Page 1 :
The Principle of Effective Demand
Page 2 :
What is Aggregate Demand?, , * In macroeconomics, Aggregate Demand (AD) refers to demand for all, goods and services in the economy during a period of time, (generally,one year)., , * It is impossible to add up physical quantities of all the goods, demanded in the economy., , * Accordingly, AD is measured in terms of expenditure on all the goods, and services in the economy during a period of time., , * Briefly, AD may be defined as the sum total of expenditure on the, domestically produced goods and services during the period of an, accounting year.
Page 3 :
Components of Aggregate Demand (AD), , * C (Private Consumption Expenditure), * I (Private Investment Expenditure), , ¢ G (Government Expenditure), , ¢ X-M (Net Exports), , ¢ Therefore, AD =C +1+G+X-M
Page 4 :
What is Aggregate Supply (AS) ?, , * Aggregate supply (AS) refers to aggregate production as planned by the, producers during an accounting year., , * It implies the flow of goods and services in the economy during an, accounting year., , ° We know production of goods and services implies 'value addition’, and, value addition implies 'income generation’., , * Our knowledge of national income accounting tells us that 'value added’ and, ‘income generated’ are identical to each other., , * Accordingly, AS implies flow of Income (Y) in the economy during an, accounting year., , ¢ Since Y=C+S, we can state that AS = C+S.
Page 5 :
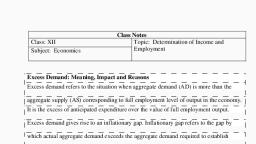
“THE PRINCIPLE OF EFFECTIVE DEMAND :, AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY, , , , INTRODUCTION, , The logical starting point of Keynes's theory of employment is the principle of effective demand. Ina, capitalist economy, the level of employment depends on effective demand, Thus unemployment resuts from, a deficiency of effective demand and the level of employment can be raised by increasing the level of effective, , demand.
 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic





































 Learn better on this topic
Learn better on this topic









