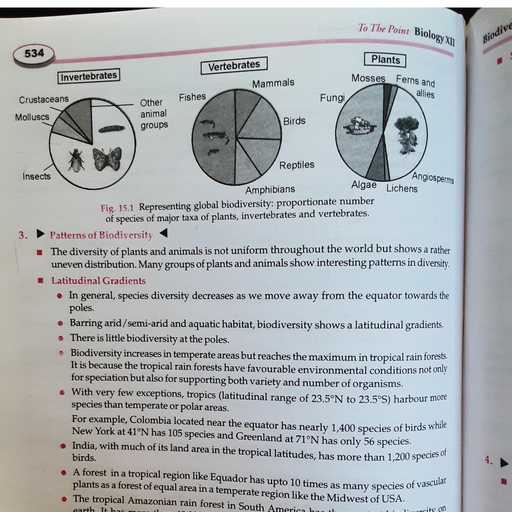
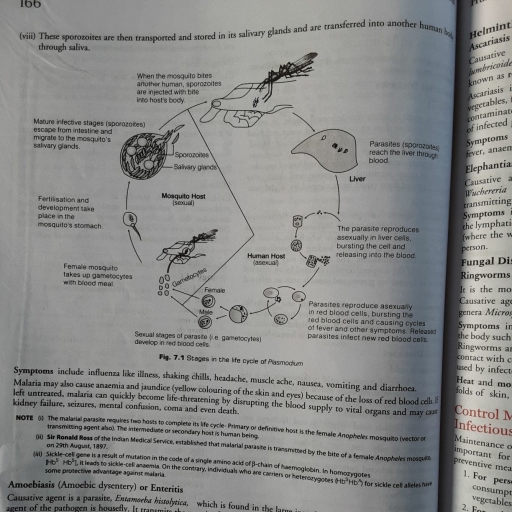
Page 1 :
0000, 10000, QOD00, 0., • Each photosystem has one specific chlorophyll a, and hundreds of other pigment molecules bound, to proteins., Primary acceptor, • The single chlorophyll a forms the reaction, centre, while the other pigment molecules form, the light harvesting system, also called antennae, Reaction, centre, Photon, Pigment, molecules, (Fig. 13.4)., • In PSI, the reaction chlorophyll a, has an, absorption peak at 700 nm hence is called, ,while in PS II, it has absorption maxima at, 00L, 680 nm, and is called P, P,, Fig. 13.4. Light harvesting complex, .089, Process of Photosynthesis, • Photosynthesis occurs in two phases-, (i) Light reaction or Photochemical phase, and, (ii) Dark reaction or Biosynthetic phase., (i) Photochemical phase-, • The photochemical phase directly depends on light, and include- (a) light absorption,, (b) photolysis of water (water splitting), (c) oxygen release and (d) the formation of, high energy chemical intermediates, ATP and NADPH., Electron Transport, In PS II, the reaction centre chlorophyll a absorbs 680 nm wavelength (red light,, which make the electrons to become excited., These electrons are taken up by the eletron acceptor that passes them to an electrou, transport system (ETS) consisting of cytochromes., This movement of electron is down hill in terms of an oxidation-reduction (redox, potential scale., Then the electron pass to PS I., Simultaneously, electrons in the reaction centre of PSI are also excited, when, later receive light of wavelength 700 nm (red light); these electrons are transter, to another acceptor molecule and finally to NADP+ which is reduced to NADPH+", by the enzyme NADP+ reductase., This is called the 'Z-scheme' due to its characterstic shape, formed when an, carrier are placed in a sequence on a redox potential scale (Fig 13.5)., |, -, -, -, Photosystem I, Photosystem II, NADPH, e acceptor, NADP*, Light, e acceptor, ADP + iP ATP, Electron, transport, system, e acceptor, LHC, H,0 → + 2e + 2H* + [0], Fig. 13.5. Z-scheme, non-cyclic photophosphorylation.