5. Teeth are Heterodont type: different, types of teeth like incisors, canines,, premolars and molars., 6. Two pair of pentadactyle limbs, digits, with claws / hoof / nails etc., 7. Presence of diaphragm, a muscular, layer, separating the thoracic cavity from, abdominal cavity., 8. Heart is four chambered, with only left, aortic arch. RBC’s are enucleated, (except camel & Llama)., 9. Brain well developed with corpus, callosum (white matter of fore brain),, corpora quadrigemina (four lobes of, mid brain) & 12 pairs of cranial nerves., 10. They are viviparous; Primitive mammals, are egg-laying (called Monotremes /, Prototherians)., 11. Extra embryonic membranes like, amnion, allantois, chorion, yolk sac, and placenta are present., , Ranga Rao R H, Sira, , Prototherians form connecting link, b/w reptiles & mammals., Marsupium = brood pouch., Placenta, is, an, extra, embryonic, membrane formed b/w embryo & uterus, wall of mother. It is a tissue connection, that helps in exchange of materials., In mammals testes are present outside, the body (except in elephant). This is, because the sperms cannot with stand the, body temperature., Other skin glands in mammals:, Cerumial glands (produce ear wax),, lacrimal glands (produce tears)., Dentary: It is the single jaw bone in, mammals, which bear teeth. It is the only, movable bone in the skull., Thecodont: teeth embedded in sockets of, jaw bone., Diphyodont: 2 sets of teeth produced in, lifetime (milk set & permanent set)., Larynx (= voice box) contain two vocal, cords, which produce sound., Frugivorous = fruit eating animals., Saungivorous = blood feeding animals, Bat is true flying mammal., Hepatic portal system: Liver supplied, with both pure and impure blood by, hepatic artery and portal vein., , Differences b/n:, 1, 2, 3, , 4, 5, , 6, 7, 8, , Chordata, (vertebrata), Notochord / back, bone present., Nerve cord is, dorsal & tubular., Respiration by, pharyngeal gills, / lungs., Heart is ventral,, myogenic., Endoskeleton is, bony /, cartilagenous., Haemoglobin, present in RBC, Tail present., Hepatic portal, system present., , Non - chordata, (invertebrata), 1 Notochord / back, bone absent., 2 Nerve cord is, ventral and solid., 3 Respiration by, dermal gills / skin., 4 Heart is dorsal &, neurogenic., 5 bony / cartilagenous endoskeleton absent., 6 Haemoglobin, present in plasma., 7 Tail absent., 8 Hepatic portal, system absent., , NOTE, , Mammals are grouped under amniota, Gynaecomastism:, The, phenomenon, where both male and female parents, produce milk & nourish their young ones., Eg: Platypus & Echidna, , *****