Page 1 :
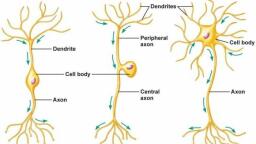
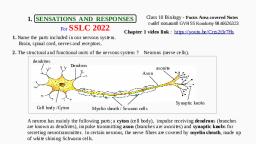
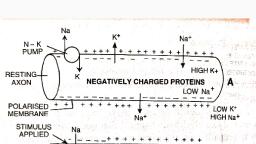
220, 16,, , 17., , A diagram showing axon terminal and synapse is, given. Identify correctly at least two of A - D., , , , (a) A - Neurotransmitter, B - Synaptic cleft, (b) C - Neurotransmitter, D - Ca**, (c) A- Receptor, C - Synaptic vesicles, (d) B - Synaptic connection, D- K* (NEET 2013), ‘The figure shows an axon terminal and synapse., Select the option giving correct identification of, labels A-D., , A, , D, , c, , (a) A-Action potential, C-Neurotransmitter, , (b) B-Neurotransmitter, D- Receptor capsules, , (c) C-Receptor, D-Synaptic vesicles, , (d) A-Axon terminal, B- Serotonin complex, (Karnataka NEET 2013), , When a neuron is in resting state i.c., not conducting, , any impulse, the axonal membrane is, , (a) comparatively more permeable to Na* ions and, nearly i to K* fons, , (b) equally permeable to both Na’ and K* ions, , (c) impermeable to both Na* and K’ ions, , (d) comparatively more permeable to K* ions and, nearly impermeable to Na* jons. (2011), , Alzheimer's disease in humans is associated with the, , deficiency of, , (a) glutamic acid (b) acetylcholine, , (c) gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), , (d) dopamine. (2009), , During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the, , action potential results from the movement of, , (a) K* ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular, fluid, , (b) Na’ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular, fluid, , (c) K* ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular, , fluid, (d) Na’ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular, fluid. (2008), , , , 21. During the transmission of nerve impulse through, , a nerve fibre, the potential on the inner side of the, , plasma membrane has which type of electric charge?, , (a) First positive, then negative and continue to be, negative, , (b) First negative, then positive and continue to be, positive, , (c) First positive, then negative and again back to, positive, , (d) First negative, then positive and again back to, negative. (2007), , Which one of the following does not act as a, , neurotransmitter?, (a) Cortisone (b) Acetylcholine, (c) Epinephrine (d) Norepinephrine, , (2006), , |. Parkinson's disease (characterized by tremors, , and progressive rigidity of limbs) is caused by, degeneration of brain neurons that are involved in, movement control and make use of neurotransmitter, (a) acetylcholine (b) norepinephrine, , (c) dopamine (d) GABA. (2005), In the resting state of the neural membrane,, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed,, would drive, , (a) K° into the cell, , (b) K* and Na* out of the cell, , (c) Na* into the cell, , (d) Na® out of the cell. (2004), , . What used to be described as Nissl’s granules in a, , nerve cell are now identified as, (a) cell metabolites (b) fat granules, (c) ribosomes (d) mitochondria. (2003), , Which of the following statement is correct for node, , of Ranvier of nerve?, , (a) Neurilemma is discontinuous., , (b) Myelin sheath is discontinuous., , (c) Both neurilemma and myelin sheath are, discontinuous., , (d) Covered by myelin sheath. (2002), , . Depolarization of axolemma during nerve, , conduction takes place because of, , (a) equal amount of Na* and K* move out across, axolemma, , (b) Na* move inside and K* move more outside, , (c) more Na* outside, , (d) none of these. (2000), , ‘The junction between the axon of one neuron and, the dendrite of the next is called, (a) constant bridge (b) junction point, , (c) ajoint (d) a synapse. (1999)
Page 2 :
SEpean natty, In a man, abducens nerve is injured. Which one of, the following functions will be affected?, (a) Movement of the eyeball, (b) Movement of the tongue, (c) Swallowing, (d) Movement of the neck (2005), , 2. Injury to vagus nerve in humans is not likely to, , affect, , (a) tongue movements, , (b) gastrointestinal movements, , (c) pancreatic secretion, , (d) cardiac movements. (2004), 3. Which cranial nerve has the highest number of, , branches?, , (a) Vagus nerve (b) Trigeminal nerve, , (c) Facial nerve (d) None of these (1999), 4. Sympathetic nervous system induces, , (a) secretion of digestive juices, , (b) heart beat, , (c) secretion of saliva, , (d) all of these. (1999), 5. The vagus nerve is the cranial nerve numbering, , (a) 7 (b) 5, , (c) 10 (d) 9. (1997), 6. By which nervous system and of what type, the, , blood is supplied into visceral organs?, , (a) Both SNS and PNS, involuntary, , (b) Para-sympathetic nervous system involuntary, , (c) Sympathetic nervous system, involuntary, , (d) Sympathetic nervous system, voluntary (1996), 7. The sympathetic nerves, in mammals, arise from, , (a) sacral nerves, , (b) 3", 7%, 9 and 10" cranial nerves, , (c) thoraco-lumbar nerves, , (d) cervical nerves. (1995), , 8. Afferent nerve fibres carry impulses from, (a) effector organs to CNS, , , , 10., , (b) receptors to CNS, , (c) CNS to receptors, , (d) CNS to muscles. (1992), Vagus nerve is, , (a) X (b) IX, , (co) VIL (d) V. (1992), , One function of parasympathetic nervous system is, (a) contraction of hair muscles, , (b) stimulation of sweat glands, , (c) acceleration of heart beat, , (d) constriction of pupil. (1990), Which of the following cranial nerves can regulate, heart beat?, , (a) X (b) IX, , (c) Vill (d) VI (1989), , EBB Neuron as Structural and Functional Unit, , 2, , 13., , uu., , 15., , of Neural System, Nissl's bodies are mainly composed of, (a) proteins and lipids, (b) DNA and RNA, (c) nucleic acids and SER, (d) free ribosomes and RER. (NEET 2018), Myelin sheath is produced by, (a) astrocytes and Schwann cells, (b) oligodendrocytes and osteoclasts, (c) osteoclasts and astrocytes, (d) Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes., (NEET 2017), Receptor sites for neurotransmitters are present on, (a) pre-synaptic membrane, (b) tips of axons, (c) post-synaptic membrane, (d) membranes of synaptic vesicles. (NEET 2017), ‘The most abundant intracellular cation is, (a) HY (b) K, (c) Na’ (d) Car’., (NEET 2013)