Page 1 :
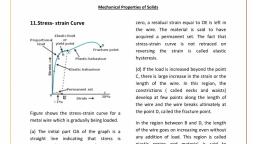
ACCURATE, ‘DIPAK PHYSICS CLASSES", +, , , , , , MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS [SET, , , Marks: 180, , 1. The following four wires are made up of the same mate~, tial. Which of these will have the largest extension when, the same tension is applied?, , (a) Length = 50 cm, Diameter = 0.5 mm, (b) Length = 100 cm, Diameter = 1 mm, {c) Length = 200 cm, Diameter = 2 mm, (d) Length = 300 cm, Diameter = 3 mm, , 2. Copper of fixed volume V is drawn into wire of length, L When this wire is subjected to a constant force F, the, extension produced in the wire is Al. Which of the, , following graphs is a straight line?, (@) Al versus! (0) Al versus, © Al vera = (a) Al versus !, , 3. The bulk modulus of a spherical object is B. If it is subjected to uniform pressure P the fractional decrease in, radius is:, , B 3p, (a) = () =, P P, © 3 @5, , 4. ‘The Young's modulus of brass and steel are, respectively,, 1010” N/m? and 2x 10!° Nj'm? . A brass wire and a, steel wire of the same length are extended by 1 mm under, the same force; the radii of brass and steel wires are Ry, and Rg, respectively. Then:, , R,, (@) Rs =v2Ry 0) Rs=E, Re, (6) Rg=4Ry () Rs=—2, , 5. Asolid sphere of radius R, made of material of bulk modulus B, i surrounded by a liquid in a cylindrical container. A massless piston of area A floats on the surface, of the liquid, When a mass M is placed on the piston to, compress the liquid, the fractional change in the radius of, the sphere is, , , , « Me, (a) BA (b) 3BA, 3Mg Me, © na () Spar, , 6. The strain-sress curves of three wires of different, materials are shown in the figure, 2 Q, and R are the, elastic limits of the wires., , Strain, , (a) Elasticity of wire P is maxinnum,, , (b) Elasticity of wire Q is maximum., , (c) Tensile strength of R is maximum., , (@ None of these, , Which one of the following statements is wrong?, , (a) Young's modulus for a perfectly rigid body is xem., , (b) Bulk modulus is relevant for solids, liquids, and gases., , {c) Rubber is less elastic than steel., , (d@) The Young's modulus and shear modulus are relevant, for solids., , ‘An metal tod of Young's modulus 2x10" Nim? ,, , undergnes an clastic strain of 0.06%. The energy per, , unie volume stored in J/ mn? is:, , (a) 3600, , (co) 1800, , (b) 7200, (Q #0, , ‘The Young's modulus and strain for steel at the break, ing point are 210" N/m? and 0.15, respectively: What, will be the stress at the breaking point in Nav” for steel?, , () 1.33x10" (b) 1.3310", , ( 3x10” (@ 3x10!, , Read the below starements and choose the correct option., (A) Glass is more elastic than rubber,, , (B) Rubber is more elastic than glass., , (C) Steel is more elastic than rubber,, , (D) Rubber is more elastic than steel., , (a) (A) and (B) are correct., , (b) (A) and (C) are correct., , (©) (B) and (C) are correct., , (@ (B) and (D) are correct., , ‘Two similar balls, one of which is made of ivory while the, other, of clay, are dropped from the same height, chen:, (a) The ivory ball will bounce to a greater height., , (b) The clay ball will bounce to a greater height., , (c) Both the balls will bounce to the same height., , (@ The ivory ball will not bounce ar all,
Page 2 :
12,, , 3., , “ae, , 15., , 16., , 17., , 1, , 19%., , 20., , “2s, , ‘The longitedinal extension of any elastic material is very, small. In order to have an appreciable change, the maretial must be in the form of:, , (a) thin block of any cross section., , (0) thick block of any cross section,, , (@) ong thin wire, , (@ short thin wire., , On withdrawing the applied force on some objects, the, called:, , (a) Elastic farigue, , (0) Elastic lamar, , (@) Coefficient of elasticity, , () Elastic after effect, , On stretching some substances, why is permanent elongation caused?, , {a} They are perfectly elasnc., , (0) They are perfectly plastic., , (c) More stress acts on them., , (a) Their strain is infinite., , Que of the following whose elasticity is independent af, temperature?, , (a) Steel (b) Copper, , (c) Lawvar steel (d) Glass, , On withdrawing the external apphed force on bodies, within the elastic limit, the body:, , (a) regains its previous state very quickly., () regains its previous state after some time., (@) regain its previous state after 2 very long time., , (q) does not regain its previous state., , (On abruptly withdrawing the stretching force acting an a, wire, its temperature wilt, , (a) increase, , (8) decrease, , (¢) remain unchanged, , (@) nothing can be stared, , Which of the following is not dimensionless?, , {a} Poisson ratio (b) Shearing strain, (©) Longinudinal strain (d) Vobame stress, , The ‘@' of a marerial is 0.20. If a Jongirudinal strain of, 4.0x107 is caused, by what percentage will the volume, , change?, a) 0.48% @) 032%, (e) 0.24% d) 0.50%, , Steel is mare elastic than rubber because for a given load, the strain produced in steel as compared to that produced, in rubber is:, , {a} more, , (B) bess, , (2) equal, , (q@) noching can be said, , a., , In a wire stretched by hanging a weight from its end,, the elastic potential energy per unit volume in terms, of longitudinal strain @ and modulus of elasticity Y, =, , Yo/2 ) Yo/2, 2¥0°/2 @ Yo/2, , The modulus of elasticity of a material does noc depend, upon:, , (a) shape, , (b) temperature, , {e) nature of material, , (@ impurities mixed, , A steel wire is stretched by 1 kg wt. If the radius of the, wire is doubled, its Young's modulus will, , (a) remain unchanged, , (b) become half, , (c) become double, , (@) become four times, , |. A-cable that can support a load Wis cut into two equal, , parts. The marxinvura load that can be supported by either, partis:, o@ o ©, 4 2, Ww @2W, How many times is the adiabatic modulus of elasncity of gas, 3 compared to its isothernsal modulus of elasticiry., (a) Two times (0) Three times, (©) ¥ times (@ 1/y times, , ‘What is the effect of temperature on the value of Young’s, , modulus of esticity for various subsances, in genera?, , (a) Tt increases with increase in temperature,, , (b) Remains consamt., , (c) Decreases with rise in temperature., , {d) Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases with, temperature., , ‘The number of independent elastic consants of a solid ix, @t ) 2, , 3 @4, , ‘The ratio of coefficient of isothermal and adiabanc elas, ticities of a gas i, , @y or, , oh @ A, , ). To what depth below the surface of sea should a rubber, , ball be taken as to decrease its volume by (1,16?, (Take: density of sea water = 1000 kgm”, Bulk modubas, of rubber = 9 x 10° Nan”; acceleration due to gravity, , = 10m, @) 9m (0) 18m, {c) 180m @ %m
Page 3 :
30. An iton rod of length | and of crosssection! area A is, heated from 0°C to 100°C. If che rod neither expands nor, , bends, then the developed F is proportional to:, @! °, gr @at, , 31. When a wire is stretched, an amount of work is done,, What is the amount of work done in stretching a wire, through 0.1 mum, if is length is 2 m and area of crosssec, tion, 10° m? {Y= 2% 10!" N/m?), , @) sx] @) Sxioy, , (9 Sxt0y (dy Sxi0y, , 32. An iron bar of length | cm and cress section A cm? is, pulled by a force of F dynes from ends so as to produce, an elongation | cm. Which of the following statement is, correct?, , (2), Elongation is inversely proportional to length., , (b) Elongation is directly proportional to cross section A, , {) Elongation is inversely proportional to A., , (@ Elongation is directly prmportioml to Youngs, modulus., , 33. A cylinder is of length | and diameter d, On sresching, the cylinder, an increment Al in length and decrease Ad, in diameter are caused. The Poisson ratio is:, , 1 Md, o=-=x—, © oT, , Ad 1a, i om, , 34, The maxinmum load a wire can withstand without breaking, when its Jength is reduced to half of its original, leogth, will:, , {@) be double, (6) be four tienes, , (b) be half, , (d) retain same, , 35. Arild steel wire of length 2L and cross-sectional area A is, two pillar. A mass m is suspended from the mid point of, the wire, Strain in the wire ix, , , , 36. A rectangular frame is to be suspended symmetrically by, ‘two strings of equal length on two supports. It can be, done in one of the following three ways., , @\ | ; , :, ‘The tension in the strings will be:, (a) the same in all cases (b) least in (a), {c) least in (b) (d) least a {c), , 37. The stres-strain graphs for two matenuls are: (assume, same scale),, , , , , , (a) Material (i) is moee elastic than material () and, hence, material (2) is more brine., , {b) Material (i) and (i) have the same elasticity and the, same brittleness., , {C) Material (i) is clastic over a larger region of strain as, compared to (x)., , (@) Material (i) as more brittle than material (i)., , 38. A wire is suspended from the ceiling and streeched under, the action of a weaght F suspended from its other end. The, force exerted by the ceiling on it is equal and apposite to, the weight. Which of the fallawing aptians is correct?, , (a) Texmile stress at any cross section A of the wire is F/A., , (b) Teenie stress at any cross section is zero., , {C) Tensile stress at amy cross section A of the ware is, 2FIA,, , {@) Tension at amy cross section A of the wire is 2F ,
Page 4 :
39., , 4., , -4, A rod of length ! and negligible mass is suspended at its, two ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium, (wire B) of equal lengths. The cros-sectional areas of, wires A and B are 1.0 mm? and 2.0 mm? , respectively,, , [Ya = 70x10°Nm“? and Ye = 20x10 Nn], , (a) Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have, ‘equal stresses in boch the wires., , (b) Mass m should be sunpended in middle of A and B to, have equal stresses in both the wires., , (©) Mass m should be suspended at the middle of the, wires to have equal stresses in both the wires., , (d) Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have, equal strain in both wires., , |. A copper and a steel wire of the same diameter are con, nected end to end. A deforming force F is applied to this, composite wire which causes a total elongation of 1 cm,, ‘The two wires will have:, (a) Same stress, , (c) the same rain, , (b) different stress, (d) different strain, , Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is:, (a) infinity, () ww, , (¢) unity, (d) some finite small non-zero constant valae, , 42. The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s mod, ulus of elasticity:, , {a) will ako double, , {b) will become four times, {Q) will remain ame, , (a) will decrease, , 43. A rigid bar of mass M is supported symmetrically by three, , ‘wires cach of length |, Those at cach end are of copper and, the muddle one is of iron. The ratio of their diamesers, if, , each is to have the same tension, is equal to:, Yoon, 8) Yeopper / Yin () \Varee, , 2, , @ t= @ fee., , Y ¥, copper empper, , 44. Foe am ideal liquid:, , Q) The bulk modulus is zero., {b) The bulk modulus is 2era., {c) The shear modulus is infinite., {@) The shear modulus is zero., , 45. Consider two cylindrical rods of identical dimensicas, one, , caf rubber and the other of steel. Both the rods are fixed, , snigidly at one end to the roof. A mans M is attached wo each, , cof the free ends at the centre of the rods. Which of the fol, Jowing tatements is correct?, , {a) Both the rods will elongate bat there shall be no perceptible change in shape., , {b) The steel rod will elongate and change shape but the, rubber rod will only elongate., , {c) The steel rod will elongate without any perceptible, change in shape, but the rubber rod will elongate, and the shape of the bottom edge will change to an, ellipse,, , {@ The steel rod will elongate, without any perceptible, change in shape, bue the rubber rod will elongate, , with the shape of the bottom edge tapered to a tip at, the centre., , , , , , B.Sc. [1* Class] Physics [Hons] [C.U.], M.Sc. [1* Class] Pure Physics [J.U.], Mob: 9831845763 / 6290491600, , CLASS: X, XI, XII [ICSE, ISC, CBSE BOARDS], ENTRANCE EXAMS: JEE / WBJEE/ NEET