Page 1 :
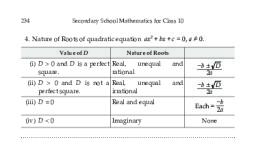
234, , Secondary School Mathematics for Class 10, , = 0., 4. Nature of Roots of quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0, a Y, Nature of Roots, , Value of D, , (i) D > 0 and D is a perfect Real,, unequal, square., rational, , and, , b! D, 2a, , (ii) D > 0 and D is not a Real,, unequal, perfect square., irrational, , and, , b! D, 2a, , (iii) D = 0, , Real and equal, , (iv) D < 0, , Imaginary, , Each, , b, 2a, , None, , TEST YOURSELF, MCQ, 1. Which of the following is a quadratic equation?, (a) x 2 3 x + 2 = 0, (c) x 2 +, , 1 =, 5, x2, , 1, (b) x + x = x 2, (d) 2x 2 5x = (x 1) 2, , 2. Which of the following is a quadratic equation?, (a) (x 2 + 1) = (2 x) 2 + 3, (b) x 3 x 2 = (x 1) 3, (c) 2x 2 + 3 = (5 + x) (2x 3), , (d) None of these, , 3. Which of the following is not a quadratic equation?, (a) 3x x 2 = x 2 + 5, (b) (x + 2) 2 = 2 (x 2 5), (c) ( 2 x + 3) 2 = 2x 2 + 6, , (d) (x 1) 2 = 3x 2 + x 2, , 4. If x = 3 is a solution of the equation 3x 2 + (k 1) x + 9 = 0 then k = ?, (a) 11, , (b) –11, , (c) 13, , (d) –13, , 5. If one root of the equation 2x 2 + ax + 6 = 0 is 2 then a = ?, (a) 7, , (b) –7, , 7, (c) 2, , (d), , 7, 2, , 6. The sum of the roots of the equation x 2 6x + 2 = 0 is, (a) 2, , (b) –2, , (c) 6, , 7. If the product of the roots of the equation x, value of k is, (a) –2, , (b) –8, , (c) 8, , (d) –6, 2, , 3x + k = 10 is –2 then the, (d) 12
Page 2 :
Quadratic Equations, , 235, , 8. The ratio of the sum and product of the roots of the equation, 7x 2 12x + 18 = 0 is, (a) 7 : 12, , (b) 7 : 18, , (c) 3 : 2, , (d) 2 : 3, , 1, 9. If one root of the equation 3x 2 10x + 3 = 0 is 3 then the other root is, 1, 1, (a) 3, (b) 3, (c) –3, (d) 3, 10. If one root of 5x 2 + 13x + k = 0 be the reciprocal of the other root then, the value of k is, (a) 0, , (b) 1, , (c) 2, , (d) 5, , 11. If the sum of the roots of the equation kx 2 + 2x + 3k = 0 is equal to their, product then the value of k is, 2, 1, 2, 1, (b) 3, (c) 3, (d) 3, (a) 3, 12. The roots of a quadratic equation are 5 and –2. Then, the equation is, (a) x 2 3x + 10 = 0, (b) x 2 3x 10 = 0, (c) x 2 + 3x 10 = 0, , (d) x 2 + 3x + 10 = 0, , 13. If the sum of the roots of a quadratic equation is 6 and their product is, 6, the equation is, (a) x 2 6x + 6 = 0, (b) x 2 + 6x 6 = 0, (c) x 2 6x 6 = 0, , (d) x 2 + 6x + 6 = 0, , 1 1, 14. If and are the roots of the equation 3x 2 + 8x + 2 = 0 then c + m = ?, (a), , 3, 8, , 2, (b) 3, , (c) –4, , (d) 4, , 15. The roots of the equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 will be reciprocal of each, other if, (a) a = b, (b) b = c, (c) c = a, (d) none of these, 16. If the roots of the equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0 are equal then c = ?, b, (a) 2a, , b, (b) 2a, , (c), , b2, 4a, , b2, (d) 4a, , 17. If the equation 9x 2 + 6kx + 4 = 0 has equal roots then k = ?, (a) 2 or 0, , (b) –2 or 0, , (c) 2 or –2, , (d) 0 only, , 18. If the equation x 2 + 2 (k + 2) x + 9k = 0 has equal roots then k = ?, (a) 1 or 4, , (b) –1 or 4, (c) 1 or – 4, (d) –1 or – 4, 19. If the equation 4x 3kx + 1 = 0 has equal roots then k = ?, 2, , 2, (a) ! 3, , 1, (b) ! 3, , 3, (c) ! 4, , 4, (d) ! 3
Page 3 :
236, , Secondary School Mathematics for Class 10, , = 0 are real and unequal, if (b 2 4ac) is, 20. The roots of ax 2 + bx + c = 0, a Y, (a) > 0, , (b) = 0, (c) < 0, (d) none of these, 2, 21. In the equation ax + bx + c = 0, it is given that D = (b 4ac) > 0. Then,, the roots of the equation are, (a) real and equal, (b) real and unequal, (c) imaginary, (d) none of these, 22. The roots of the equation 2x 2 6x + 7 = 0 are, 2, , (a) real, unequal and rational, (c) real and equal, , (b) real, unequal and irrational, (d) imaginary, 23. The roots of the equation 2x 2 6x + 3 = 0 are, (a) real, unequal and rational, (b) real, unequal and irrational, (c) real and equal, (d) imaginary, 24. If the roots of 5x 2 kx + 1 = 0 are real and distinct then, (a), , 2 5<k<2 5, , (c) k < 2 5 only, , (b) k > 2 5 only, (d) either k > 2 5 or k < 2 5, , 25. If the equation x + 5kx + 16 = 0 has no real roots then, 8, 8, (a) k > 5, (b) k < 5, 8, 8, (c) 5 < k < 5, (d) none of these, 2, , 26. If the equation x 2 kx + 1 = 0 has no real roots then, (a) k < –2, (b) k > 2, (c) –2 < k < 2, (d) none of these, 27. For what values of k, the equation kx 2 6x 2 = 0 has real roots?, 9, (a) k # 2, (c) k # 2, , 9, (b) k $ 2, (d) None of these, , 1, 28. The sum of a number and its reciprocal is 2 20 $ The number is, 5, 4, 4, 3, 5, 6, 1, (a) 4 or 5, (b) 3 or 4, (c) 6 or 5, (d) 6 or 6, 29. The perimeter of a rectangle is 82 m and its area is 400 m 2 . The breadth, of the rectangle is, (a) 25 m, (b) 20 m, (c) 16 m, (d) 9 m, 30. The length of a rectangular field exceeds its breadth by 8 m and the area, of the field is 240 m 2 . The breadth of the field is, [CBSE 2014], (a) 20 m, (b) 30 m, (c) 12 m, (d) 16 m
Page 4 :
Quadratic Equations, , 31. The roots of the quadratic equation 2x 2 x 6, , 237, , 0 are, , [CBSE 2012], , 3, 3, 3, 3, (b) 2, 2, (c) 2, 2, (d) 2, 2, 2, 2, 32. The sum of two natural numbers is 8 and their product is 15. Find the, numbers., [CBSE 2012], (a), , Very-Short-Answer Questions, 33. Show that x = –3 is a solution of x 2 + 6x + 9 = 0., 34. Show that x = –2 is a solution of 3x 2 + 13x + 14 = 0., , [CBSE 2008], [CBSE 2008], , 1, 35. If x = 2 is a solution of the quadratic equation 3x 2 + 2kx 3 = 0, find, the value of k., [CBSE 2015], 36. Find the roots of the quadratic equation 2x 2 x 6 = 0., [CBSE 2012], 37. Find the solution of the quadratic equation 3 3 x 2 + 10x + 3 = 0., [CBSE 2009], , 38. If the roots of the quadratic equation 2x + 8x + k = 0 are equal then, find the value of k., [CBSE 2014], 2, 39. If the quadratic equation px 2 5 px + 15 = 0 has two equal roots then, find the value of p., [CBSE 2015], 2, 2, 40. If 1 is a root of the equation ay + ay + 3 = 0 and y + y + b = 0 then find, the value of ab., [CBSE 2012], 2, 41. If one zero of the polynomial x 4x + 1 is (2 + 3 ), write the other, zero., [CBSE 2010], 2, 42. If one root of the quadratic equation 3x 10x + k = 0 is reciprocal of, the other, find the value of k., [CBSE 2014], 43. If the roots of the quadratic equation px (x 2) + 6 = 0 are equal, find, the value of p., [CBSE 2013], 2, 44. Find the values of k so that the quadratic equation x 4kx + k = 0 has, equal roots., [CBSE 2012], 2, 45. Find the values of k for which the quadratic equation 9x 3kx + k = 0, has equal roots., [CBSE 2014], 2, , Short-Answer Questions, 46. Solve: x 2 ( 3 + 1) x + 3 = 0., , [CBSE 2015], , 47. Solve: 2x 2 + ax a 2 = 0., , [CBSE 2014], , 48. Solve: 3x + 5 5 x 10 = 0., , [CBSE 2014], , 2, , 49. Solve:, , 3 x + 10x 8 3 = 0., 2, , [CBSE 2014], , \, , \
Page 5 :
238, , Secondary School Mathematics for Class 10, , 50. Solve:, , 3 x 2 2 2 x 2 3 = 0., , [CBSE 2014], , 51. Solve: 4 3 x + 5x 2 3 = 0., , [CBSE 2013], , 52. Solve: 4x + 4bx (a, , b ) = 0., , [CBSE 2015], , 53. Solve: x + 5x (a + a 6) = 0., , [CBSE 2015], , 54. x 2 + 6x (a 2 + 2a 8) = 0, , [CBSE 2015], , 2, , 2, , 2, , 2, , 2, , 2, , -, , 55. x, , 2, , 4ax + 4a, , b =0, , 2, , 2, , [CBSE 2012], , ANSWERS (TEST YOURSELF), , 1. (d), , 2. (b), , 3. (c), , 4. (b), , 8. (d), , 9. (d), , 14. (c) 15. (c) 16. (d) 17. (c), , 18. (a), , 19. (d) 20. (a), , 21. (b) 22. (d) 23. (b) 24. (d) 25. (c) 26. (c), , 27. (b), , 28. (a) 29. (c), , 30. (c) 31. (b), , 10. (d) 11. (d) 12. (b) 13. (a), , 9, , 5. (b), , 3, , 36. x = 2 or x = 2, , 39. p = 3, , 40. ab = 3, , 1, , 52. x =, , 3 or x, , 3), , 42. k = 3, , 41. (2, , 48. x = 2 5 or x = 3, , 2, 3, , 51. x =, , (b + a), (a b), or x = 2, 2, , 54. x = (a + 4) or x = (a, , 2), , 1, 3 3, , 43. p = 6, , 49. x = 4 3 or x =, , 3, 2, or x = 4, 3, 53. x = (a + 3) or x = (a, 55. x = (2a + b) or x = (2a, , HINTS TO SOME SELECTED QUESTIONS, 7. Given equation is x 2 3x + (k 10) = 0., Product of roots = (k 10) . So, k 10, 12 18, 8. Required ratio = 7 : 7 = 2 : 3., 1, 9. Let the other root be . Then, #, 3, So, the other root is 3., 1·, 10. Let the roots be and, Then,, k, 1, product of roots = b # l = 1. So,, 5, , 2&k, , 3, 3, , 8., , 1&, , 1&k, , 38. k = 8, , 46. x = 3 or x = 1, , 5, , a, , 50. x = 6 or x =, , 37. x, , 45. k = 0 or k = 1, , 47. x = a or x = 2, , 7. (c), , 32. 3 and 5, , 35. k = 4, , 44. k = 0 or k = 4, , 6. (c), , 3., , 5., , 2), b), , 2, 3