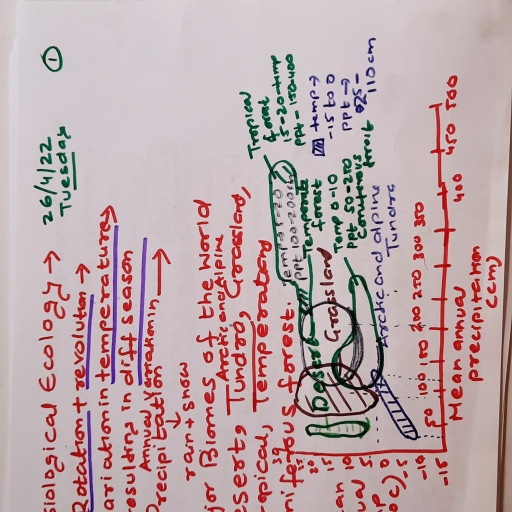
Page 1 :
4. {0 mature mammalian erythrocytes, the respiration, , (1) Aerobic, , (2) Anaerobic, , (3) Sometimes aerobic and sometimes anaerobic, (4) Absent, , Which of the following is not a character of, respiratory surface’?, , (1) Thin, permeable to gases, (2) Extensive, , (3) Least vascular, , (4) Moist, , Skin of man cannot act as respiratory organ, because, , (1) itis dry, , (2) It is not thin, , (3) tis not permeable to O, and CO,, , (4) All of these, , In cockroach, inspiration is brought about by, (1) Contraction of tergo-sternal muscles, (2) Relaxation of tergo-sternal muscles, , (3) Relaxation of abdominal muscles and it is a, passive process, , (4) Both (2) & (3), In case of insects, one of the statements is wrong, , (1) Contraction of abdominal muscles drives air, out from the tracheal system through spiracles, , (2) Relaxation of abdominal muscles draws in air, through spiracles, trachea and tracheoles, , (3) Abdominal muscles have nothing to do with, respiration, , (4) Both (1) & (2), , n., , In birds, exchange of gases occurs, , (1) First in the lungs and then in air sacs, (2) First in the alr sacs and then in lungs, (3) Simultaneously in lungs and air sacs, (4) In the lungs only and not in air sacs, , In man which of the following structures is, analogous to the spiracles of cockroach?, , (1) Alveoll, , (2) Bronchicles, , @) Lungs, , (4) Nostriis, , Conchae are located in, , (1) Traches, , (2) Bronchioles, , @) Ventricle, , (4) Nasal chambers, , Glottis is an opening in the floor of, (1) Diaphragm, , (2) Pharyngeal cavity, , (3) Trachea, , (4) None of these, , Adam's apple is another name for, (1) Sound box in birds, , (2) Sound box in man, , (3) Epigiottis, , (4) Thyrold cartilage, , Ring like cartilage of larynx is known as, (1) Thyroid cartilage, , (2) Arytenoid cartilage, , (3) Cricold cartilage, , (4) Cartilage of Santorini
Page 2 :
13., , 15., , 16., , 17., , 18., , Which of the following prevents collapsing of, trachea?, , (1) Muscles, , (2) Diaphragm, , @) Ribs, , (4) Cartilaginous rings, , Trachea is lined with incomplete rings of, (1) Fibrous cartilage, , (2) Calcified cartilage, , (3) Elastic cartilage, , (4) Hyaline cartilage, , . Number of alveoli in the human lungs has been, , estimated to be approximately, (1) 100 million, , (2) 300 million, , (3) 125 million, , (4) 300 billion, , In human, oblique fissure is present in, , (1) Right lung, , (2) Left lung, , (3) Both of these, , (4) None of these, , The covering of the lung is called, , (1) Pericardium, , (2) Perichondrium, , (3) Pleural membrane, , (4) Peritoneurn, , The terminal bronchiole is lined by, , (1) Simple squamous epithelium, , (2) Ciliated columnar or cuboidal epithelium, (3) Stratified epithelium, , (4) Pseudostratified epithelium, , Which of the following muscle contract during, normal expiration?, , (1) Internal intercostal muscles, , (2) Diaphragm, , (3) Abdominal muscies, , (4) None of these, , 19. Chast movements are inconspicuous during, , 21., , (1) Normal breathing, (2) Abdominal breathing, (3) Thoracic breathing, (4) Both (1) & (2), Tidal volume is, , (1) The volume of air breathed in or out in one, normal inspiration/expiration, , (2) Volume of air breathed out by forced expiration, after normal inspiration, , @) Volume of air breathed out by forced expiration, after forced inspiration, , (4) Volume of air that remains in lungs even after, maximum expiration, , Which of the following pulmonary volume can't be, measured by spirometer directly?, , (1) Tidal volume, , (2) Vital capacity, , (3) Inspiratory capacity, , (4) Residual volume, , Ribs move outwards during respiration with, (1) Intercostal muscles, , (2) Petrohyal muscles, , (3) Pharyngeal muscles, , (4) None of these, Functional residual capacity (FRC) includes, a WV b. IRV, , c. RV d. ERV, , (1) ate 2) bed, , @) etd (4) a+bed, , If @ person exhales out forcefully by applying all his, efforts. What will the pulmonary volume inhaled by, , him immediately under notmal condition without, applying any extra effort?, , (1) TV +IRV, (2) TV only, , (3) TV+ERV, , (4) TV+IRV+ERV
Page 3 :
25., , The Peo, level in the expired air under normal, condition is approximately, , (1) 46 mm of Hg, , (2) 100 mm of Hg, , (3) 32mm of Hg, , (4) 116 mm of Hg, , Which of mi following factor will decrease, (1) High Hb, , (2) Increased blood flow, , (3) Anaemia, , (4) Increased blood volume, , Which statement is wrong?, , (1) Partial pressure of CO,(Pco, ) is higher in the, , air inside the lungs than inside the venous, blood, , (2) Partial pressure of ©,(Po, ) is higher in the air, inside the tungs than in the arterial blood, , (3) Partial pressure of ©,(Po, ) is lower inside the, venous blood than in the air in the lung, , (4) Partial pressure of CO, (Peo, ) is higher inside, the venous blood than in the air, , Exchange of gases between alveolar air and, alveolar capillaries occurs by, , (1) Osmosis, (2) Active transport, (3) Absorption, (4) Diffusion, , The amount of oxygen transported by one litre of, blood under strenous condition is approximately, , @ 5m, (4) 150 mi, , |. In alveoli surfectant is produced by, , (1) Type | pneumocyte, (2) Type I! pneumocyte, (3) Kupffer's cells, , (4) Dust cells, , 31, Tho combination of O, wilh haemoglobin can be, , increased mostly by, , () Increasing O, concentration in air, , (2) Decreasing O, concentration in blood, , (3) Increasing CO, concentration in air, , (4) Decreasing CO, concentration in blood, , The effect of CO, concentration on dissociation of, , oxyhaemoglobin was explained by, (1) GS. Cartor (2) Yapp, (3) William Hoar (4) Christian Bohr, , Oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve will shift to, fight on decrease of, , (1) Acidity, , (2) Carbon dioxide concentration, (3) Temperature, , (4) pH, , . If CO, level gets increased in the blood, it favours, , (1) Loading of O, in the blood, , (2) Unloading of O, from the blood, , (3) Decreased availability of oxygen to tissues, (4) Both (1) & (3), , if oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curves are drawn, for maternal and foetal haemoglobin, which of the, following is true?, , (1) Maternal curve will be on the right side, , (2) Foetal curve will be on the right side, (3) Both will overlap each other, , (4) It will depend upon Peo, level, Reverse of the chloride shift occurs during, (1) Internal respiration, , (2) External respiration, , (3) Cellular respiration, , (4) Anaerobic respiration, , . Percentage amount of CO, carried or transported, , by Hb is, (1) 10% (2) 80%, (3) 70% (4) 23%
Page 4 :
41., , 43,, , In the process of transport of co, which, phenomenon occurs between RBCs and plasma?, , (1) Osmosis (2) Adsorption, (3) Chloride shift (4) Absorption, , Which of the following can be termed as opposite, of Bohr's effect?, , (1) Haldane’s effect, , (2) Hamburger’s phenomenon, (3) Hering - Breuer reflex, (4) None of these, , The impulse for voluntary muscles for forced, breathing starts in, , (1) Cerebellum (2) Medulla, , (3) Vagus nerve (4) Cerebrum, Respiratory control centre lies in, , (1) Pons (2) Medulla oblongata, 3) Cerebrum (4) Both (1) & (2), Which of the following statement is wrong?, , (1) The inspiratory centre increases the strength, of contraction of rib muscles, , (2) Pneumotaxic centre controls the switch off, point of inspiration, , (3) Breathing movernents are caused by change, in concentration of CO, in the blood, , (4) Expiratory centre ties in pans and inspiratory, centre lies in medulla, , Which of the following controls the switch off point, of inspiration?, , (1) Apneustic centre (2) Pneumotaxic centre, (3) Pons varoli (4) Cerebrum, , Which of the following is not possible when, pneumotaxic centre is sending a strong signal?, , (1) Rate of breathing increases, , (2) Complete filling of lungs, , (3) Decreased duration of inspiration, , (4) Decreased duration of expiration, Overstretching of the lungs is prevented due to, (1) Bohr's effect (2) Hering-Brever refiex, (3) Conditioned reflex (4) Haldane's effect, , 46., , 47., , 48., , 51., , Rate and depth of respiration shall increase when, (1) Oxygen concentration increases, , (2) CO, concentration increases in alveolar air, (3) Bicarbonate concentration increases, , (4) Bicarbonate concentration decreases, , The ‘mountain sickness’ in persons climbing to high, altitudes without any aid of oxygen cylinders is due, to, , (1) Anaemic hypoxia, , (2) Arterial hypoxia, , (3) Lack of sufficient amount of haemoglobin, (4) Lack of sufficient number of erythrocytes, Cyanide poisoning will lead to, , (1) Hypoxic hypoxia, , (2) Histotoxic hypoxia, , (3) Stagnant hypoxia, , (4) Anaemic hypoxia, , Asthma is caused due to, , (1) Infection of trachea, , (2) Infection of lungs, , {3) Bleeding into pleural cavity, , (4) Spasm in bronchial muscles, , Which of the following is related to occupational, lung disease, , (1) Silicosis, , (2) Asbestosis, , (3) Fibrosis of upper part of lung, (4) All of these, , Breakdown of alveoli of lungs resulting in the, reducing surface area for gas exchange is, known as, , (1) Emphysema (2) Sneezing, (3) Pneumonia (4) Tuberculosis, , if thorax is injured and pleura damaged, the air, enters the pleural cavity and the lungs are, collapsed. This condition is known as, , (1) Hyponea (2) Orthopnoea, (3) Dyspnoea (4) Preumothorax
Page 5 :
. Protective respiratory blast is, , (1) Hiccupping (2) Coughing, , (3) Sneezing (4) None of these, . Low oxygen tension in the blood causes, , (1) Coughing (2) Hiccups, , (3) Sneezing (4) Yawning, , . Disorder/disease related with bubbling of N, in the, blood resulting in pain or severe problem is, , (1) Caisson's disease, (2) Cheyne-stokes respiration, (3) Hypopnoea, , (4) Asthma, , . With the increase of temperature the respiratory, rate will, , (1) Increase, , (2) Decrease rapidly, (3) Remain unaffected, (4) Decrease slowly, , . Which of the following gases makes the most, stable combination with the haemoglobin of red, blood cells?, , (1) CO, (2) Co, , @) oO (4) N,, , One of the following is not a respiratory pigment, (1) Haemoglobin (2) Chlorocruorin, , (3) Haemocyanin (4) Haemozoin, Pneumonia can be caused by, , (1) Bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae), , (2) Protozoan, , (3) Fungi, , (4) All of these, , . Asbestosis or Silicosis is characterised by, proliferation of fibrous tissue in, , (1) Respiratory tract, (2) Upper part of lung, (3) Lower part of lung, (4) Pulmonary capillary