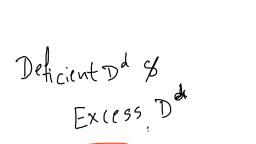Question 1 :
Planning commission, the erstwhile central planning authority in the country, has been
replaced by ________
Question 4 :
During colonial period, India’s demographic profile showed:
a) High birth rate
b) High death rate
c) High infant mortality
d) All of these
Question 5 :
(A): Zamindari (Semi Feudal Economy) in the colonial era were also responsible for the
misery of the cultivators.
(R): The terms of revenue settlement system introduced were harsh on the Zamindars.
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R)are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of
Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation
of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R)is true.
Question 6 :
What was the life expectancy at birth in India on the eve of Independence?
a) 44 years
(B) 50 years
(C) 60 years
(D) All of these
Question 7 :
Where was the first iron and steel company established?
a) Kolkata
(B) Jamshedpur
(C) Patna
(D) Ranchi
Question 8 :
What does the export surplus mean? When
a) Revenue from exports is equal to imports
b) Revenue from exports is greater than imports
c) Revenue from exports is less than imports
d) None of above
Question 9 :
Which industries were adversely affected due to partition?
a) Silk
b) Cotton & Jute textiles
c) Ivory
Question 10 :
The opening of Suez Canal served as a direct route for ship operating between:
a) India and America
b) India and Sri Lanka
c) India and Pakistan
d) India and Britain
Question 11 :
Assertion (A): Tariffs and quotas in the economic policy post-independence were used to
assist domestic industries.
Reason (R) : Our planners wanted to use foreign exchange for importing luxury goods.
a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion.
b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of
Assertion.
c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false
d) Assertion is false but Reason is true
Question 12 :
ASSERTION (A): Public sector was given leading role in industrialization during the period of
planning.
REASON (R) Private sector was not having enough capital and also market was not so big to
encourage industrialists to undertake big projects even if they had capital to do so.
Alternatives:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true (R) is correct explanation of (A)
b) Both (A) and (R) are true (R) is not correct explanation of (A)
c) (A) is true (R) is false.
d) (A) is false (R) is true
Question 13 :
Who was the chairman of India’s First Five Year Plans”
a) P. C. Mahalanobis
b) Mahatma Gandhi
c) Jawaharlal Nehru
d) None of these.
Question 14 :
Which of the states got success in Land Reform?
a) Kerala and West Bengal
b) Punjab and Haryana
c) Rajasthan and Assam
d) None of these
Question 15 :
Schedule C industries development were left to:
a) Public sector
b) Private sector
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these.
Question 16 :
Match the following:-
Column-I
Column-II
1. Demonetization
(A) 1950
2. Planning Commission
(B) 2015
3. NITI Aayog
(C) 1951
4. First five-year plan
. (D) 2016
a) 1A, 2B, 3C, 4D
b) 1B, 2A, 3D, 4C
c) 1D, 2A, 3B, 4C
d) 1C, 2A, 3B, 4D
Question 17 :
Match the following:
Column-I
Column-I
1. Architect of Indian Planning
(A) 1881
2. Green Revolution
(B) P. C. Mahalanobis
3. 1st Census of India. (C) 1956-61
4. Second plan
(D) 1967-68
a) 1A, 2B, 3C, 4D
b) 1B, 2D, 3A, 4C
c) 1D, 2A, 3B, 4C
d) 1C, 2A, 3B, 4D
Question 20 :
Which of the following economist estimated per capita income during colonial period
a) William Digby
b) Findley Shirras
c) Dada Bhai Naoroji
d) All of these
Question 21 :
New Economic Policy of India was launched in the year 1991 under the leadership of …(
(choose the correct alternative))
a) P. V. Narasimha Rao
b) Atal Bihari Bajpayi
c) Sharad Pawar
d) None of these
Question 24 :
Which of the following was not a reason for the public sector to play a major role in the
initial phase of Indian Economic Planning?
(a)Private entrepreneurs lacked sufficient capital for investment.
(b)Government aimed at social welfare.
(c) The market was big enough to encourage private industrialists for investment.
(d)The government wanted to protect the indigenous producers from the foreign
competition.
Question 25 :
Assertion (A) and Reason ( R)
Assertion (A): Many public sector undertakings incurred huge losses due to operational
inefficiencies.
Reason (R): Red-tapism was one of the reasons for continuation of such enterprises.Select
the correct alternative from the following:
Alternatives:
a. Both Assertion (A) and Reason(R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of
Assertion (A).
b. Both Assertion (A) and Reason(R) are true and Reason(R) is not the correct explanation
of Assertion (A).
c. Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is True.
d. Assertion (A) is false but Reason(R) are is true.
Question 26 :
Which of the following is not an element of fiscal reforms?
(a) Taxation reforms
(b) Public expenditure reforms
(c) Change in interest rate
(d) Control on public debt
Question 27 :
. In the context of Indian experience, controls were imposed by the government with a view
to:
(a) checking the growth of private monopolies
(b) minimising the hold of large industrial houses on the financial resources of the country
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Question 28 :
Liberalisation implies:
(a) greater role of public sector
(b) reduction in governments control over the private sector
(c) free economy with no controls
(d) none of these
Question 29 :
GST carries the slogan of 'one tax, one nation, one market'. ??
Question 30 :
Which of the following is not an example of indirect tax?
(a) Income tax
(b) Wealth tax
(c) Goods and services tax
(d) None of these
Question 32 :
Increase in the proportion of casual worker as the proportion of the total work force is
known as _
Question 33 :
Women participation in rural areas is found to be higher in rural areas as compared with
area in India due to which the following reason.
A. Widespread poverty
B. Male member do not earn sufficient income
C. Wages level are low in rural areas
D. all the above
Question 34 :
Assertion (A)Mr. X is relatively richer than Mr. Y. But both can be poor.
Reason (R) Mr. X may have higher income than Mr. Y. But, both X and Y may not have
enough income to buy the essentials of life. So that, both are poor.
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason(R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct 1
explanation of Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason(R) are true and Reason(R) is not the correct
explanation of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason(R) are is true
Question 35 :
Those who regularly move in and out of poverty are called
(A) Chronically poor
(B) Churning poor
(C) Occasionally poor
(D) Transient poor
Question 36 :
Which of the following is the poverty determination measure?
(A) Head Count Ratio
(B) Sen Index
(C) Poverty Gap Index
(D) All of these
Question 37 :
When was the Task Force on Projections of Minimum Needs and Effective Consumption
Demand was formed?
(A) 1969
(B) 1979
(C) 1989
(D) 1999
Question 38 :
In 2011-12, poverty line was defined worth ______as consumption per person a month
for rural areas and _______ for urban areas.
(A) ₹816 and ₹1,000
(B) ₹1,012 and ₹1,210
(C) ₹550 and ₹860
D) ₹860 and ₹673
Question 39 :
The most vulnerable social groups for poverty are:
(A) Scheduled Tribes
(B) Urban Casual Labourers
(C) Rural Agricultural Labourers
(D) Scheduled Castes.
Question 40 :
In which year was N R E G A enacted?
(A)2005
(B)2000
(C) 1999
(D) 1993.
Question 41 :
When was fist report on HRD was published.
a. In 1998
b. In 2000
c. In 2001
d. In 2005
Question 42 :
Green Electricity means
a) La zlectricity produced from renewable sources of energy
b) Electricity from Thermal plants
c) Electricity from Gas-powered plants
d) Hydro-power
Question 43 :
Assertion (A): India become self-reliant in the agricultural production after introducing
green revolution.
Reason(R): shortage of food grains due to drought and lack of irrigation facilities in the
early 1960’s.
a) Both assertion(A) and reason(R) are true and reasons (R) is the correct explanation of
assertion (A).
b) Both assertion and reason are true and reason (R) is not the correct explanation of
assertion(A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true
Question 44 :
Assertion (A): India became an exporter of primary products and an importer of finished
consumer and capital goods produced in Britain.
Reason (R): Restrictive policies of commodity production, trade and tariff pursued by the
colonial government adversely affected the structure, composition and volume of India’s
foreign trade.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of
Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation
of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Question 45 :
. .............five-year plan recognised the importance of human capital?
(a) seventh (b) third (c)eight. (d) sixth
Question 46 :
how much educational cess has been imposed by the government on all union taxes ?
(a) 1 percent(b) 2percent (c) 4 percent (d) 5percent
Question 47 :
the objectives of the mid-day meal scheme is.......................?
(a) to boost universalisation of primary education
(b) to boost nutritional status of children in schools
(c) to increase enrollment, attendence and retention.
(d)to boost universalisation of uper primary level of education
Question 48 :
govt. uses____ as a proxy for income of household to measure poverty
Question 51 :
Which one of the following is not a non-institutional source of credit?
(a) Money lenders
(b) Co-operative Credit
(c) Trader and commission agents
(d) Land development bank
Question 52 :
------was set up in 1982 as an apex body to coordinate the activities of all
institutions involved inthe rural financing system
Question 53 :
ASSERTION (A): Rural people not only face problems with regard to finance, but also
encounter difficulties in marketing their goods.
REASONING (R): Agriculture Marketing’ needs urgent attention in the scheme of securing
rapid rural development.
a. Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation
of Assertion (A)
b. Both ASsertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct
explanation of Assertion (A)
c. Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d. Assertion (A) isfalse but Reason (R) is true.
Question 54 :
Organic farming is very useful due to ……..
A. Less use of pesticides
B. Less use of insecticides
C. Improvement in soil fertility
D. All of the above
Question 55 :
Regional rural banks contribute in institution credit……….
A. 32Percentage
B. 22 percentage
C. 12 percentage
D. 60 percentage
Question 56 :
When were regional rural banks initiated in India?
A. 1970
B. 1975
C. 1980
D. 1985
Question 57 :
India occupies-----------------place in milk production in the world.
A. Fourth
B. First
C. Second
D. Fifth
Question 60 :
Who was the founder of High Yielding Varieties(HYV) of seeds:
A. Normen E. Barlang
B. Dada Bhai Nauroji
C. Dr.Swaminathan
D. None of these